Abstract
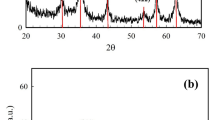
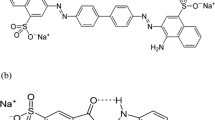
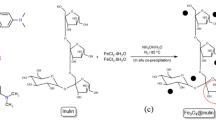
In this study, the decolorization of a dye solution via bio-Fenton process with in situ generation of H2O2 by enzymatic catalyzed oxidation of glucose was investigated. For this purpose, magnetite was synthesized and was used as the support for glucose oxidase immobilization. The particle size of the magnetite was estimated to be around 42 nm according to the obtained scanning electron microscope images. The magnetite crystal size was obtained approximately 26 nm by X-ray diffraction spectrum. Effective variables on immobilization were investigated. The best immobilization conditions were achieved at pH 6, temperature of 10 °C, glucose oxidase/support ratio of 1800 U/g, and time of 2.5 h. In these conditions, 450 U of glucose oxidase was immobilized per grams of magnetite. The immobilized glucose oxidase was used for the decolorization of acid yellow 12 in batch experiments. Decolorization conditions were optimized by response surface methodology. Four parameters including pH, temperature, glucose, and Fe2+ concentrations in five levels were investigated. The optimum conditions were obtained as follows: pH = 4.5, T = 29 °C, initial glucose concentration of 1.5 g/L, and Fe+2 concentration of 1.4 g/L. Decolorization efficiency after 120 min at optimal conditions in the presence of 0.3 g immobilized enzyme (450 U/g) in 100 cm3 solution was observed to be equal to 62.27 %.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abboud, M., Youssef, S., Podlecki, J., Habchi, R., Germanos, G., & Foucaran, A. (2015). Superparamagnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles, synthesis and surface modification. Materials Science in Semiconductor Processing. doi:10.1016/j.mssp.2015.05.035.
Aber, S., & Sheydaei, M. (2012). Removal of COD from industrial effluent containing indigo dye using adsorption method by activated carbon cloth: optimization, kinetic, and isotherm studies. CLEAN – Soil, Air, Water. doi:10.1002/clen.201000434.
Aber, S., Mehrizade, H., & Khataee, A. R. (2011). Preparation of ZnS nanocrystal and investigation of its photocatalytic activity in removal of C.I. acid blue 9 from contaminated water. Desalination and Water Treatment. doi:10.5004/dwt.2011.2207.
Amani-Ghadim, A.R., Aber, S., Olad, A., & Ashassi-Sorkhabi, H. (2013). Optimization of electrocoagulation process for removal of an azo dye using response surface methodology and investigation on the occurrence of destructive side reactions. Chemical Engineering and Processing: Process Intensification. doi: 10.1016/j.cep.2012.10.012.
Anjum Zia, M., Khalil-Ur-Rahman, K., Saeed, M., Andaleeb, F. I., Rajoka. M. A., Sheikh, M., et al. (2007). Thermal characterization of purified glucose oxidase from a newly isolated aspergillus niger UAF-1. Journal of Clinical Biochemistry and Nutrition. doi: 10.3164/jcbn.2007018.
Ayoubi-Feiz, B., Aber, S., Khataee, A., & Alipour, E. (2014). Preparation and application of α-Fe2O3/TiO2/activated charcoal plate nanocomposite as an electrode for electrosorption-assisted visible light photoelectrocatalytic process. Journal of Molecular Catalysis A: Chemical. doi:10.1016/j.molcata.2014.09.006.
Ba, S., Jones, J. P., & Cabana, H. (2014). Hybrid bioreactor (HBR) of hollow fiber microfilter membrane and cross-linked laccase aggregates eliminate aromatic pharmaceuticals in wastewaters. Journal of Hazardous Materials. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2014.08.062.
Babaei, M., Karimi, A., & Hejazi, M. (2014). Use of mesoporous MnO2 as a support for immobilization of lipase from Candida rugosa. Chemical Industry and Chemical Engineering Quarterly. doi:10.2298/CICEQ121009019B.
Bankar, S. B., Bule, M. V., Singhal, R. S., & Ananthanarayan, L. (2009). Glucose oxidase—an overview. Biotechnology Advances. doi:10.1016/j.biotechadv.2009.04.003.
Celikbicak, O., Bayramoglu, G., Yılmaz, M., Ersoy, G., Bicak, N., Salih, B., et al. (2014). Immobilization of laccase on hairy polymer grafted zeolite particles: degradation of a model dye and product analysis with MALDI–ToF-MS. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials. doi:10.1016/j.micromeso.2014.08.003.
Chang, Q., & Tang, H. (2014). Immobilization of horseradish peroxidase on NH2-modified magnetic Fe3O4/SiO2 particles and its application in removal of 2,4-dichlorophenol. Molecules. 10.3390/molecules191015768.
Cowan, D. A., & Fernandez-Lafuente, R. (2011). Enhancing the functional properties of thermophilic enzymes by chemical modification and immobilization. Enzyme and Microbial Technology. doi:10.1016/j.enzmictec.2011.06.023.
De Cazes, M., Belleville, M. P., Mougel, M., Kellner, H., & Sanchez-Marcano, J. (2015). Characterization of laccase-grafted ceramic membranes for pharmaceuticals degradation. Journal of Membrane Science. doi:10.1016/j.memsci.2014.11.044.
Hong, E., Choi, T., & Kim, J. (2015). Application of content optimized ZnS-ZnO-CuS-CdS heterostructured photocatalyst for solar water splitting and organic dye decomposition. Korean Journal of Chemical Engineering. doi:10.1007/s11814-014-0394-7.
Huang, J., Zhao, R., Wang, H., Zhao, W., & Ding, L. (2010). Immobilization of glucose oxidase on Fe3O4/SiO2 magnetic nanoparticles. Biotechnology Letters. doi:10.1007/s10529-010-0217-9.
Jolivalt, C., Brenon, S., Caminade, E., Mougin, C., & Pontié, M. (2000). Immobilization of laccase from Trametes versicolor on a modified PVDF microfiltration membrane: characterization of the grafted support and application in removing a phenylurea pesticide in wastewater. Journal of Membrane Science. doi:10.1016/S0376-7388(00)00522-6.
Karimi, A., Mahdizadeh, F., Salari, D., & Niaei, A. (2011). Bio-deoxygenation of water using glucose oxidase immobilized in mesoporous MnO2. Desalination. doi:10.1016/j.desal.2011.02.053.
Karimi, A., Aghbolaghy, M., Khataee, A., & Shoa Bargh, S. (2012a). Use of enzymatic bio-Fenton as a new approach in decolorization of malachite green. The Scientific World Journal. doi:10.1100/2012/691569.
Karimi, A., Mahdizadeh, F., & Eskandarian, M. (2012b). Enzymatic in-situ generation of H2O2 for decolorization of acid blue 113 by Fenton process. Chemical Industry and Chemical Engineering Quarterly. doi:10.2298/CICEQ110722050K.
Khataee, A. R., Fathinia, M., Aber, S., & Zarei, M. (2010). Optimization of photocatalytic treatment of dye solution on supported TiO2 nanoparticles by central composite design: intermediates identification. Journal of Hazardous Materials. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.05.096.
Lee, D. G., Ponvel, K. M., Kim, M., Hwang, S., Ahn, I.-S., & Lee, C. H. (2009). Immobilization of lipase on hydrophobic nano-sized magnetite particles. Journal of Molecular Catalysis B: Enzymatic. doi:10.1016/j.molcatb.2008.06.017.
Liu, & Cui, Z. (2007). Optimization of operating conditions for glucose oxidation in an enzymatic membrane bioreactor. Journal of Membrane Science. doi: 10.1016/j.memsci.2007.06.044.
Liu, Guan, Y., Shen, R., & Liu, H. (2005). Immobilization of lipase onto micron-size magnetic beads. Journal of Chromatography B. doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2005.06.001.
Lu, A.H., Salabas, E.L., & Schüth, F. (2007). Magnetic nanoparticles: synthesis, protection, functionalization, and application. Angewandte Chemie International Edition. doi:10.1002/anie.200602866.
Mahdizadeh, F., Karimi, A., & Ranjbarian, L. (2012). Immobilization of glucose oxidase on synthesized superparamagnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles; application for water deoxygenation. International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research. doi:10.1088/1742-6596/431/1/012010.
Mahdizadeh, F., Aber, S., & Karimi, A. (2015). Synthesis of nano zinc oxide on granular porous scoria: application for photocatalytic removal of pharmaceutical and textile pollutants from synthetic and real wastewaters. Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers. doi:10.1016/j.jtice.2014.11.021.
Rasouli, F., Aber, S., Salari, D., & Khataee, A. R. (2014). Optimized removal of Reactive Navy Blue SP-BR by organo-montmorillonite based adsorbents through central composite design. Applied Clay Science. 87(0). doi: 10.1016/j.clay.2013.11.010.
Salehi, Z., Sohrabi, M., Vahabzadeh, F., Fatemi, S., & Kawase, Y. (2010). Modeling of p-nitrophenol biodegradation by Ralstonia eutropha via application of the substrate inhibition concept. Journal of Hazardous Materials. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.12.072.
Sheydaei, M., & Aber, S. (2013). Preparation of nano-lepidocrocite and an investigation of its ability to remove a metal complex dye. CLEAN – Soil, Air, Water. doi:10.1002/clen.201200510.
Sheydaei, M., Aber, S., & Khataee, A. (2014). Preparation of a novel γ-FeOOH-GAC nano composite for decolorization of textile wastewater by photo Fenton-like process in a continuous reactor. Journal of Molecular Catalysis A: Chemical. doi:10.1016/j.molcata.2014.05.019.
Shoaebargh, S., & Karimi, A. (2014). RSM modeling and optimization of glucose oxidase immobilization on TiO2/polyurethane: feasibility study of AO7 decolorization. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering. doi:10.1016/j.jece.2014.06.013.
Tavares, A. P. M., Pinho, B., Rodriguez, O., & Macedo, E. A. (2012). Biocatalysis in ionic liquid: degradation of phenol by laccase. Procedia Engineering. doi: 10.1016/j.proeng.2012.07.413.
Tzanov, T., Costa, S. A., Gübitz, G. M., & Cavaco-Paulo, A. (2002). Hydrogen peroxide generation with immobilized glucose oxidase for textile bleaching. Journal of Biotechnology. doi:10.1016/S0168-1656(01)00386-8.
Wu, J. C. Y., Hutchings, C. H., Lindsay, M. J., Werner, C. J., & Bundy, B. C. (2015). Enhanced enzyme stability through site-directed covalent immobilization. Journal of Biotechnology. doi:10.1016/j.jbiotec.2014.10.039.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aber, S., Mahmoudikia, E., Karimi, A. et al. Immobilization of Glucose Oxidase on Fe3O4 Magnetic Nanoparticles and its Application in the Removal of Acid Yellow 12. Water Air Soil Pollut 227, 93 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-016-2754-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-016-2754-x