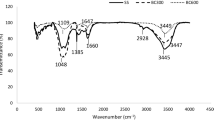
Abstract
The level of radioactivity in the soil has been increasing unpredictably due to the human uranium mining exploitation of uranium over the past 100 years. Remediation of metals in actual soil confronts many challenges, remaining poorly understood. This study intends to investigate the concentrations and distributions of U, Cd, Zn, Pb, and Cu in soils surrounded by a uranium mill tailing pond. Furthermore, a phosphorus-modified bio-char was prepared in order to determine its role in immobilizing uranium in soil samples. Results show that the contents of U and Pb are much higher than that of the background values, due to the influence of the uranium mill tailing pond. Phosphorus can enhance the immobilization efficiency of U, Cd, Pb, and Cu in soil samples. The concentration of uranium in the leaching supernatant of phosphorus-modified bio-char group is lower than that of control and unmodified bio-char groups due to the fact that the biosorption occurred in the exterior surface of the biomass, which imply that phosphorus-modified bio-char is a potential immobilization material to reduce the leaching rate of metals. These findings can provide references for remediation technology of metals in natural soil.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad, M., Rajapaksha, A. U., Lim, J. E., Zhang, M., Bolan, N., Mohan, D., & Ok, Y. S. (2014). Biochar as a sorbent for contaminant management in soil and water: A review. Chemosphere, 99, 19–33.
Carvalho, F. P., Oliveira, J. M., & Malta, M. (2016). Radioactivity and water quality in areas of old uranium mines (Viseu, Portugal). Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 227(8), 252.
Chen, S. B., Zhu, Y. G., & Hu, Q. H. (2005). Soil to plant transfer of 238 U, 226 Ra and 232 Th on a uranium mining-impacted soil from southeastern China. Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 82, 223–236.
Ebbs, S. D., Norvell, W. A., & Kochian, L. V. (1998). The effect of acidification and chelating agents on the solubilization of uranium from contaminated soil. Journal of Environmental Quality, 27, 9.
Fernandes, H. M., & Franklin, M. R. (2001). Assessment of acid rock drainage pollutants release in the uranium mining site of Poços de Caldas—Brazil. Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 54(1), 5–25.
Gavrilescu, M., Pavel, L. V., & Cretescu, I. (2009). Characterization and remediation of soils contaminated with uranium. Journal of Hazardous Material, 163, 475–510.
Hettiarachchi, G. M., Pierzynski, G. M., & Ransom, M. D. (2000). In situ stabilization of soil lead using phosphorus and manganese oxide. Environmental Science & Technology, 34(21), 4614–4619.
Kim, S. S., Han, G. S., Kim, G. N., Koo, D. S., Kim, I. G., & Choi, J. W. (2016). Advanced remediation of uranium-contaminated soil. Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 164, 239.
Laird, D. A., Fleming, P., Davis, D. D., Horton, R., Wang, B., & Karlen, D. L. (2010). Impact of biochar amendments on the quality of a typical Midwestern agricultural soil. Geoderma, 158(3–4), 443–449.
McGowen, S. L., Basta, N. T., & Brown, G. O. (2001). Use of diammonium phosphate to reduce heavy metal solubility and transport in smelter-contaminated soil. Journal of Environmental Quality, 30(2), 493–500.
Mihalík, J., Tlustoš, P., & Szaková, J. (2011). The impact of an abandoned uranium mining area on the contamination of agricultural land in its surroundings. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 215(1–4), 693–700.
Miretzky, P., Avendaño, M. R., Muñoz, C., & Carrillo-Chavez, A. (2011). Use of partition and redistribution indexes for heavy metal soil distribution after contamination with a multi-element solution. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 11(4), 619–627.
Nelissen, V., Saha, B. K., Ruysschaert, G., & Boeckx, P. (2014). Effect of different biochar and fertilizer types on N2O and NO emissions. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 70, 244–255.
Pan, Y. (2009). Status and countermeasures for decommissioning of uranium mine and mill facilities in China. Radiation Protection, 29, 167–166.
Pearson, M. S., Maenpaa, K., Pierzynski, G. M., & Lydy, M. J. (2000). Effects of soil amendments on the bioavailability of lead, zinc, and cadmium to earthworms. Journal of Environmental Quality, 29(5), 1611–1617.
Radu, A. D., Panturu, E., Woinaroschy, A., & Isopescu, R. (2015). Experimental design and process optimization for uranium polluted soils decontamination by acid washing. Water Air & Soil Pollution, 226, 127.
Rout, S., Kumar, A., Ravi, P. M., & Tripathi, R. M. (2016). Understanding the solid phase chemical fractionation of uranium in soil and effect of ageing. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 317, 457–465.
Santos-Francés, F., Gil Pacheco, E., Martínez-Graña, A., Alonso Rojo, P., Ávila Zarza, C., & García Sánchez, A. (2018). Concentration of uranium in the soils of the west of Spain. Environmental Pollution, 236, 1–11.
Shin, W., Oh, J., Choung, S., Cho, B. W., Lee, K. S., Yun, U., & Kim, H. K. (2016). Distribution and potential health risk of groundwater uranium in Korea. Chemosphere, 163, 108–115.
Sivaswamy, V., Boyanov, M. I., Peyton, B. M., Viamajala, S., Gerlach, R., Apel, W. A., & Borch, T. (2011). Multiple mechanisms of uranium immobilization by Cellulomonas sp. strain ES6. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 108(2), 264–276.
Stanislawska-Glubiak, E., & Korzeniowska, J. (2018). Time factor influence on soil heavy metal concentration in relation to soil contamination assessment. Archives of Environmental Protection, 44(3), 68–76.
Wang, X., Pei, Y., Lu, M., Lu, X., & Du, X. (2015). Highly efficient adsorption of heavy metals from wastewaters by graphene oxide-ordered mesoporous silica materials. Journal of Materials Science, 50(5), 2113–2121.
Acknowledgments
Authors appreciate the valuable comments from K. Mumford and anonymous reviewers.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant number 11605087), China scholarship council (grant number 20170830225), China’s Post-doctoral Science Fund (grant number 2017M610500), and the double first class cinstruct program of USC (grant number 2017SYL05).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tan, Wf., Wang, Yc., Ding, L. et al. Effects of Phosphorus Modified Bio-char on Metals in Uranium-Containing Soil. Water Air Soil Pollut 230, 35 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-018-4074-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-018-4074-9