Abstract
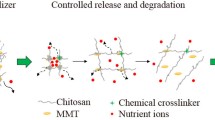
Controlled-release fertilizers (CRFs) are an effective approach in providing essential nutrients for plant growth while minimizing the loss of nutrients in water and air, reducing contamination risks. However, commercial CRFs often release nutrients either too quickly or slowly due to the properties of their coating materials (polymer or sulfur). In this work, a novel CRF technology was developed using chitosan (CS) and graphene oxide (GO) nanocomposites as coating materials. CS and GO solutions were applied at varying ratios in preparing different nanocomposites. CS and GO formed homogeneous nanocomposite films through their interactions with each other. Fertilizer beads were successfully encapsulated by the CS-GO films using the simple dipping method. Resulting CRFs showed controlled-release behaviors, with nutrient release lasting for about a week. Although additional investigations are required for further evaluation and optimization, this method presents a promising concept for an alternative fertilizer-coating technology.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen, M. J., Tung, V. C., & Kaner, R. B. (2010). Honeycomb carbon: a review of graphene. Chemical Reviews, 110, 132–145.
Beenken, K. E., Smith, J. K., Skinner, R. A., Mclaren, S. G., Bellamy, W., Gruenwald, M. J., Spencer, H. J., Jennings, J. A., Haggard, W. O., & Smeltzer, M. S. (2014). Chitosan coating to enhance the therapeutic efficacy of calcium sulfate-based antibiotic therapy in the treatment of chronic osteomyelitis. Journal of Biomaterials Applications. https://doi.org/10.1177/0885328214535452.
Blouin, G. M., Rindt, D. W., & Moore, O. E. (1971). Sulfur-coated fertilizers for controlled release. Pilot-plant production. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 19, 801–808.
D’Almeida, M., Amalric, J., Brunon, C., Grosgogeat, B., & Toury, B. (2015). Relevant insight of surface characterization techniques to study covalent grafting of a biopolymer to titanium implant and its acidic resistance. Applied Surface Science, 327, 296–306.
Jamnongkan, T., & Kaewpirom, S. (2010). Controlled-release fertilizer based on chitosan hydrogel: phosphorus release kinetics. Science Journal UBU, 1, 43–50.
Jamnongkan, T., Wattanakornsiri, A., Pansila, P. P., Migliaresi, C., & Kaewpirom, S. (2012). 'Effect of poly (vinyl alcohol)/chitosan ratio on electrospun-nanofiber morphologies. Advanced Materials Research, Trans Tech Publ, 463-464, 734–738.
Jarrell, W. M., & Boersma, L. (1980). Release of urea by granules of sulfur-coated urea. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 44, 418–422.
Jianglian, D., & Shaoying, Z. (2013). Application of chitosan based coating in fruit and vegetable preservation: a review. Journal of Food Processing & Technology, 4, 227–230.
Kabiri, S., Degryse, F., Tran, D. N., da Silva, R. C., McLaughlin, M. J., & Losic, D. (2017). Graphene oxide: a new carrier for slow release of plant micronutrients. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 9, 43325–43335.
Landels, S. P. (1994). Controlled release fertilisers: supply and demand trends in US nonfarm markets, Proc. ACS National Meeting, Division of Fertilisers and Soil Chemistry. Washington, DC: ACS Publications.
Liu, X. Q., Yang, Y. C., Gao, B., & Li, Y. C. (2016). Organic silicone-modified transgenic soybean oil as bio-based coating material for controlled-release urea fertilizers. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 133.
Liu, X. Q., Yang, Y. C., Gao, B., Li, Y. C., & Wan, Y. S. (2017). Environmentally friendly slow-release urea fertilizers based on waste frying oil for sustained nutrient release. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 5, 6036–6045.
Longstroth, M. (2012). Lowering soil pH with sulfur. East Lansing: Michigan State University https://www.canr.msu.edu/uploads/files/Lowering_Soil_pH_with_Sulfur.pdf. Accessed 8 May 2019.
Meng, F., Zheng, S., Li, H., Liang, Q., & Liu, T. (2006). Formation of ordered nanostructures in epoxy thermosets: a mechanism of reaction-induced microphase separation. Macromolecules, 39, 5072–5080.
Oertli, J. J. (1974a). Effect of coating properties on nitrogen release from sulfur-incapsulated urea. Agrochimica, 18, 3–9.
Oertli, J. J. (1974b). The effect of coating properties on the nitrogen release from sulfur incapsulated urea. Agrochimica., 18, 3–8.
Peppas, N. A. (1987). Hydrogels in medicine and pharmacy: polymers. Boca Raton: CRC 184 pp.
Raban, S. (1994). 'Release mechanisms of membrane coated fertilisers', Engn. Haifa: Technion-IIT.
Ritger, P. L., & Peppas, N. A. (1987). A simple equation for description of solute release II. Fickian and anomalous release from swellable devices. Journal of Controlled Release, 5(1), 37–42.
Sempeho, S. I., Kim, H. T., Mubofu, E., & Hilonga, A. (2014). Meticulous overview on the controlled release fertilizers. Advances in Chemistry, 2014, 1–16.
Shao, L., Chang, X., Zhang, Y., Huang, Y., Yao, Y., & Guo, Z. (2013). Graphene oxide cross-linked chitosan nanocomposite membrane. Applied Surface Science, 280, 989–992.
Shaviv, A. (2001). Advances in controlled-release fertilizers. Advances in Agronomy, 71, 1–49.
Sonia, T. A., & Sharma, C. P. (2011). Chitosan and its derivatives for drug delivery perspective. Advances in Polymer Science, 243, 23–53.
Stahl, S. M. (2003). At long last, long-lasting psychiatric medications: an overview of controlled-release technologies. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry, 64, 355–356.
Tang, Y. F., Yang, X. Y., Yang, Y. C., Gao, B., Wan, Y. S., Li, Y. C. C., & Cheng, D. D. (2017a). Activated-lignite-based super large granular slow-release fertilizers improve apple tree growth: synthesis, characterizations, and laboratory and field evaluations. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 65, 5879–5889.
Tang, Y. F., Yang, Y. C., Cheng, D. D., Gao, B., Wan, Y. S., & Li, Y. C. C. (2017b). Value-added humic acid derived from lignite using novel solid-phase activation process with Pd/CeO2 nanocatalyst: a physiochemical study. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 5, 10099–10110.
Teixeira, M. A., Paterson, W. J., Dunn, E. J., Li, Q., Hunter, B. K., & Goosen, M. F. A. (1990). Assessment of chitosan gels for the controlled release of agrochemicals. Industrial and Engineering Chemistry Research, 29, 1205–1209.
Trenkel, M. E. (2010). Slow- and controlled-release and stabilized fertilizers. Paris, France: International Fertilizer Industry Association.
Wan, S., He, F., Wu, J., Wan, W., Gu, Y., & Gao, B. (2016). Rapid and highly selective removal of lead from water using graphene oxide-hydrated manganese oxide nanocomposites. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 314, 32–40.
Wan, W., Ji, R., & He, F. (2017). Recent advances in graphene based separation membranes. Progress in Chemistry, 29, 833–845.
Wang, S. F., Shen, L., Zhang, W. D., & Tong, Y. J. (2005). Preparation and mechanical properties of chitosan/carbon nanotubes composites. Biomacromolecules, 6, 3067–3072.
Wang, X., Lü, S., Gao, C., Xu, X., Wei, Y., Bai, X., Feng, C., Gao, N., Liu, M., & Wu, L. (2014). Biomass-based multifunctional fertilizer system featuring controlled-release nutrient, water-retention and amelioration of soil. RSC Advances, 4, 18382–18389.
Wood, J. (2005). Controlled release using a molecular valve nanotechnology. Mater Today, 8, 13–13.
Wu, L., & Liu, M. (2008). Preparation and properties of chitosan-coated NPK compound fertilizer with controlled-release and water-retention. Carbohydrate Polymers, 72, 240–247.
Xie, J. Z., Yang, Y. C., Gao, B., Wan, Y. S., Li, Y. C. C., Xu, J., & Zhao, Q. H. (2017). Biomimetic superhydrophobic biobased polyurethane-coated fertilizer with atmosphere “Outerwear”. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 9, 15868–15879.
Yang, X., Tu, Y., Li, L., Shang, S., & Tao, X.-m. (2010). Well-dispersed chitosan/graphene oxide nanocomposites. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2, 1707–1713.
Yang, Y., Wu, W. Q., Zhou, H. H., Huang, Z. Y., Ye, T. T., Liu, R., & Kuang, Y. F. (2014). Adsorption behavior of cross-linked chitosan modified by graphene oxide for Cu(II) removal. Journal of Central South University, 21, 2826–2831.
Zhang, M., Gao, B., Chen, J. J., Li, Y. C., Creamer, A. E., & Chen, H. (2014). Slow-release fertilizer encapsulated by graphene oxide films. Chemical Engineering Journal, 255, 107–113.
Zhang, S. G., Yang, Y. C., Gao, B., Wan, Y. S., Li, Y. C., & Zhao, C. H. (2016). Bio-based interpenetrating network polymer composites from locust sawdust as coating material for environmentally friendly controlled-release urea fertilizers. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 64, 5692–5700.
Zhang, S. G., Yang, Y. C., Gao, B., Li, Y. C., & Liu, Z. G. (2017). Superhydrophobic controlled-release fertilizers coated with bio-based polymers with organosilicon and nano-silica modifications. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 5, 19943–19953.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, T., Gao, B., Tong, Z. et al. Chitosan and Graphene Oxide Nanocomposites as Coatings for Controlled-Release Fertilizer. Water Air Soil Pollut 230, 146 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-019-4173-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-019-4173-2