Abstract
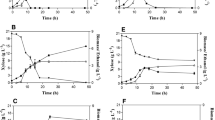
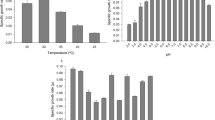
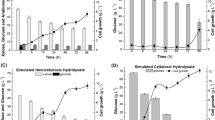
This research was designed to maximize ethanol production from a glucose-xylose sugar mixture (simulating a sugar cane bagasse hydrolysate) by co-fermentation with Zymomonas mobilis and Pachysolen tannophilus. The volumetric ethanol productivity of Z. mobilis with 50 g glucose/l was 2.87 g/l/h, giving an ethanol yield of 0.50 g/g glucose, which is 98% of the theoretical. P. tannophilus when cultured on 50 g xylose/l gave a volumetric ethanol productivity of 0.10 g/l/h with an ethanol yield of 0.15 g/g xylose, which is 29% of the theoretical. On optimization of the co-fermentation with the sugar mixture (60 g glucose/l and 40 g xylose/l) a total ethanol yield of 0.33 g/g sugar mixture, which is 65% of the theoretical yield, was obtained. The co-fermentation increased the ethanol yield from xylose to 0.17 g/g. Glucose and xylose were completely utilized and no residual sugar was detected in the medium at the end of the fermentation. The pH of the medium was found to be a good indicator of the fermentation status. The optimum conditions were a temperature of 30°C, initial inoculation with Z. mobilis and incubation with no aeration, inactivation of bacterium after the utilization of glucose, followed by inoculation with P. tannophilus and incubation with limited aeration.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bari IS, Cuna D, Nanna F, Braccio G (2004) Ethanol production in immobilized cell bioreactors from mixed sugar syrups and enzymatic hydrolysates of steam-exploded biomass. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 114:539–557
Bravo V, Camacho F, Sanchez S, Castro E (1995) Influence of the concentrations of D-xylose and yeast extract on ethanol production by Pachysolen tannophilus. J Ferment Bioeng 79:566–571
Chandrakant P, Bisaria VS (1998) Simultaneous bioconversion of cellulose and hemicellulose to ethanol. Crit Rev Biotechnol 18:295–331
Davis L, Jeon Y, Svenson C, Rogers P, Pearce J, Peiris P (2005) Evaluation of wheat stillage for ethanol production by recombinant Zymomonas mobilis. Biomass Bioenerg 29:49–59
Grootjen DRJ, Jansen ML, Van der Lans RGJM, Luyben KChAM (1991a) Reactors in series for the complete conversion of glucose/xylose mixtures by Pichia stipitis and Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Enzyme Microb Technol 13:828–833
Grootjen DRJ, Meijlink LHHM, Vleesenbeek R, Van der Lans RGJM, Luyben KChAM (1991b) Cofermentation of glucose and xylose with immobilized Pichia stipitis in combination with Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Enzyme Microb Technol 13:530–536
Kordowska-wiater M, Targonski Z (2002) Ethanol fermentation on glucose/xylose mixture by co-cultivation of restricted glucose catabolite repressed mutants of Pichia stipitis with respiratory deficient mutants of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Acta Microbiol Pol 51:345–352
Kruse B, Schugerl K (1995) Investigation of ethanol formation by Pachysolen tannophilus from xylose and glucose/xylose co-substrates. Process Biochem 31:389–407
Laplace JM, Delgenes JP, Moletta R, Navarro JM (1993a) Effects of culture conditions on the co-fermentation of a glucose and xylose mixture to ethanol by a mutant of Saccharomyces distaticus associated with Pichia stipitis. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 39:760–763
Laplace JM, Delgenes JP, Moletta R, Navarro JM (1993b) Cofermentation of glucose and xylose to ethanol by a respiratory-deficient mutant of Saccharomyces cerevisiae co-cultivated with a xylose-fermenting yeast. J Ferment Bioeng 75:207–212
Lebeau T, Jouenne T, Junter GA (1997) Simultaneous fermentation of glucose and xylose by pure and mixed cultures of Saccharomyces and Candida shehatae immobilized in a two-chambered bioreactor. Enzyme Microb Technol 21:265–272
Lee J (1997) Biological conversion of lignocellulosic biomass to ethanol. J Biotechnol 56:1–24
Maleszka R, Schneider H (1982) Concurrent production and consumption of ethanol by cultures of Pachysolen tannophilus growing on D-xylose. Appl Environ Microbiol 44:909–912
Martin GJO, Knepper A, Zhou B, Pamment NB (2006) Performance and stability of ethanologenic Escherichia coli strain FBR5 during continuous culture on xylose and glucose. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 33:834–844
Miller GL, Blum R, Glennon WE, Burton AL (1960) Measurement of carboxymethylcellulage activity. Anal Biochem 2:127–132
Qian M, Tian S, Li X, Zhang J, Pan Y, Yang X (2006) Ethanol production from dilute-acid softwood hydrolysate by co-culture. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 134:273–283
Rebros M, Rosenberg M, Stloukal R, Kristofikova L (2005) High efficiency ethanol fermentation by entrapment of Zymomonas mobilis into Lentikats®. Lett Appl Microbiol 41:412–416
Rortrup-Nielsen JR (2005) Chemistry: making fuels from biomass. Science 308:1421–1422
Saha BC (2003) Hemicellulose bioconversion. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 30:279–291
Sanchez S, Bravo V, Castro E, Moya AJ, Camacho F (2002) The fermentation of mixtures of D-glucose and D-xylose by Candida shehatae, Pichia Stipitis or Pachysolen tannophilus to produce ethanol. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 77:641–648
Sanchez S, Bravo V, Moya AJ, Castro E, Camacho F (2004) Influence of temperature on the fermentation of D-xylose by Pachysolen tannophilus to produce ethanol and xylitol. Process Biochem 39:673–679
Shi X-Q, Jeffries TW (1998) Anaerobic growth and improved fermentation of Pichia stipitis bearing a URA1 gene from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 50:339–345
Skoog K, Hahn-hagerdal B, Degn H, Jacobsen JP, Jacobsen HS (1992) Ethanol reassimilation and ethanol tolerance in Pichia stipitis CBS 6054 as studied by 13C nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Appl Environ Microbiol 58:2552–2558
Taniguchi M, Itaya T, Tohma T, Fujii M (1997) Ethanol production from a mixture of glucose and xylose by co-culture of Pichia stipitis and a respiratory-deficient mutant of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Ferment Bioeng 83:364–370
van Maris AJA, Abbott DA, Bellissimi E, van den Brink J, Kuyper M, Luttik MAH, Wisselink HW, Scheffers WA, van Dijken JP, Pronk JT (2006) Alcoholic fermentation of carbon sources in biomass hydrolysates by Saccharomyces cerevisiae: current status. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 90:391–418
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fu, N., Peiris, P. Co-fermentation of a mixture of glucose and xylose to ethanol by Zymomonas mobilis and Pachysolen tannophilus . World J Microbiol Biotechnol 24, 1091–1097 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-007-9613-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-007-9613-2