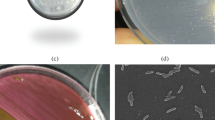
Abstract
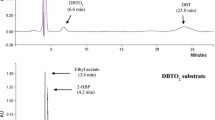
Oil-polluted soils were sampled from National Iranian South Oil Company (NISOC) for isolation and screening of C–S and not C–C targeted Dibenzothiophene (DBT) degrading microorganisms. Microbacterium sp. NISOC-06, a C–S targeted DBT degrading bacterium, was selected and its desulfurization ability was studied in aqueous phase and water-gasoline biphasic systems. The 16srRNA gene was amplified using universal eubacteria-specific primers, PCR product was sequenced and the sequence of nearly 1,500 bp 16srDNA was studied. Based on Gas Chromatography results Microbacterium sp. NISOC-06 utilized 94.8% of 1 mM DBT during the 2 weeks of incubation. UV Spectrophotometry and biomass production measurements showed that the Microbacterium sp. NISOC-06 was not able to utilize DBT as a carbon source. There was no accumulation of phenolic compounds as Gibb’s assay showed. Biomass production in a biphasic system for which DBT-enriched gasoline was used as the sulfur source indicated the capability of Microbacterium sp. NISOC-06 to desulfurize gasoline.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baldi F, Pepi M, Fava F (2003) Growth of Rhodosporidium toruloides strain DBVPG 6662 on dibenzothiophene crystals and orimulsion. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:4689–4696
Duarte GF, Rosado AS, Seldin L, De Araujo W, Van Elsas JD (2001) Analysis of bacterial community structure in sulfurous-oil-containing soils and detection of species carrying dibenzothiophene desulfurization (dsz) genes. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:1052–1062
Etemadifar Z, Emtiazi G, Peimanfar S (2006) Removal of dibenzothiophene, biphenyl and phenol from waste by Trichosporon sp. Sci Res Essay 1:72–76
Garc′ia-Cruz I, Valencia D, Klimova T, Oviedo-roa R, Mart′inez-magad′an JM, G′omez-Balderas R, Illas F (2008) Proton affinity of S-containing aromatic compounds: implications for crude oil hydrodesulfurization. J Mol Catal A Chem 281:79–84
Gilbert SC, Morton J, Buchanan S, Oldfield C, McRoberts A (1998) Isolation of a unique benzothiophene desulphurizing bacterium, Gordona sp. Strain 213E (NCIMB 40816), and characterization of the desulphurization pathway. Microbiology 144:2545–2553
Grossman MJ, Lee MK, Prince RC, Garrett KK, George GN, Pickering IJ (1999) Microbial desulfurization of a crude oil middle-distillate fraction: analysis of the extent of sulfur removal and the effect of removal on remaining sulfur. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:181–188
Grossman MJ, Lee MK, Prince RC, Minak-Bernero V, George GN, Pickering IJ (2001) Deep desulfurization of extensively hydrodesulfurized middle distillate oil by Rhodococcus sp. strain Ecrd-1. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:1949–1952
Guerinik K, Al-Mutawah Q (2003) Isolation and characterization of oil-desulphurizing bacteria. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 19:941–945
Gupta PK, Roychoudhury JK (2005) Biotechnology of desulfurization of diesel: prospects and challenges. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 66:356–366
Kertesz MA (1999) Riding the sulfur cycle—metabolism of sulfonates and sulfate esters in Gram-negative bacteria. FEMS Microbiol Rev 24:135–175
Kilbane JJ II (2006) Microbial biocatalyst developments to upgrade fossil fuels. Curr Opin Biotechnol 17:305–314
Kirkwood KM, Foght JM, Gray MR (2007) Selectivity among organic sulfur compounds in one- and two-liquid-phase cultures of Rhodococcus sp. strain JVH1. Biodegradation 18:473–480
Kropp KG, Andersson JT, Fedorak PM (1997) Bacterial transformations of 1, 2, 3, 4-Tetrahydro-dibenzothiophene and dibenzothiophene. Appl Environ Microbiol 63:3032–3042
Lee MK, Senius JD, Grossman MJ (1995) Sulfur-specific microbial desulfurization of sterically hindered analogs of dibenzothiophene. Appl Environ Microbiol 61:4362–4366
Li W, Zhang Y, Wang MD, Shi Y (2005) Biodesulfurization of dibenzothiophene and other organic sulfur compounds by a newly isolated Microbacterium strain ZD-M2. FEMS Microbiol Lett 247:45–50
Okada H, Nomura N, Nakahara T, Maruhashi K (2002a) Analyses of substrate specificity of the desulfurizing bacterium Mycobacterium sp. G3. J Biosci Bioeng 93:228–233
Okada H, Nomura N, Nakahara T, Maruhashi K (2002b) Analysis of dibenzothiophene metabolic pathway in Mycobacterium strain G3. J Biosci Bioeng 93:491–497
Rashidi L, Mohebali G, Darian JT, Rasekh B (2006) Biodesulfurization of dibenzothiophene and its alkylated derivatives through the sulfur-specific pathway by the bacterium RIPI-S81. Afr J Biotechnol 5:351–356
Rashtchi M, Mohebali GH, Akbarnejad MM, Towfighi J, Rasekh B, Keytash A (2006) Analysis of biodesulfurization of model oil system by the bacterium, strain RIPI-22. Biochem Eng J 29:169–173
Seo JS, Keum YS, Cho IK, Li QX (2006) Degradation of dibenzothiophene and carbazole by Arthrobacter sp. P1-1. Int biodet biodegrad 58:36–43
Soleimani M, Bassi A, Margaritis A (2007) Biodesulfurization of refractory organic sulfur compounds in fossil fuels. Biotechnol Adv 25:570–596
Song C, Ma X (2003) New design approaches to ultra-clean diesel fuels by deep desulfurization and deep dearomatization. Appl Catal B Environ 41:207–238
Van der Ploeg JR, Leisinger EET (2001) Sulfonate-sulfur metabolism and its regulation in Escherichia coli. Arch Microbiol 176:1–8
Weisburg WG, Barns SM, Pelletier DA, Lane DJ (1991) 16s ribosomal DNA amplification for phylogenetic study. J Bacteriol 173:697–703
Acknowledgment
This work was kindly supported by the vice chancellor for research office of Shahid Chamran Univesity, Iran and National Iranian South Oil Company (NISOC), Department of Research and Development and Department of Chemicals and Laboratories. Great thanks to Seied Abbas Dibaj, GC-man of gas chromatography laboratory of NISOC.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Papizadeh, M., Ardakani, M.R., Ebrahimipour, G. et al. Utilization of dibenzothiophene as sulfur source by Microbacterium sp. NISOC-06 . World J Microbiol Biotechnol 26, 1195–1200 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-009-0288-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-009-0288-8