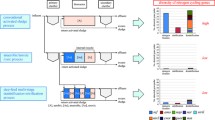
Abstract
A novel DNA microarray analysis targeting key functional genes involved in most nitrogen cycling reactions was developed to comprehensively analyze microbial populations associated with the nitrogen cycle. The developed microarray contained 876 oligonucleotide probes based on the nucleotide sequences of the nif, amo, hao/hzo, nap, nar, nirK, nirS, nrf, cnor, qnor and nos genes. An analytical method combining detection by the designed microarray with whole community genome amplification was then applied to monitor the nitrogen cycling microorganisms in river water and wastewater treatment sludge samples. The developed method revealed that nitrogen cycling microorganisms in river water appeared to become less diverse in response to input of effluent from municipal wastewater treatment plants. Additionally, the nitrogen cycling community associated with anaerobic ammonium oxidation and partial nitrification reactors could be reasonably analyzed by the developed method. However, the results obtained for two activated sludge samples from municipal wastewater treatment plants with almost equivalent wastewater treatment performance differed greatly from each other. These results suggested that the developed method is useful for comprehensive analysis of nitrogen cycling microorganisms, although its applicability to complex samples with abundant untargeted populations should be further examined.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abell GCJ, Robert SS, Frampton DMF, Volkman JK, Rizwi F, Csontos J, Bodrossy L (2012) High-throughput analysis of ammonia oxidiser community composition via a novel, amoA-based functional gene array. PLoS ONE 7:e51542
Amann RI, Ludwig W, Schelifer KH (1995) Phylogenetic identification and in situ detection of individual microbial cells without cultivation. Microbiol Rev 59:143–169
Bartossek R, Nicol GW, Lanzen A, Klenk HP, Schleper C (2010) Homologues of nitrite reductases in ammonia-oxidizing archaea: diversity and genomic context. Environ Microbiol 12:1075–1088
Casciotti KL, Ward BB (2001) Dissimilatory nitrite reductase genes from autotrophic ammonia-oxidizing bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:2213–2221
Casciotti KL, Ward BB (2005) Phylogenetic analysis of nitric oxide reductase gene homologues from aerobic ammonia-oxidizing bacteria. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 52:197–205
Cébron A, Garnier J (2005) Nitrobacter and Nitrospira genera as representatives of nitrite-oxidizing bacteria: detection, quantification and growth along the lower Seine River (France). Water Res 39:4979–4992
Cébron A, Coci M, Garnier J, Laanbroek HJ (2004) Denaturing gradient gel electrophoretic analysis of ammonia-oxidizing bacterial community structure in the lower Seine River: impact of Paris wastewater effluents. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:6726–6737
Duc L, Neuenschwander S, Rehrauer H, Wagner U, Sobek J, Schlapbach R, Zeyer J (2009) Development and experimental validation of a nifH oligonucleotide microarray to study diazotrophic communities in a glacier forefield. Environ Microbiol 11:2179–2189
Edgcomb VP, McDonald JH, Devereux R, Smith DW (1999) Estimation of bacterial cell numbers in humic acid-rich salt marsh sediments with probes directed to 16S ribosomal DNA. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:1516–1523
Farrelly V, Rainey FA, Stackebrandt E (1995) Effect of genome size and rrn gene copy number on PCR amplification of 16S rRNA genes from a mixture of bacterial species. Appl Environ Microbiol 61:2798–2801
Garbeva P, Baggs EM, Prosser JI (2007) Phylogeny of nitrite reductase (nirK) and nitric oxide reductase (norB) genes from Nitrosospira species isolated from soil. FEMS Microbiol Lett 266:83–89
Guschin DY, Mobarry BK, Proudnikov D, Stahl DA, Rittmann BE, Mirzabekov AD (1997) Oligonucleotide microchips as genosensors for determinative and environmental studies in microbiology. Appl Environ Microbiol 63:2397–2402
Hashimoto K, Matsuda M, Inoue D, Ike M (2014) Bacterial community dynamics in a full-scale municipal wastewater treatment plant employing conventional activated sludge process. J Biosci Bioeng 118:64–71
He Z, Deng Y, Zhou J (2012) Development of functional gene microarrays for microbial community analysis. Curr Opin Biotechnol 23:49–55
Inoue D, Nakama K, Sawada K, Watanabe T, Takagi M, Sei K, Yang M, Hirotsuji J, Hu J, Nishikawa J, Nakanishi T, Ike M (2010) Contamination with retinoic acid receptor agonists in two rivers in the Kinki region of Japan. Water Res 44:2409–2418
Moisander PH, Morrison AE, Ward BB, Jenkins BD, Zehr JP (2007) Spatial–temporal variability in diazotroph assemblages in Chesapeake Bay using an oligonucleotide nifH microarray. Environ Microbiol 9:1823–1835
Nakagawa Y, Takai K, Sei K, Soda S, Ike M (2011) Nitrogen removal by combination of anammox bacteria and heterotrophic denitrifying bacteria in a batch mode. Proc of First Int Anammox Symposium, pp 311–312
Park S, Ely RL (2008) Candidate stress genes of Nitrosomonas europaea for monitoring inhibition of nitrification by heavy metals. Appl Environ Microbiol 74:5475–5482
Philippot L (2002) Denitrifying genes in bacterial and archaeal genomes. Biochim Biophys Acta 1577:355–376
Philippot L (2006) Use of functional genes to quantify denitrifiers in the environment. Biochem Soc Trans 34:101–103
Prosser JI, Embley TM (2002) Cultivation-based and molecular approaches to characterization of terrestrial and aquatic nitrifiers. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 81:165–179
Quan ZX, Rhee SK, Zuo JE, Yang Y, Bae JW, Park JR, Lee ST, Park YH (2008) Diversity of ammonium-oxidizing bacteria in a granular sludge anaerobic ammonium-oxidizing (anammox) reactor. Environ Microbiol 10:3130–3139
Schmid M, Twchtmann U, Klein M, Strous M, Juretchko S, Jetten M, Metzger JW, Schleifer K, Wagner M (2000) Molecular evidence for genus level diversity of bacteria capable of catalyzing anaerobic ammonium oxidation. Syst Appl Microbiol 23:93–106
Sei K, Asano K, Tateishi N, Mori K, Ike M, Kohno T, Fujita M (2000) Development of simple methods of DNA extraction from environmental samples for monitoring microbial community based on PCR. Jpn J Water Treat Biol 36:193–204
Sei K, Inaba M, Upadhye R, Inoue D, Ike M (2009) Development of DNA microarray for the evaluation of environmental functions. Water Sci Technol 59:97–107
Seviour RJ, Nielsen PH (2010) Microbial ecology of activated sludge. IWA Publishing, London
Shinozaki H, Fukui M (2002) Comparison of 16S rRNA, ammonia monooxygenase subunit A and hydroxylamine oxidoreductase gene, in chemolithotrophic ammonia-oxidizing bacteria. J Gen Appl Microbiol 48:173–176
Smith VH, Tilman GD, Nekola JC (1999) Eutrophication: impacts of excess nutrient inputs on freshwater, marine, and terrestrial ecosystems. Environ Pollut 100:179–196
Song B, Tobias CR (2011) Molecular and stable isotope methods to detect and measure anaerobic ammonium oxidation (anammox) in aquatic ecosystems. Methods Enzymol 496:63–89
Taroncher-Oldenburg G, Griner EM, Francis CA, Ward BB (2003) Oligonucleotide microarray for the study of functional gene diversity in the nitrogen cycle in the environment. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:1159–1171
Van Nostrand JD, He Z, Zhou J (2012) Use of functional gene arrays for elucidating in situ biodegradation. Front Microbiol 3:339
Ward BB, Eveillard D, Kirshtein JD, Nelson JD, Voytek MA, Jackson GA (2007) Ammonia-oxidizing bacterial community composition in estuarine and oceanic environments assessed using a functional gene microarray. Environ Microbiol 9:2522–2538
Wu L, Thompson DK, Li G, Hurt RA, Tiedje JM, Zhou J (2001) Development and evaluation of functional gene array for detection of selected genes in the environment. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:5780–5790
Wu L, Liu X, Schadt CW, Zhou J (2006) Microarray-based analysis of subnanogram quantities of microbial community DNAs by using whole-community genome amplification. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:4931–4941
Yang XE, Wu X, Hao HL, He ZL (2008) Mechanisms and assessment of water eutrophication. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B 9:197–209
Yergeau E, Kang S, He Z, Zhou J, Kowalchuk GA (2007) Functional microarray analysis of nitrogen and carbon cycling genes across an Antarctic latitudinal transect. ISME J 1:163–179
Zhang L, Hurek T, Reihold-Hurek B (2006) A nifH-based oligonucleotide microarray for functional diagnostics of nitrogen-fixing microorganisms. Microb Ecol 53:456–470
Acknowledgments
This study was partly supported by the Global COE Program, “Evaluation of Research and Education on Integrated River Basin Management in Asian Region” of the University of Yamanashi, which was sponsored by the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS) and by a grant from the Kurita Water Environment Foundation, Japan. We thank Dr. Kazuichi Isaka from Hitachi Plant Technologies, Ltd., Japan (Presently, Hitachi, Ltd., Japan) for kindly providing the partial nitrification sludge samples.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Inoue, D., Pang, J., Matsuda, M. et al. Development of a whole community genome amplification-assisted DNA microarray method to detect functional genes involved in the nitrogen cycle. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 30, 2907–2915 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-014-1718-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-014-1718-9