Abstract
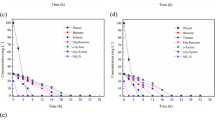
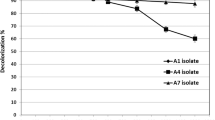
The study aimed to investigate the efficiency of exogenous bacterial consortium (Enterobacter cloacae and Pseudomonas otitidis) decorated (immobilized) with Fe3O4 Nanoparticles for the treatment of petroleum hydrocarbon-contaminated wastewater. Glycine coated magnetite Nanoparticles (Fe3O4 NPs) were prepared using reverse co-precipitation method and were characterized using X-ray diffraction, transmission and scanning electron microscopy and vibrating sample magnetometer. They were used to decorate exogenous bacterial consortium (Enterobacter cloacae and Pseudomonas otitidis) at 3 different Fe3O4/bacteria ratios (1:1, 1:3 and 3:1 w/w). Bioremediation of oil contaminated wastewater collected from one of the petroleum distribution companies, Alexandria was conducted for 168 h using Fe3O4/bacterial association at the best ratio (3:1) and compared with non-decorated consortium and the indigenous bacteria in the control. Analysis indicated crystalline structure of Fe3O4 NPs with spherical particles (size: 15–20 nm) and superparamagnetic properties. Glycine modified-Fe3O4 exhibited high ability to immobilize bacteria which acquired its magnetic properties. The highest coating efficiency (92%) was achieved at 3:1 Fe3O4/bacteria ratio after 1 h. This ratio positively affected bacterial growth reaching the highest growth rate (5.07 fold higher than the control) after 4 h. The highest removal efficiencies of the total suspended solids (TSS), chemical oxygen demands (COD), oil and grease (O&G) and total petroleum hydrocarbons (TPH) recording 96, 65.4, 83.9 and 85% reaching residual concentrations of 9.5, 598, 99 and 60 mg/l respectively were achieved after 4 h by the Fe3O4-bacteria assembly. Compared with the maximum permissible limits of the tested parameters, TSS residue was highly compiled with its limit (50 mg/l), while COD, O&G and TPH were 7.5, 9.9, and 120-folds higher than their limits (100, 15 and 0.5 mg/l respectively). To the best of our knowledge it is first time to use integrated Enterobacter cloacae and Pseudomonas otitidis consortium decorated with Fe3O4 NPs for the treatment of petroleum hydrocarbon-contaminated wastewater. The proposed system proved to be a very efficient, economical and applicable for the removal of the included contaminants in very short running time which increases its biotechnological added value.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdelwahab O, Amin N, El-Ashtoukhy EZ (2009) Electrochemical removal of phenol from oil refinery wastewater. J Hazard Mater 163:711–716
Al Zarooni M, Elshorbagy W (2006) Characterization and assessment of Al Ruwais refinery wastewater. J Hazard Mater 136:398–405
Alizadeh A, Khodaei MM, Beygzadeh M, Kordestani D, Feyzi M (2012) Biguanide-functionalized Fe3O4/SiO2 magnetic nanoparticles: an efficient heterogeneous organosuperbase catalyst for various organic transformations in aqueous media. Bull Korean Chem Soc 33:2546–2552
Altaş L, Büyükgüngör H (2008) Sulfide removal in petroleum refinery wastewater by chemical precipitation. J Hazard Mater 153:462–469
Ansari F, Grigoriev P, Libor S, Tothill IE, Ramsden JJ (2009) DBT degradation enhancement by decorating Rhodococcus erythropolis IGST8 with magnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles. Biotechnol Bioeng 102(5):1505–1512
Baghaie AH, Jabari AG (2019) Effect of nano Fe-oxide and endophytic fungus (P. indica) on petroleum hydrocarbons degradation in an arsenic contaminated soil under barley cultivation. J Environ Health Sci Eng 1–9
Bardania H, Raheb J, Mohammad-Beigi H, Rasekh B, Arpanaei A (2013) Desulfurization activity and reusability of magnetite nanoparticle–coated Rhodococcus erythropolis FMF and R. erythropolis IGTS8 bacterial cells. Biotechnol Appl Biochem 60(3):323–329
Boniek D, Figueiredo D, dos Santos AFB, de Resende Stoianoff MA (2015) Biodesulfurization: a mini review about the immediate search for the future technology. Clean Technol Environ Policy 17:29–37
Bruno A, Correa J, Peláez-Abellán E, Urones-Garrote E (2018) A novel method for the functionalization of aminoacids l-glycine, l-glutamic acid and l-arginine on maghemite/magnetite nanoparticles. J Magn Magn Mater 456:87–91
Changmai M, Pasawan M, Purkait M (2019) Treatment of oily wastewater from drilling site using electrocoagulation followed by microfiltration. Sep Purif Technol 210:463–472
Chen J, Liu S, Qi X, Yan S, Guo Q (2018) Study and design on chemical oxygen demand measurement based on ultraviolet absorption. Sens Actuat B Chem 254:778–784
Chen M, Zhu L, Chen J, Yang F, Tang CY, Guiver MD, Dong Y (2020) Spinel-based ceramic membranes coupling solid sludge recycling with oily wastewater treatment. Water Res 169:115180
Choi O, Hu Z (2008) Size dependent and reactive oxygen species related nanosilver toxicity to nitrifying bacteria. Environ Sci Technol 42:4583–4588
Clesceri L, Greenberg A, Eaton A (1999) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 20th edn. American Public Health Association, American Water Work Association, Water Environment Federation, Washington, DC, APHA-AWWA-WEF
Crini G, Lichtfouse E (2019) Advantages and disadvantages of techniques used for wastewater treatment. Environ Chem Lett 17:145–155
Darabdhara G, Boruah PK, Hussain N, Borthakur P, Sharma B, Sengupta P, Das MR (2017) Magnetic nanoparticles towards efficient adsorption of gram positive and gram negative bacteria: an investigation of adsorption parameters and interaction mechanism. Colloids Surf Physicochem Eng Aspects 516:161–170
Das N, Chandran P (2011) Microbial degradation of petroleum hydrocarbon contaminants: an overview. Biotechnol Res Int. https://doi.org/10.4061/2011/941810
Diya’uddeen BH, Daud WMAW, Aziz AA (2011) Treatment technologies for petroleum refinery effluents: a review. Process Saf Environ Prot 89:95–105
El Bestawy E, Ahmed A-H, Amer R, Kashmeri RA (2014) Decontamination of domestic wastewater using suspended individual and mixed bacteria in batch system. J Bioremed Biodegred 5:1
El-Bestawy E, El-KHeir EA, El-Fatah HA, Hassouna S (1998) Enhancement of bacterial efficiency for metal removal using mutation techniques. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 14:853–856
El-Boubbou K, Gruden C, Huang X (2007) Magnetic glyco-nanoparticles: a unique tool for rapid pathogen detection, decontamination, and strain differentiation. J Am Chem Soc 129(44):13392–13393
El-Subruiti G, Eltaweil A, Sallam S (2019) Synthesis of active MFe2O4/γ-Fe2O3 nanocomposites (metal = Ni or Co) for reduction of nitro-containing pollutants and methyl orange degradation. NANO 14:1950125
Escobar AM, Blanco MN, Martínez JJ, Cubillos JA, Romanelli GP, Pizzio LR (2019) Biomass derivative valorization using nano core-shell magnetic materials based on keggin-heteropolyacids: levulinic acid esterification kinetic study with n-butanol. J Nanomater 2019
Gubin SP, Koksharov YA, Khomutov G, Yurkov GY (2005) Magnetic nanoparticles: preparation, structure and properties. Russ Chem Rev 74:489
Guobin S, Huaiying Z, Weiquan C, Jianmin X, Huizhou L (2005) Improvement of biodesulfurization rate by assembling nanosorbents on the surfaces of microbial cells. Biophys J 89(6):L58–L60
He K, Chen G, Zeng G, Huang Z, Guo Z, Huang T, Peng M, Shi J, Hu L (2017) Applications of white rot fungi in bioremediation with nanoparticles and biosynthesis of metallic nanoparticles. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 101:4853–4862
Henshaw PF, Zhu W (2001) Biological conversion of hydrogen sulphide to elemental sulphur in a fixed-film continuous flow photo-reactor. Water Res 35:3605–3610
Hou J, Liu F, Wu N, Ju J, Yu B (2016) Efficient biodegradation of chlorophenols in aqueous phase by magnetically immobilized aniline-degrading Rhodococcus rhodochrous strain. J Nanobiotechnol 14:5
Jia X, Zhang S, Li J, Xia J, Yao R, Zhao X, Wu B, Bai F, Xiao Y (2019) Engineered bacterial biofloc formation enhancing phenol removal and cell tolerance. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 1–13
Kafayati ME, Raheb J, Torabi Angazi M, Alizadeh S, Bardania H (2013) The effect of magnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles on the growth of genetically manipulated bacterium, Pseudomonas aeruginosa (PTSOX4). Iran J Biotechnol 11(1):41–46
Kalfa OM, Yalçınkaya Ö, Türker AR (2009) Synthesis of nano B2O3/TiO2 composite material as a new solid phase extractor and its application to preconcentration and separation of cadmium. J Hazard Mater 166:455–461
Katam K, Bhattacharyya D (2019) Simultaneous treatment of domestic wastewater and bio-lipid synthesis using immobilized and suspended cultures of microalgae and activated sludge. J Ind Eng Chem 69:295–303
Khan F, Lee J-W, Pham DTN, Lee J-H, Kim H-W, Kim Y-K, Kim Y-M (2019) Streptomycin mediated biofilm inhibition and suppression of virulence properties in Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 1–18
Kiser MA, Ryu H, Jang H, Hristovski K, Westerhoff P (2010) Biosorption of nanoparticles to heterotrophic wastewater biomass. Water Res 44:4105–4114
Konate A, Wang Y, He X, Adeel M, Zhang P, Ma Y, Ding Y, Zhang J, Yang J, Kizito S (2018) Comparative effects of nano and bulk-Fe3O4 on the growth of cucumber (Cucumis sativus). Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 165:547–554
Kumari B, Singh D (2016) A review on multifaceted application of nanoparticles in the field of bioremediation of petroleum hydrocarbons. Ecol Eng 97:98–105
Li Y-G, Gao H-S, Li W-L, Xing J-M, Liu H-Z (2009) In situ magnetic separation and immobilization of dibenzothiophene-desulfurizing bacteria. Bioresour Technol 100(21):5092–5096
Liu Y, Feng H, Fu R, Zhang N, Du W, Shen Q, Zhang R (2019a) Induced root-secreted d-galactose functions as a chemoattractant and enhances the biofilm formation of Bacillus velezensis SQR9 in an McpA-dependent manner. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 1–13
Liu Y, Wang W, Shah SB, Zanaroli G, Xu P, Tang H (2019b) Phenol biodegradation by Acinetobacter radioresistens APH1 and its application in soil bioremediation. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 1–11
Mahmoudi M, Simchi A, Milani A, Stroeve P (2009) Cell toxicity of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. J colloid Interface Sci 336(2):510–518
Mahmoudi M, Shokrgozar MA, Sardari S, Moghadam MK, Vali H, Laurent S, Stroeve P (2011) Irreversible changes in protein conformation due to interaction with superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. Nanoscale 3(3):1127–1138
Mailoud OM, Elsayed AH, Abo-Elazm A, Fetouh H (2018) Synthesis and study the structure, optical, thermal and dielectric properties of promising glycine copper nitrate (GCN) single crystals. Results Phys 10:512–520
Meng L, Bao M, Sun P (2018) Construction of long-chain alkane degrading bacteria and its application in bioremediation of crude oil pollution. Int J Biol Macromol 119:524–532
Pardeshi S, Patil A (2008) A simple route for photocatalytic degradation of phenol in aqueous zinc oxide suspension using solar energy. Sol Energy 82:700–705
Polak J, Lu BC-Y (1973) Mutual solubilities of hydrocarbons and water at 0 and 25 °C. Can J Chem 51:4018–4023
Poulopoulos S, Voutsas E, Grigoropoulou H, Philippopoulos C (2005) Stripping as a pretreatment process of industrial oily wastewater. J Hazard Mater 117:135–139
Qiao N, Gao M, Zhang X, Du Y, Fan X, Wang L, Liu N, Yu D (2019) Trichosporon fermentans biomass flocculation from soybean oil refinery wastewater using bioflocculant produced from Paecilomyces sp. M2-1. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 103:2821–2831
Raee MJ, Ebrahiminezhad A, Ghoshoon MB, Gholami A, Ghasemi Y (2019) Synthesis and characterization of L-lysin coated iron oxide nanoparticles as appropriate choices for cell immobilization and magnetic separation. Nanosci Nanotechnol-Asia 9:462–466
Ranmadugala D, Ebrahiminezhad A, Manley-Harris M, Ghasemi Y, Berenjian A (2018) Magnetic immobilization of bacteria using iron oxide nanoparticles. Biotechnol Lett 40:237–248
Rathnayake D, Sathasivan A, Kastl G, Krishna KB (2019) Hydrogen sulphide control in sewers by catalysing the reaction with oxygen. Sci Total Environ 689:1192–1200
Reddy LH, Arias JL, Nicolas J, Couvreur P (2012) Magnetic nanoparticles: design and characterization, toxicity and biocompatibility, pharmaceutical and biomedical applications. Chem Rev 112:5818–5878
Sallam S, El-Subruiti G, Eltaweil A (2018) Facile synthesis of Ag-γ-Fe2O3 superior nanocomposite for catalytic reduction of nitroaromatic compounds and catalytic degradation of methyl orange. Catal Lett 148:3701–3714
Samanta B, Yan H, Fischer NO, Shi J, Jerry DJ, Rotello VM (2008) Protein-passivated Fe3O4 nanoparticles: low toxicity and rapid heating for thermal therapy. J Mater Chem 18(11):1204–1208
Sarafzadeh P, Hezave AZ, Ravanbakhsh M, Niazi A, Ayatollahi S (2013) Enterobacter cloacae as biosurfactant producing bacterium: differentiating its effects on interfacial tension and wettability alteration mechanisms for oil recovery during MEOR process. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 105:223–229
Sathishkumar M, Binupriya AR, Baik SH, Yun SE (2008) Biodegradation of crude oil by individual bacterial strains and a mixed bacterial consortium isolated from hydrocarbon contaminated areas. Clean-Soil Air Water 36:92–96
Schwaminger SP, García PF, Merck GK, Bodensteiner FA, Heissler S, Günther S, Berensmeier S (2015) Nature of interactions of amino acids with bare magnetite nanoparticles. J Phys Chem C 119:23032–23041
Shan G, Xing J, Zhang H, Liu H (2005) Biodesulfurization of dibenzothiophene by microbial cells coated with magnetite nanoparticles. Appl Environ Microbiol 71(8):4497–4502
Shin M, Nguyen T, Ramsay J (2002) Evaluation of support materials for the surface immobilization and decoloration of amaranth by Trametes versicolor. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 60:218–223
Soares-Castro P, Yadav TC, Viggor S, Kivisaar M, Kapley A, Santos PM (2019) Seasonal bacterial community dynamics in a crude oil refinery wastewater treatment plant. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 103:9131–9141
Stoll U, Gupta H (1997) Management strategies for oil and grease residues. Waste Manage Res 15:23–32
Sulistyaningsih T, Santosa SJ, Siswanta D, Rusdiarso B (2017) Synthesis and characterization of magnetites obtained from mechanically and sonochemically assissted co-precipitation and reverse co-precipitation methods. Int J Mater Mech Manuf 5:16–19
Sze K, Lu Y, Wong P (1997) Removal and recovery of copper ion (Cu2+) from electroplating effluent by a bioreactor containing magnetite-immobilized cells of Pseudomonas putida 5X. Stud Environ Sci 66:131–149
Tanudjaja HJ, Hejase CA, Tarabara VV, Fane AG, Chew JW (2019) Membrane-based separation for oily wastewater: a practical perspective. Water Res 156:347–365
Viota J, Arroyo F, Delgado A, Horno J (2010) Electrokinetic characterization of magnetite nanoparticles functionalized with amino acids. J Colloid Interface Sci 344:144–149
Wang Z, Fingas M (1995) Differentiation of the source of spilled oil and monitoring of the oil weathering process using gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr 712:321–343
Wang Y-D, Li X-L, Liu Z-X, Zhang X-X, Hu J, Lü J-H (2017) Discrimination of foodborne pathogenic bacteria using synchrotron FTIR microspectroscopy. Nucl Sci Technol 28:49
Wu C, He H, Gao H, Liu G, Ma R, An Y, Shi L (2010) Synthesis of Fe3O4@ SiO2@ polymer nanoparticles for controlled drug release. Sci China Chem 53:514–518
Wu X, He H, Yang WL, Yu J, Yang C (2018) Efficient removal of atrazine from aqueous solutions using magnetic Saccharomyces cerevisiae bionanomaterial. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 102:7597–7610
Xia M, Fu D, Chakraborty R, Singh RP, Terry N (2019) Enhanced crude oil depletion by constructed bacterial consortium comprising bioemulsifier producer and petroleum hydrocarbon degraders. Bioresour Technol 282:456–463
Xu X, Zhu X (2004) Treatment of refectory oily wastewater by electro-coagulation process. Chemosphere 56:889–894
Xu P, Yu B, Li FL, Cai XF, Ma CQ (2006) Microbial degradation of sulfur, nitrogen and oxygen heterocycles. Trends Microbiol 14:398–405
Xu P, Zeng GM, Huang DL, Feng CL, Hu S, Zhao MH, Lai C, Wei Z, Huang C, Xie GX (2012) Use of iron oxide nanomaterials in wastewater treatment: a review. Sci Total Environ 424:1–10
Yu L, Han M, He F (2017) A review of treating oily wastewater. Arabian J Chem 10:S1913–S1922
Yu L, Yang Y, Yang B, Li Z, Zhang X, Hou Y, Lei L, Zhang D (2018) Effects of solids retention time on the performance and microbial community structures in membrane bioreactors treating synthetic oil refinery wastewater. Chem Eng J 344:462–468
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest. This article does not contain any studies with animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bestawy, E.E., El-Shatby, B.F. & Eltaweil, A.S. Integration between bacterial consortium and magnetite (Fe3O4) nanoparticles for the treatment of oily industrial wastewater. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 36, 141 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-020-02915-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-020-02915-1