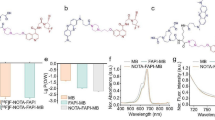
Abstract
Purpose
We examine the feasibility of fluorescent imaging system for sentinel lymph node detection by using functionalized silica nanoparticles.
Materials and Methods
We developed a functionalized RITC-SiO2 nanoparticles containing fluorescent dye, C28H31N2O3Cl (rhodamine B isothiocyanate) inside, and subsequently synthesized 68Ga-NOTA-RITC-SiO2 nanoparticles.
Results
At 5 min after RITC-doped silica nanoparticles injection, fluorescent signals were shown in both right axillary lymph node (ALN) and injection site of living mice. Fluorescent signals were also observed at these locations in a biodistribution study. In addition, fluorescence was detected in frozen ALN sections microscopically. The percentages of doses injected per gram of tissue of axillary and brachial lymph nodes near footpad treated with 68Ga-NOTA-RITC-SiO2 nanoparticles were 308.3 ± 3.4 and 41.5 ± 6.1, respectively. Little 68Ga radioactivity was found in other organs.
Conclusion
Our data provide strong evidence that functionalized silica nanoparticles has a promising potential as organic lymphatic tracer in biomedical imaging such as pre- and intraoperative surgical guidance.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Radovanovic Z, Golubovic A, Plzak A, Stojiljkovic B, Radovanovic D (2004) Blue dye versus combined blue dye-radioactive tracer technique in detection of sentinel lymph node in breast cancer. Eur J Surg Oncol 30:913–917
Rodier JF, Velten M, Wilt M et al (2007) Prospective multicentric randomized study comparing periareolar and peritumoral injection of radiotracer and blue dye for the detection of sentinel lymph node in breast sparing procedures: FRANSENODE trial. J Clin Oncol 25:3664–3669
Roberts AA, Cochran AJ (2004) Pathologic analysis of sentinel lymph nodes in melanoma patients: current and future trends. J Surg Oncol 85:152–161
Aikou T, Kitagawa Y, Kitajima M et al (2006) Sentinel lymph node mapping with GI cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev 25:269–277
Nejc D, Wrzesien M, Piekarski J et al (2006) Sentinel node biopsy in patients with breast cancer—evaluation of exposure to radiation of medical staff. Eur J Surg Oncol 32:133–138
Hardman R (2006) A toxicologic review of quantum dots: toxicity depends on physicochemical and environmental factors. Environ Health Perspect 114:165–172
Zhang T, Stilwell JL, Gerion D et al (2006) Cellular effect of high doses of silica-coated quantum dot profiled with high throughput gene expression analysis and high content cellomics measurements. Nano Lett 6:800–808
Sevick-Muraca EM, Sharma R, Rasmussen JC et al (2008) Imaging of lymph flow in breast cancer patients after microdose administration of a near-infrared fluorophore: feasibility study. Radiology 246:734–741
Kobayashi H, Hama Y, Koyama Y et al (2007) Simultaneous multicolor imaging of five different lymphatic basins using quantum dots. Nano Lett 7:1711–1716
Kim S, Lim YT, Soltesz EG et al (2004) Near-infrared fluorescent type II quantum dots for sentinel lymph node mapping. Nat Biotechnol 22:93–97
Pelosi E, Ala A, Bello M et al (2005) Impact of axillary nodal metastases on lymphatic mapping and sentinel lymph node identification rate in patients with early stage breast cancer. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 32:937–942
Josephson L, Mahmood U, Wunderbaldinger P, Tang Y, Weissleder R (2003) Pan and sentinel lymph node visualization using a near-infrared fluorescent probe. Mol Imaging 2:18–23
Simmons RM, Smith SM, Osborne MP (2001) Methylene blue dye as an alternative to isosulfan blue dye for sentinel lymph node localization. Breast J 7:181–183
Rety F, Clement O, Siauve N et al (2000) MR lymphography using iron oxide nanoparticles in rats: pharmacokinetics in the lymphatic system after intravenous injection. J Magn Reson Imaging 12:734–739
Karakousis CP, Velez AF, Spellman JE Jr, Scarozza J (1996) The technique of sentinel node biopsy. Eur J Surg Oncol 22:271–275
Alex JC, Krag DN (1993) Gamma-probe guided localization of lymph nodes. Surg Oncol 2:137–143
Alex JC, Weaver DL, Fairbank JT, Rankin BS, Krag DN (1993) Gamma-probe-guided lymph node localization in malignant melanoma. Surg Oncol 2:303–308
Hirsch JI (1980) Use of blue dyes in lymphography. Am J Hosp Pharm 37:1182–1183
Yoon TJ, Yu KN, Kim E et al (2006) Specific targeting, cell sorting, and bioimaging with smart magnetic silica core–shell nanomaterials. Small 2:209–215
Wang J, Liu G, Lin Y (2006) Electroactive silica nanoparticles for biological labeling. Small 2:1134–1138
Barik TK, Sahu B, Swain V (2008) Nanosilica—from medicine to pest control. Parasitol Res 103:253–258
Yoon TJ, Kim JS, Kim BG et al (2005) Multifunctional nanoparticles possessing a “magnetic motor effect” for drug or gene delivery. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 44:1068–1071
Wang L, Tan W (2006) Multicolor FRET silica nanoparticles by single wavelength excitation. Nano Lett 6:84–88
Stöber W, Fink A, Bohn E (1968) Controlled growth of monodisperse silica spheres in the micron size range. J Colloid Interface Sci 26:62–69
Smith JE, Wang L, Tan W (2006) Bioconjugated silica-coated nanoparticles for bioseparation and bioanalysis. TrAC, Trends Anal Chem 25:848–855
Santra S, Liesenfeld B, Dutta D et al (2005) Folate conjugated fluorescent silica nanoparticles for labeling neoplastic cells. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 5:899–904
Rutgers EJ (2008) Sentinel node biopsy: interpretation and management of patients with immunohistochemistry-positive sentinel nodes and those with micrometastases. J Clin Oncol 26:698–702
Zhang H, Yee D, Wang C (2008) Quantum dots for cancer diagnosis and therapy: biological and clinical perspectives. Nanomedicine 3:83–91
Chen K, Li ZB, Wang H, Cai W, Chen X (2008) Dual-modality optical and positron emission tomography imaging of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor on tumor vasculature using quantum dots. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 35:2235–2244
Misra RD (2008) Quantum dots for tumor-targeted drug delivery and cell imaging. Nanomedicine 3:271–274
Michalet X, Pinaud FF, Bentolila LA et al (2005) Quantum dots for live cells, in vivo imaging, and diagnostics. Science 307:538–544
Kobayashi H, Brechbiel MW (2003) Dendrimer-based macromolecular MRI contrast agents: characteristics and application. Mol Imaging 2:1–10
Hama Y, Koyama Y, Urano Y, Choyke PL, Kobayashi H (2007) Two-color lymphatic mapping using Ig-conjugated near infrared optical probes. J Invest Dermatol 127:2351–2356
Kim JS, Yoon TJ, Yu KN et al (2006) Toxicity and tissue distribution of magnetic nanoparticles in mice. Toxicol Sci 89:338–347
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Interdisciplinary Research Initiatives Program of the College of Natural Sciences and the College of Medicine, Seoul National University 2008 and by Research Division of Human Life Science of the second stage Brain Korea 21 Project in 2009.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Yong Hyun Jeon and Young-Hwa Kim contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Table S1
Biodistribution of 68Ga-NOTA-RITC-SiO2 nanoparticles in nude mice. The %ID/g values of axillary and brachial lymph nodes near footpad treated with 68Ga-NOTA-RITC-SiO2 nanoparticles were 308.3 ± 3.4 and 41.5 ± 6.1, respectively. Little 68Ga radioactivity was found in other organs. (e.g., liver, lung, brain, spleen, and kidney) ALN axillary lymph node, IN inguinal lymph node, SN sciatic lymph node, BLN brachial lymph node, SCN superficial cervical lymph node. Data are expressed as %ID/g of tissue. n = 5 mice (PDF 482 KB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jeon, Y.H., Kim, YH., Choi, K. et al. In Vivo Imaging of Sentinel Nodes Using Fluorescent Silica Nanoparticles in Living Mice. Mol Imaging Biol 12, 155–162 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11307-009-0262-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11307-009-0262-8