Abstract
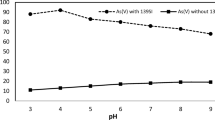
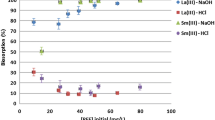
In this work, removal of arsenic (III) from aqueous solution by living cells (Bacillus cereus), biosorption mechanism, and characterization studies have been reported. B. cereus cell surface was characterized using SEM-EDX and FTIR. Dependence of biosorption on pH of the solution, biosorbent dose, initial arsenic (III) concentration, contact time, and temperature had been studied to achieve optimum condition. The maximum biosorption capacity of living cells of B. cereus for arsenic (III) was found to be 32.42 mg/g at pH 7.5, at optimum conditions of contact time of 30 min, biomass dosage of 6 g/L, and temperature of 30 ± 2 °C. Biosorption data of arsenic (III) are fitted to linearly transformed Langmuir isotherm with R 2 (correlation coefficient) > 0.99. The pseudo-second-order model description of the kinetics of arsenic (III) is successfully applied to predict the rate constant of biosorption. Thermodynamic parameters reveal the endothermic, spontaneous, and feasible nature of sorption process of arsenic (III) onto B. cereus biomass. The arsenic (III) ions are desorbed from B. cereus using both 1 M HCl and 1 M HNO3.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aksu Z (2002) Determination of the equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic parameters of the batch biosorption of nickel (II) ions onto Chlorella vulgaris. Process Biochem 38:89–99
Allievi MC, Sabbione F, Prado-Acosta M, Palomino MM, Ruzal SM, Sanchez-Rivas C (2011) Metal biosorption by surface layer protein from Bacillus species. J Microbiol Biotechnol 21(2):147–153
Baciocchi R, Chiavola A, Gavasci R (2005) Ion exchange equilibrium of arsenic in the presence of high sulphate and nitrate concentrations. Water Sci Technol: Water Supply 5(5):67–74
Balasubramanian N, Kojima T, Ahmed Basha C, Srinivasakannan C (2009) Removal of arsenic from aqueous solution using electrocoagulation. J Hazard Mater 167:66–969
Boddu VM, Abburib K, Talbottc JL, Smitha ED, Haaschd R (2008) Removal of arsenic (III) and arsenic (V) from aqueous medium using chitosan-coated biosorbent. Water Res 42:633–642
Chowdhury MR, Mulligan CN (2011) Biosorption of arsenic from contaminated water by anaerobic biomass. J Hazard Mater 190(1–3):486–492
Costa AD, Carlos A, Pereira F (2001) Bioaccumulation of copper, zinc, cadmium and lead by Bacillus sp., Bacillus cereus, Bacillus sphaericus and Bacillus subtilis. Braz J Microbiol 32:1–5
Dursun AY, Uslu G, Cuci Y, Aksu Z (2003) Bioaccumulation of copper (II), lead (II) and chromium (VI) by growing Aspergillus niger. Process Biochem 38:1647–1651
François F, Lombard C, Guigner JM, Soreau P, Brian-Jaisson MG, Vandervennet M, Garcia D, Molinier AL, Pignol D, Peduzzi J, Zirah S, Rebuffat S (2012) Isolation and characterization of environmental bacteria capable of extracellular biosorption of mercury. Appl Environ Microbiol 78:1097–1106
Giri AK, Patel RK, Mahapatra SS (2011) Artificial neural network (ANN) approach for modeling of arsenic(III) biosorption from aqueous solution by living cells of Bacillus cereus biomass. Chem Eng J178:15–25
Greenberg AE, Trussell RR, Clesceri LS (2005) Standard methods for the examination of water and waste water, 16th edn. APHA AWWA WPCF, Washington, DC
Hansen HK, Ribeiro A, Mateus E (2006) Biosorption of arsenic (V) with Lessonia nigrescens. Miner Eng 19(5):486–490
Ho YS, McKay G (1999) Pseudo-second order model for sorption processes. Process Biochem 34:451–465
Iwamoto T, Nasu M (2001) Current bioremediation practice and perspective. J Biosci Bioeng 32:1–8
Kapoor A, Viraraghavan T, Cullimore DR (1999) Removal of heavy metals using Aspergillus niger. Biores Technol 70:95–104
Kotiranta A, Lounatmaa K, Haapasalo M (2000) Epidemiology and pathogenesis of Bacillus cereus infections. Microbes Infect 2:189–198
Kumari P, Sharma P, Srivastava S, Srivastava MM (2006) Biosorption studies on shelled Moringa oleifera Lamarck seed powder: removal and recovery of arsenic from aqueous system. Int J Miner Process 78:131–139
Lagergren S (1898) Zur theorie der sogenannten adsorption geloster stoffe, Kungliga Sevenska Vetenskapsakademiens. Handlingar 24:1–39
Langmuir I (1918) The adsorption of gases on plane surfaces of glass, mica and platinum. J Am Chem Soc 40:1361–1403
Mashitah MD, Zulfadhly Z, Bhatia S (1999) Binding mechanism of heavy metals biosorption by Pycnoporus sanguineus. J Artif Cells Blood Substit Immobil Biotechnol 27(5/6):441–445
McNeill S, Edwards M (1997) Predicting arsenic removal during metal hydroxide precipitation. J Am Water Works Assoc 89:75–82
Merroun ML, Raff J, Rossberg A, Hennig C, Reich T, Selenska-Pobell S (2005) Complexation of uranium by cells and S-layer sheets of Bacillus sphaericus JG-A12. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:5532–5543
Mohan D, Pittman CU Jr (2007) Arsenic removal from water/wastewater using adsorbents—a critical review. J Hazard Mater 142:1–53
Murugesan GS, Sathishkumar M, Swaminathan K (2006) Arsenic removal from groundwater by pretreated waste tea fungal biomass. Bioresour Technol 97(3):483–487
Pangnanelli F, Papini PM, Toro M, Veglio F (2000) Biosorption of metal ions on Arthrobacter sp.: biomass characterization and biosorption modeling. Environ Sci Technol 34:2773–2778
Pokhrel D, Viraraghavan T (2007) Arsenic removal from an aqueous solution by modified A. niger biomass: batch kinetic and isotherm studies. J Hazard Mater 150:818–825
Prasad KS, Subramanian V, Paul J (2011) Biosorption of As(III) ion on Rhodococcus sp. WB-12: biomass characterization and kinetic studies. Sep Sci Technol 46(16):2517–2525
Ranjan D, Talat MH, Hasan SH (2009) Biosorption of arsenic from aqueous solution using agricultural residue ‘rice polish’. J Hazard Mater 166:1050–1059
Sari A, Tuzen M (2009) Biosorption of As(III) and As(V) from aqueous solution by macrofungus (Inonotus hispidus) biomass: equilibrium and kinetic studies. J Hazard Mater 164:1372–1378
Seki H, Suzuki A, Maruyama H (2005) Biosorption of chromium (VI) and arsenic (V) onto methylated yeast biomass. J Colloid Interf Sci 281(2):261–266
Sharma VK, Sohn M (2009) Aquatic arsenic: toxicity, speciation, transformations, and remediation. Environ Int 35:743–759
Smedley PL, Kinniburgh DG (2005) Sources and behavior of arsenic in natural water. Chapter 1 in United Nations Synthesis Report on Arsenic in Drinking
Smith AH, Lopipero PA, Bates MN, Steinmaus CM (2002) Arsenic epidemiology and drinking water standards. Science 296(21):2145–2146
Thomas SY, Choong TG, Robiah Y, Gregory Koay FL, Azni I (2007) Arsenic toxicity, health hazards and removal techniques from water: an overview. Desalination 217:139–166
Veglio F, Beolchini F (1997) Removal of metals by biosorption: a review. Hydrometallurgy 44:301–316
Velásquez L, Dussan J (2009) Biosorption and bioaccumulation of heavy metals on dead and living biomass of Bacillus sphaericus. J Hazard Mater 167:713–716
Watanabe K, Baker WP (2000) Environmentally relevant microorganisms. J Biosci Bioeng 89(1):1–11
WHO (2008) Guidelines for drinking-water quality [electronic resource]: incorporating 1st and 2nd addenda, vol. 1, Recommendations, 3rd edn. World Health Organization, Geneva
Yan L, Yin H, Zhang S, Leng F, Nan W, Li H (2010) Biosorption of inorganic and organic arsenic from aqueous solution by Acidothiobacillus ferrooxidans BY-3. J Hazard Mater 178:209–217
Acknowledgments
The authors are thankful to Prof. S. K. Sarangi, Director, National Institute of Technology, Rourkela, for providing financial assistance and necessary facilities to help carry out this research work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Robert Duran
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Giri, A.K., Patel, R.K., Mahapatra, S.S. et al. Biosorption of arsenic (III) from aqueous solution by living cells of Bacillus cereus . Environ Sci Pollut Res 20, 1281–1291 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-012-1249-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-012-1249-6