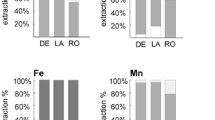
Abstract
Toxicity profiles of two soils (a brownfield in Legazpi and an abandoned iron mine in Zugaztieta; Basque Country) contaminated with several metals (As, Zn, Pb and Cu in Legazpi; Zn, Pb, Cd and Cu in Zugaztieta) and petroleum hydrocarbons (in Legazpi) were determined using a multi-endpoint bioassay approach. Investigated soils exceeded screening values (SVs) of regulatory policies in force (Basque Country; Europe). Acute and chronic toxicity bioassays were conducted with a selected set of test species (Vibrio fischeri, Dictyostelium discoideum, Lactuca sativa, Raphanus sativus and Eisenia fetida) in combination with chemical analysis of soils and elutriates, as well as with bioaccumulation studies in earthworms. The sensitivity of the test species and the toxicity endpoints varied depending on the soil. It was concluded that whilst Zugaztieta soil showed very little or no toxicity, Legazpi soil was toxic according to almost all the toxicity tests (solid phase Microtox®, D. discoideum inhibition of fruiting body formation and developmental cycle solid phase assays, lettuce seed germination and root elongation test, earthworm acute toxicity and reproduction tests, D. discoideum cell viability and replication elutriate assays). Thus, albeit both soils had similar SVs, their ecotoxicological risk, and therefore the need for intervening, was different for each soil as unveiled after toxicity profiling based on multiple endpoint bioassays. Such a toxicity profiling approach is suitable to be applied for scenario-targeted soil risk assessment in those cases where applicable national/regional soil legislation based on SVs demands further toxicity assessment.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alef K, Nannipieri P (1995) Estimation of microbial activities. In: Kassem A, Paolo N (eds) Methods in applied soil microbiology and biochemistry. Academic Press, London, pp 193–270
Alvarenga P, Palma P, Gonçalves A, Fernandes R, de Varennes A, Vallini G, Duarte E, Cunha-Queda A (2008) Evaluation of tests to assess the quality of mine-contaminated soils. Environ Geochem Health 30:95–99
Asensio V (2009) Health assessment of polluted soils after Eisenia foetida ex-situ bioassays based on conventional and in vitro cellular biomarkers and microarray technology. Ph.D.Thesis, University of the Basque Country
Asensio V, Rodríguez-Ruiz A, Garmendia L, Andre J, Kille P, Morgan AJ, Soto M, Marigómez I (2013) Towards an integrative soil health assessment strategy: a three tier (integrative biomarker response) approach with Eisenia fetida applied to soils subjected to chronic metal pollution. Sci Tot Environ 442:344–365
Azur Environmental (1995a) Microtox acute toxicity basic test procedures. Carlsbad, CA, USA
Azur Environmental (1995b) Microtox basic solid-phase test (basic SPT). Carlsbad, CA, USA
Balbo A, Bozzaro S (2008) A novel bioassay for evaluating soil bio-hazards using Dictyostelium as biosensor: validation and application to the Bio-Bio Project. Fresenius Environ Bull 17:1137–1143
Beeby A (1991) Toxic metal uptake and essential metal regulation in terrestrial invertebrates: a review. In: Newman MC, McIntosh AW (eds) Metal ecotoxicology: concepts and applications. Lewis, Chelsea, MI, USA, pp 65–89
Beeby A (2001) What do sentinels stand for? Environ Pollut 112:285–298
Belfroid A, Sikkenk M, Seinen W, Hermens J, Van Gestel K (1994) The toxicokinetic behavior of chlorobenzenes in earthworm (Eisenia andrei) experiments in soil. Environ Toxicol Chem 13:93–99
Bierkens J, Klein G, Corbisier P, Van Den Heuvel R, Verschaeve L, Weltens R, Schoeters G (1998) Comparative sensitivity of 20 bioassays for soil quality. Chemosphere 37:2935–2947
Bogan BW, Beardsley KE, Sullivan WR, Hayes TD, Soni BK (2005) Effect of volatile hydrocarbon fractions on mobility and earthworm uptake of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from soils and soil/lampblack mixtures. Environ Toxicol Chem 24:181–189
Brown RB, (2003). Soil texture. Univ Florida, IFAS Extension. Available: http://ufdc.ufl.edu/IR00003107/00001 (last access, 11/03/2014)
Button M, Jenkin GRT, Bowman KJ, Harrington CF, Brewer TS, Jones GDD, Watts MJ (2010) DNA damage in earthworms from highly contaminated soils: assessing resistance to arsenic toxicity by use of the Comet assay. Mutat Res 696:95–100
Carlon C (ed.) (2007) Derivation methods of soil screening values in Europe. A review and evaluation of national procedures towards harmonization. European Commission, Joint Research Centre, Ispra, EUR 22805-EN, 306 pp
Chang LW, Meier JR, Smith MK (1997) Application of plant and earthworm bioassays to evaluate remediation of a lead-contaminated soil. Archiv Environ Contam Toxicol 32:166–171
Contreras-Ramos SM, Alvarez-Bernal D, Dendooven L (2006) Eisenia fetida increased removal of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from soil. Environ Pollut 141:396–401
Critto A, Torresan S, Semenzin E, Giove S, Mesman M, Schouten AJ, Rutgers M, Marcomini A (2007) Development of a site-specific ecological risk assessment for contaminated sites: Part I. A multi-criteria based system for the selection of ecotoxicological tests and ecological observations. Sci Tot Environ 379:16–33
Davies NA, Hodson ME, Black S (2003) The influence of time on lead toxicity and bioaccumulation determined by the OECD earthworm toxicity test. Environ Pollut 121:55–61
Diatta J, Wirth S, Chudzinska E (2011) Spatial distribution of Zn, Pb, Cd, Cu, and dynamics of bioavailable forms at a polish metallurgical site. Fresenius Environ Bull 20:976–982
Diez M, Simon M, Martin F, Dorronsoro C, Garcia I, Van Gestel CAM (2009) Ambient trace element background concentrations in soils and their use in risk assessment. Sci Tot Environ 407:4622–4632
DIN (1984) DIN 38414-S4 Deutsche Einheitsverfahren zur Wasser-, Abwasser- und Schlammuntersuchung-Schlamm und Sedimente-Bestimmung der Eluierbarkeit mit Wasser. Deutsches Institut für Normung e.V. Berlin, Germany
Dondero F, Jonsson H, Rebelo M, Pesce G, Berti E, Pons G, Viarengo A (2006) Cellular responses to environmental contaminants in amoebic cells of the slime mould Dictyostelium discoideum. Comp Biochem Physiol 143C:150–157
Dorn PB, Vipond TE, Salanitro JP, Wisniewski HL (1998) Assessment of the acute toxicity of crude oils in soils using earthworms, microtox, and plants. Chemosphere 37:845–860
EC (2006) Communication from the Commission to the Council, the European Parliament, the European Economic and Social Committee and the Committee of the Regions—Thematic strategy for soil protection. COM(2006)231
Eijsackers H, Van Gestel CAM, De Jonge S, Muijs B, Slijkerman D (2001) Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon-polluted dredged peat sediments and earthworms: a mutual interference. Ecotoxicology 10:35–50
Eisentraeger A, Rila JP, Hund-Rinke K, Roembke J (2004) Proposal of a testing strategy and assessment criteria for the ecotoxicological assessment of soil or soil materials. J Soils Sed 4:123–128
EJ/GV (2007) Plan de suelos contaminados del País Vasco (2007-2012). Eusko Jaurlaritza/Gobierno Vasco, Vitoria-Gasteiz, Autonomous Community of the Basque Country (Spain) (in Spanish)
Environment Canada (2002) Biological test method: reference method for determining the toxicity of sediment using luminescent bacteria in a solid-phase test EPS 1/RM/42. Environment Canada, Ottawa, Ontario, Canada
Eom IC, Rast C, Veber AM, Vasseur P (2007) Ecotoxicity of a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH)-contaminated soil. Ecotox Environ Safety 67:190–205
Fernández MD, Cagigal E, Vega MM, Urzelai A, Babin M, Pro J, Tarazona JV (2005) Ecological risk assessment of contaminated soils through direct toxicity assessment. Ecotoxicol Environ Safety 62:174–184
Foerster B, Firla C, Junker T (2009) Plant tests Ecotoxicological characterization of waste. Results and experiences of an international ring test. Springer, New York, pp 117–128
Gascón JA, Arce M, Unzueta I, Susaeta I (2007) BIOSOIL project for the sustainable management of polluted soils. Residuos 97:76–85 (in Spanish)
Gastaldi L, Ranzato E, Capri F, Hankard P, Peres G, Canesi L, Viarengo A (2007) Application of a biomarker battery for the evaluation of the sublethal effects of pollutants in the earthworm Eisenia andrei. Comp Biochem Physiol 146C:398–405
Giller KE, Witter E, McGrath SP (1998) Toxicity of heavy metals to microorganisms and microbial processes in agricultural soils: a review. Soil Biol Biochem 30:1389–1414
Gleyzes C, Tellier S, Astruc M (2002) Fractionation studies of trace elements in contaminated soils and sediments: a review of sequential extraction procedures. Trac-Trend Anal Chem 21:451–467
Gonzalez-Ora JA, Rozas MA, Alkorta I, Garbisu C (2008) Dendroremediation of heavy metal polluted soils. Rev Environ Hlth 23:223–234
Greene JC, Bartels CL, Warren-Hicks WJ, Parkhurst BR, Linder GL, Peterson SA, Miller WE (1989) Protocols for short term toxicity screening of hazardous waste sites, USEPA, Corvallis, OR, 1989, EPA 600/3-88/029
Hamers T, Legler J, Blaha L, Hylland K, Marigómez I, Schipper CA, Segner H, Vethaak AD, Witters H, de Zwart D, Leonards PE (2013) Expert opinion on toxicity profiling—report from a NORMAN expert group meeting. Integr Environ Assess Manag 9:185–191
Harkey GA, Young TM (2000) Effect of soil contaminant extraction method in determining toxicity using the Microtox® assay. Environ Toxicol Chem 19:276–282
Harmsen J, Rulkens W, Eijsackers H (2005) Bioavailability: concept for understanding or tool for predicting? Land Cont Recl 13:161–171
Hoekstra NJ, Bosker T, Lantinga EA (2002) Effects of cattle dung from farms with different feeding strategies on germination and initial root growth of cress (Lepidium sativum L.). Agr Ecosyst Environ 93:189–196
Ihobe SA (1998a) Valores indicativos de evaluación (VIE-A). Nivel de referencia. Eusko Jaurlaritza/Gobierno Vasco, Vitoria-Gasteiz, Autonomous Community of the Basque Country (Spain), 45 pp (in Spanish)
Ihobe SA (1998b) Valores indicativos de evaluación (VIE-B, VIE-C) para la protección de los ecosistemas. Eusko Jaurlaritza/Gobierno Vasco, Vitoria-Gasteiz, Autonomous Community of the Basque Country (Spain), 104 pp. (in Spanish)
INIA, IGME, MMA (2007) Versión Web de la Guía Metodológica de aplicación del RD 9/2005 (14/01/2005) por el que se establece la relación de actividades potencialmente contaminantes del suelo y los criterios y estándares para la declaración de suelos contaminados (BOE Núm. 15, 18 enero 2005). Ministerio de Medio Ambiente, Madrid, Spain, pp. 114-119 (in Spanish)
ISO (1993) Soil quality—determination of dry matter and water content on a mass basis—Gravimetric method. ISO 11465
ISO (2005) Soil quality—determination of pH. International Standard. 10390, 1–7
ISO (2012) Soil quality—Effects of pollutants on earthworms -- Part 2: Determination of effects on reproduction of Eisenia fetida/Eisenia andrei. 11268–2
Juhasz AL, Smith E, Waller N, Stewart R, Weber J (2010) Bioavailability of residual polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons following enhanced natural attenuation of creosote-contaminated soil. Environ Pollut 158:585–591
Knoke KL, Marwood TM, Cassidy MB, Liu D, Seech AG, Lee H, Trevors JT (1999) A comparison of five bioassays to monitor toxicity during bioremediation of pentachlorophenol-contaminated soil. Water, Air, Soil Pollut 110:157–169
Komiyama K, Okaue M, Miki Y, Ohkubo M, Moro I, Cooper EL (2003) Non-especific cellular function of Eisenia fetida regulated by polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Pedobiologia 47:717–723
Langdon CJ, Piearce TG, Meharg AA, Semple KT (2003) Interactions between earthworms and arsenic in the soil environment: a review. Environ Pollut 124:361–373
Linder G, Greene J, Ratsch H, Nwosu J,Smith S, Wilborn D (1989) Seed germination and root elongation toxicity tests in hazardous waste site evaluation: methods development and applications. U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Washington, D.C., EA/600/D-89/109 (NTIS PB90113184)
Lock K, Janssen CR (2001a) Modelling zinc toxicity for terrestrial invertebrates. Environ Toxicol Chem 20:1901–1908
Lock K, Janssen CR (2001b) Zinc and cadmium body burdens in terrestrial oligochaetes: use and significance in environmental risk assessment. Environ Toxicol Chem 20:2067–2072
Lock K, Janssen CR (2002) Ecotoxicity of nickel to Eisenia fetida, Enchytraeus albidus and Folsomia candida. Chemosphere 46:197–200
Luo W, Verweij RA, van Gestel CAM (2014) Determining the bioavailability and toxicity of lead contamination to earthworms requires using a combination of physicochemical and biological methods. Environ Pollut 185:1–9
Ma WC, van Kleunen A, Immerzeel J, de Maagd PGJ (1998) Bioaccumulation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by earthworms: assessment of equilibrium partitioning theory in in situ studies and water experiments. Environ Toxicol Chem 17:1730–1737
Maity S, Roy S, Chaudhury S, Bhattacharya S (2008) Antioxidant responses of the earthworm Lampito mauritii exposed to Pb and Zn contaminated soil. Environ Pollut 151:1–7
Maleri RA, Reinecke AJ, Reinecke SA (2007) A comparison of nickel toxicity to pre-exposed earthworms (Eisenia fetida, oligochaeta) in two different test substrates. Soil Biol Biochem 39:2849–2853
Margesin R, Walder G, Schinner F (2000) The impact of hydrocarbon remediation (diesel oil and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons) on enzyme activities. Acta Biotechnol 20:313–333
Margesin R, Labbe D, Schinner F, Greer CW, Whyte LG (2003) Characterization of hydrocarbon-degrading microbial populations in contaminated and pristine alpine soils. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:3085–3092
Markwell RD, Connell DW, Gabric AJ (1989) Bioaccumulation of lipophilic compounds from sediments by oligochaetes. Water Res 23:1443–1450
Martínez CE, Motto HL (2000) Solubility of lead, zinc and copper added to mineral soils. Environ Pollut 107:153–158
Matscheko N, Lundstedt S, Svensson L, Harju M, Tysklind M (2002) Accumulation and elimination of 16 polycyclic aromatic compounds in the earthworm (Eisenia fetida). Environ Toxicol Chem 21:1724–1729
Morgan AJ, Pleasance B, Kinsey H, Murphy D, Davies S (2007) The manganese relationships of ecophysiologically contrasting earthworm species (Lumbricus rubellus and Aporrectodea caliginosa) inhabiting manganese-mine soils. Eur J Soil Biol 43:S297–S302
Nahmani J, Hodson ME, Black S (2007) Effects of metals on life cycle parameters of the earthworm Eisenia fetida exposed to field-contaminated, metal-polluted soils. Environ Pollut 149:44–58
NEN (1994) Determination of organic matter content in soil as loss-on-ignition. NEN 5754
NEN (1997) Soil—determination of mineral oil content in soil and sediments with gas chromatography. NEN 5733
OECD (1984) Earthworm, acute toxicity tests. OECD guideline for the testing of chemicals No. 207
OECD (2004) Earthworm reproduction test (Eisenia fetida/andrei). OECD guideline for the testing of chemicals No. 222
Plaza G, Nalecz-Jawecki G, Ulfig K, Brigmon RL (2005) The application of bioassays as indicators of petroleum-contaminated soil remediation. Chemosphere 59:289–296
Rauret G, Lopez-Sanchez JF, Sahuquillo A, Rubio R, Davidson C, Ure A, Quevauviller P (1999) Improvement of the BCR three step sequential extraction procedure prior to the certification of new sediment and soil reference materials. J Environ Monit 1:57–61
Reinecke SA, Reinecke AJ (1996) The influence of heavy metals on the growth and reproduction of the compost worm Eisenia fetida (Oligochaeta). Pedobiologia 40:439–448
Reinecke SA, Reinecke AJ (1997) The influence of lead and manganese on spermatozoa of Eisenia fetida (Oligochaeta). Soil Biol Biochem 29:737–742
Rodríguez-Ruiz A (2010) Risk assessment in real soils from the Basque Country after soil health screening through toxicity profiles based on standard and novel multiple endpoint bioassays. Ph.D. Thesis, University of the Basque Country
Rodríguez-Ruiz A, Marigómez I, Boatti L, Viarengo A (2013) Dictyostelium discoideum developmental cycle (DDDC) assay: a tool for Hg toxicity assessment and soil health screening. Sci Tot Environ 450–451:39–50
Roth JA, Garrick MD (2003) Iron interactions and other biological reactions mediating the physiological and toxic actions of manganese. Biochem Pharmacol 66:1–13
Saterbak A, Toy RJ, Wong DCL, McMain BJ, Williams MP, Dorn PB, Brzuzy LP, Chai EY, Salanitro JP (1999) Ecotoxicological and analytical assessment of hydrocarbon-contaminated soils and application to ecological risk assessment. Environ Toxicol Chem 18:1591–1607
Sayles GD, Acheson CM, Kupferle MJ, Shan Y, Zhou Q, Meier JR, Chang L, Brenner RC (1999) Land treatment of PAH-contaminated soil: performance measured by chemical and toxicity assays. Environ Sci Technol 33:4310–4317
Scaps P, Grelle C, Descamps M (1997) Cadmium and lead accumulation in the earthworm Eisenia fetida (Savigny) and its impact on cholinesterase and metabolic pathway enzyme activity. Comp Biochem Physiol 116C:233–238
Schultz E, Joutti A, Räisänen ML, Lintinen P, Martikainen E, Lehtto O (2004) Extractability of metals and ecotoxicity of soils from two old wood impregnation sites in Finland. Sci Tot Environ 326:71–84
Scott-Fordsmand JJ, Weeks JM, Hopkin SP (1998) Toxicity of nickel to the earthworm and the applicability of the neutral red retention assay. Ecotoxicology 7:291–295
Sforzini S, Dagnino A, Torrielli S, Dondero F, Fenoglio S, Negri A, Boatti L, Viarengo A (2008) Use of highly sensitive sublethal stress responses in the social amoeba Dictyostelium discoideum for an assessment of freshwater quality. Sci Tot Environ 395:101–108
Singh KP, Mohan D, Singh VK, Malik A (2005) Studies on distribution and fractionation of heavy metals in Gomti river sediments—a tributary of the Ganges, India. J Hydrol 312:14–27
SM (2001) Oil and Grease. 5520D
Spurgeon DJ, Hopkin SP, Jones DT (1994) Effects of cadmium, copper, lead and zinc on growth, reproduction and survival of the earthworm Eisenia fetida (Savigny): assessing the environmental impact of point-source metal contamination in terrestrial ecosystems. Environ Pollut 84:123–130
Tang J, Liste HH, Alexander M (2002) Chemical assays of availability to earthworms of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in soil. Chemosphere 48:35–42
Teodorovic I, Planojevic I, Knezevic P, Radak S, Nemet I (2009) Sensitivity of bacterial vs. acute Daphnia magna toxicity tests to metals. Eur J Biol 4:482–492
Urzelai A, Vega M, Angulo E (2000) Deriving ecological risk-based soil quality values in the Basque Country. Sci Tot Environ 247:279–284
USEPA (1996a) Microwave assisted acid digestion of siliceous and organically based matrices. Method 3052:1–20
USEPA (1996b) Ultrasonic extraction. Method 3550B:1–11
USEPA (2007) Inductively coupled plasma-atomic emission spectrometry. Method 6010C:1–34
Van Gestel CAM, Van der Waarde JJ, Derksen JGM, van der Hoek EE, Veul MFXW, Bouwens S, Rusch B, Kronenburg R, Stokman GNM (2001) The use of acute and chronic bioassays to determine the ecological risk and bioremediation efficiency of oil-polluted soils. Environ Toxicol Chem 20:1438–1449
Velimirovic MB, Prica MD, Dalmacija BD, Roncevic SD, Dalmacija MB, Becelic MD, Trickovic JS (2010) Characterisation, availability, and risk assessment of the metals in sediment after aging. Water, Air, Soil Pollut 214:219–229
Venier P, Zampieron C (2005) Evidence of genetic damage in grass gobies and mussels from the Venice lagoon. Environ Int 31:1053–1064
Wang W (1987) Root elongation method for toxicity testing of organic and inorganic pollutants. Environ Toxicol Chem 6:409–414
Wang XP, Shan XQ, Zhang SZ, Wen B (2004) A model for evaluation of the phytoavailability of trace elements to vegetables under the field conditions. Chemosphere 55:811–822
Wang SJ, Yan ZG, Guo GL, Lu GL, Wang QH, Li FS (2009) Ecotoxicity assessment of aged petroleum sludge using a suite of effects-based end points in earthworm Eisenia fetida. Environ Monit Assess 1–12
Watts M, Button M, Brewer T, Jenkin G, Harrington C (2008) Quantitative arsenic speciation in two species of earthworms from a former mine site. J Environ Monit 10:753–759
Wen B, Hu XY, Liu Y, Wang WS, Feng MH, Shan XQ (2004) The role of earthworms (Eisenia fetida) in influencing bioavailability of heavy metals in soils. Biol Fertility Soils 40:181–187
Wong DCL, Chai EY, Chiu KK, Dorn PB (1999) Prediction of ecotoxicity of hydrocarbon-contaminated soils using physicochemical parameters. Environ Toxicol Chem 18:2611–2621
Acknowledgments
Authors are indebted to Dr. Lara Boatti and Prof. Aldo Viarengo (DISIT, University of Piemonte Orientale) for their excellent support and valuable scientific discussions. This research was funded by Basque Government (UE09+/58, IE03-110 and IE06-179 Research Projects; Grant to Consolidated Research Group, GIC07/26-IT-393-07), UPV/EHU Research and Formation Unit in “Ecosystem Health Protection” (UFI 11/37) and Spanish Ministry of Science and Education (C6L-2006-06154). ARR was a recipient of a pre-doctoral fellowship from Fundación Centros Tecnológicos Iñaki Goenaga.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Markus Hecker
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 113 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rodriguez-Ruiz, A., Asensio, V., Zaldibar, B. et al. Toxicity assessment through multiple endpoint bioassays in soils posing environmental risk according to regulatory screening values. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21, 9689–9708 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-2915-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-2915-7