Abstract
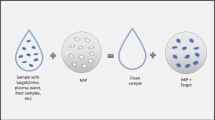
Molecularly imprinted polymers are synthetic polymers possessing specific cavities designed for target molecules. They are prepared by copolymerization of a cross-linking agent with the complex formed from a template and monomers that have functional groups specifically interacting with the template through covalent or noncovalent bonds. Subsequent removal of the imprint template leaves specific cavities whose shape, size, and functional groups are complementary to the template molecule. Because of their predetermined selectivity, molecularly imprinted polymers (MIPs) can be used as ideal materials in wastewater treatment. Especially, MIP-based composites offer a wide range of potentialities in wastewater treatment. This paper reviews the latest applications of MIPs in wastewater treatment, highlights the development of MIP-based composites in wastewater, and offers suggestions for future success in the field of MIPs.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Advincula RC (2011) Engineering molecularly imprinted polymer (MIP) materials: developments and challenges for sensing and separation technologies. Korean J Chem Eng 28(6):1313–1321
Ahmad A, Rafatullah M, Sulaiman O et al (2009) Removal of Cu (II) and Pb (II) ions from aqueous solutions by adsorption on sawdust of Meranti wood. Desalination 247(1):636–646
Aksu Z (2005) Application of biosorption for the removal of organic pollutants: a review. Process Biochem 40(3):997–1026
Andersson LI, Paprica A, Arvidsson T (1997) A highly selective solid phase extraction sorbent for pre-concentration of sameridine made by molecular imprinting. Chromatographia 46(1–2):57–62
Ansell RJ, Mosbach K (1998) Magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer beads for drug radioligand binding assay. Analyst 123(7):1611–1616
Arshady R, Mosbach K (1981) Synthesis of substrate-selective polymers by host-guest polymerization. Makromol Chem 182:687–692
Auriol M, Filali-Meknassi Y, Tyagi RD et al (2006) Endocrine disrupting compounds removal from wastewater, a new challenge. Process Biochem 41(3):525–539
Beltran A, Caro E, Marcé RM et al (2007) Synthesis and application of a carbamazepine-imprinted polymer for solid-phase extraction from urine and wastewater. Anal Chim Acta 597(1):6–11
Bergmann NM, Peppas NA (2008) Molecularly imprinted polymers with specific recognition for macromolecules and proteins. Prog Polym Sci 33(3):271–288
Bossi A, Bonini F, Turner APF et al (2007) Molecularly imprinted polymers for the recognition of proteins: the state of the art. Biosens Bioelectron 22(6):1131–1137
Brüggemann O (2001) Catalytically active polymers obtained by molecular imprinting and their application in chemical reaction engineering. Biomol Eng 18(1):1–7
Bui BTS, Haupt K (2010) Molecularly imprinted polymers: synthetic receptors in bioanalysis. Anal Bioanal Chem 398(6):2481–2492
Byun HS, Youn YN, Yun YH et al (2010) Selective separation of aspirin using molecularly imprinted polymers. Sep Purif Technol 74(1):144–153
Cacho C, Turiel E, Pérez-Conde C (2009) Molecularly imprinted polymers: an analytical tool for the determination of benzimidazole compounds in water samples. Talanta 78(3):1029–1035
Chen W, Han DK, Ahn KD et al (2002) Molecularly imprinted polymers having amidine and imidazole functional groups as an enzyme-mimetic catalyst for ester hydrolysis. Macromol Res 10(2):122–126
Chen YP, Wang DN, Yin YM et al (2012) Quantum dots capped with dummy molecularly imprinted film as luminescent sensor for the determination of tetrabromobisphenol A in water and soils. J Agr Food Chem 60(42):10472–10479
Chen HY, Zhang YQ, Gao B et al (2013) Fast determination of sulfonamides and their acetylated metabolites from environmental water based on magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers. Environ Sci Pollut R 20(12):8567–8578
Chen HC, Kong J, Yuan DY et al (2014) Synthesis of surface molecularly imprinted nanoparticles for recognition of lysozyme using a metal coordination monomer. Biosens Bioelectron 53:5–11
Chong MN, Jin B, Chow CWK et al (2010) Recent developments in photocatalytic water treatment technology: a review. Water Res 44(10):2997–3027
Cundy AB, Hopkinson L, Whitby RLD (2008) Use of iron-based technologies in contaminated land and groundwater remediation: a review. Sci Total Environ 400(1):42–51
Dai CM, Geissen SU, Zhang YL et al (2011) Selective removal of diclofenac from contaminated water using molecularly imprinted polymer microspheres. Environ Pollut 159:1660–1666
Dai CM, Zhang J, Zhang YL et al (2012) Selective removal of acidic pharmaceuticals from contaminated lake water using multi-templates molecularly imprinted polymer. Chem Eng J 211:302–309
Dai CM, Zhang J, Zhang YL et al (2013a) Application of molecularly imprinted polymers to selective removal of clofibric acid from water. PloS one 8(10):1–8
Dai CM, Zhang J, Zhang YL et al (2013b) Removal of carbamazepine and clofibric acid from water using double templates–molecularly imprinted polymers. Environ Sci Pollut R 20(8):5492–5501
Ferrer I, Lanza F, Tolokan A et al (2000) Selective trace enrichment of chlorotriazine pesticides from natural waters and sediment samples using terbuthylazine molecularly imprinted polymers. Anal Chem 72(16):3934–3941
Foo KY, Hameed BH (2009) Utilization of biodiesel waste as a renewable resource for activated carbon: application to environmental problems. Renew Sust Energ Rev 13(9):2495–2504
Foo KY, Hameed BH (2010) Insights into the modeling of adsorption isotherm systems. Chem Eng J 156(1):2–10
Foo KY, Hameed BH (2011) The environmental applications of activated carbon/zeolite composite materials. Adv Colloid Interfac 162(1):22–28
Fuchs Y, Soppera O, Haupt K (2012) Photopolymerization and photostructuring of molecularly imprinted polymers for sensor applications—A review. Anal Chim Acta 717:7–20
Gao D, Zhang Z, Wu M et al (2007) A surface functional monomer-directing strategy for highly dense imprinting of TNT at surface of silica nanoparticles. J Am Chem Soc 129(25):7859–7866
Gao B, Wang J, An F et al (2008) Molecular imprinted material prepared by novel surface imprinting technique for selective adsorption of pirimicarb. Polymer 49(5):1230–1238
Gao RX, Kong X, Su FH et al (2010) Synthesis and evaluation of molecularly imprinted core–shell carbon nanotubes for the determination of triclosan in environmental water samples. J Chromatogr A 1217(52):8095–8102
Gao RX, Su XQ, He XW et al (2011) Preparation and characterisation of core–shell CNTs@ MIPs nanocomposites and selective removal of estrone from water samples. Talanta 83(3):757–764
Ge Y, Turner APF (2008) Too large to fit? Recent developments in macromolecular imprinting. Trends Biotechnol 26(4):218–224
Ge SG, Lu JJ, Ge L et al (2011) Development of a novel deltamethrin sensor based on molecularly imprinted silica nanospheres embedded CdTe quantum dots. Spectrochim Acta A 79(5):1704–1709
Gottschalk C, Libra JA, Saupe A (2009) Ozonation of water and waste water: A practical guide to understanding ozone and its applications. John Wiley & Sons, New York
Guo HJ, Luo SL, Chen L et al (2010) Bioremediation of heavy metals by growing hyperaccumulaor endophytic bacterium Bacillus sp. L14. Bioresource Technol 101(22):8599–8605
Guo WL, Hu W, Pan J et al (2011) Selective adsorption and separation of BPA from aqueous solution using novel molecularly imprinted polymers based on kaolinite/Fe3O4 composites. Chem Eng J 171(2):603–611
Haupt K, Mosbach K (2000) Molecularly imprinted polymers and their use in biomimetic sensors. Chem Rev 100(7):2495–2504
He CY, Long YY, Pan JL et al (2007) Application of molecularly imprinted polymers to solid-phase extraction of analytes from real samples. J Biochem Bioph Meth 70(2):133–150
He CY, Long YY, Pan JL et al (2008) A method for coating colloidal particles with molecularly imprinted silica films. J Mater Chem 18(24):2849–2854
Hu X, Hu Y, Li G (2007) Development of novel molecularly imprinted solid-phase microextraction fiber and its application for the determination of triazines in complicated samples coupled with high-performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr A 1147:1–9
Huang SH, Chen DH (2009) Rapid removal of heavy metal cations and anions from aqueous solutions by an amino-functionalized magnetic nano-adsorbent. J Hazard Mater 163(1):174–179
Huang DL, Zeng GM, Jiang XY et al (2006) Bioremediation of Pb-contaminated soil by incubating with Phanerochaete chrysosporium and straw. J Hazard Mater 134(1):268–276
Javanbakht M, Eynollshi Fard S, Mohammadi A et al (2008) Molecularly imprinted polymer based potentiometric sensor for the detection of hydroxyzine in tablets and biological fluids. Anal Chim Acta 612:65–74
Ji YS, Yin JJ, Xu ZG et al (2009) Preparation of magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer for rapid determination of bisphenol A in environmental water and milk samples. Anal Bioanal Chem 395(4):1125–1133
Jing T, Wang J, Liu M et al (2014) Highly effective removal of 2, 4-dinitrophenolic from surface water and wastewater samples using hydrophilic molecularly imprinted polymers. Environ Sci Pollut R 21(2):1153–1162
Kim Y, Jeon JB, Chang JY (2012) CdSe quantum dot-encapsulated molecularly imprinted mesoporous silica particles for fluorescent sensing of bisphenol A. J Mater Chem 22(45):24075–24080
Kobya M, Demirbas E, Senturk E et al (2005) Adsorption of heavy metal ions from aqueous solutions by activated carbon prepared from apricot stone. Bioresource Technol 96(13):1518–1521
Kong X, Gao RX, He XW et al (2012) Synthesis and characterization of the core–shell magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers (Fe3O4@MIPs) adsorbents for effective extraction and determination of sulfonamides in the poultry feed. J Chromatogr A 1245:8–16
Krupadam RJ, Khan MS, Wate SR (2010) Removal of probable human carcinogenic polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from contaminated water using molecularly imprinted polymer. Water Res 44(3):681–688
Lai EPC, Maleki ZD, Wu SY (2010) Characterization of molecularly imprinted and nonimprinted polymer submicron particles specifically tailored for removal of trace 17β‐estradiol in water treatment. J Appl Polym Sci 116(3):1499–1508
Lavignac N, Allender CJ, Brain KR (2004) Current status of molecularly imprinted polymers as alternatives to antibodies in sorbent assays. Anal Chim Acta 510(2):139–145
Lee Y, Escher BI, Von Gunten U (2008) Efficient removal of estrogenic activity during oxidative treatment of waters containing steroid estrogens. Environ Sci Technol 42(17):6333–6339
Li Y, Li X, Li YQ et al (2009) Selective removal of 2, 4-dichlorophenol from contaminated water using non-covalent imprinted microspheres. Environ Pollut 157(6):1879–1885
Li Y, Li X, Chu J et al (2010) Synthesis of core-shell magnetic molecular imprinted polymer by the surface RAFT polymerization for the fast and selective removal of endocrine disrupting chemicals from aqueous solutions. Environ Pollut 158(6):2317–2323
Li H, Xu WZ, Wang NW et al (2012) Synthesis of magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer particles for selective adsorption and separation of dibenzothiophene. Microchim Acta 179(1–2):123–130
Lin ZK, Cheng WJ, Li YY et al (2012) A novel superparamagnetic surface molecularly imprinted nanoparticle adopting dummy template: an efficient solid-phase extraction adsorbent for bisphenol A. Anal Chim Acta 720:71–76
Lin ZK, He QY, Wang LT et al (2013) Preparation of magnetic multi-functional molecularly imprinted polymer beads for determining environmental estrogens in water samples. J Hazard Mater 252:57–63
Liu J, Wulff G (2008) Functional mimicry of carboxypeptidase A by a combination of transition state stabilization and a defined orientation of catalytic moieties in molecularly imprinted polymers. J Am Chem Soc 130(25):8044–8054
Liu ZH, Huan SY, Jiang JH et al (2006) Molecularly imprinted TiO2 thin film using stable ground-state complex as template as applied to selective electrochemical determination of mercury. Talanta 68(4):1120–1125
Liu JX, Chen H, Lin Z et al (2010) Preparation of surface imprinting polymer capped Mn-doped ZnS quantum dots and their application for chemiluminescence detection of 4-nitrophenol in tap water. Anal Chem 82(17):7380–7386
Liu HL, Liu DR, Fang GZ et al (2013) A novel dual-function molecularly imprinted polymer on CdTe/ZnS quantum dots for highly selective and sensitive determination of ractopamine. Anal Chim Acta 762:76–82
Liu CB, Song ZL, Pan JM et al (2014) A simple and sensitive surface molecularly imprinted polymers based fluorescence sensor for detection of λ-Cyhalothrin. Talanta 125:14–23
Lu SL, Cheng GX, Pang X (2006a) Protein-imprinted soft-wet gel composite microspheres with magnetic susceptibility. II. Characteristics. J Appl Polym Sci 99(5):2401–2407
Lu SL, Cheng GX, Zhang HG et al (2006b) Preparation and characteristics of Tryptophan‐imprinted Fe3O4/P (TRIM) composite microspheres with magnetic susceptibility by inverse emulsion–suspension polymerization. J Appl Polym Sci 99(6):3241–3250
Luo XB, Zhan YC, Tu XM et al (2011a) Novel molecularly imprinted polymer using 1-(α-methyl acrylate)-3-methylimidazolium bromide as functional monomer for simultaneous extraction and determination of water-soluble acid dyes in wastewater and soft drink by solid phase extraction and high performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr A 1218(8):1115–1121
Luo XB, Zhan YC, Huang YN et al (2011b) Removal of water-soluble acid dyes from water environment using a novel magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer. J Hazard Mater 187(1):274–282
Ma J, Yuan LH, Ding MJ et al (2011) The study of core–shell molecularly imprinted polymers of 17β-estradiol on the surface of silica nanoparticles. Biosens Bioelectron 26(5):2791–2795
Malik PK (2003) Use of activated carbons prepared from sawdust and rice-husk for adsorption of acid dyes: a case study of Acid Yellow 36. Dyes Pigments 56(3):239–249
Malitesta C, Mazzotta E, Picca RA et al (2012) MIP sensors–the electrochemical approach. Anal Bioanal Chem 402(5):1827–1846
Martín-Esteban A (2013) Molecularly-imprinted polymers as a versatile, highly selective tool in sample preparation. Trac-Trends Anal Chem 45:169–181
Mayes AG, Mosbach K (1996) Molecularly imprinted polymer beads: suspension polymerization using a liquid perfluorocarbon as the dispersing phase. Anal Chem 68(21):3769–3774
Mehdinia A, Baradaran Kayyal T, Jabbari A et al (2013) Magnetic molecularly imprinted nanoparticles based on grafting polymerization for selective detection of 4-nitrophenol in aqueous samples. J Chromatogr A 1283:82–88
Meng Z, Chen W, Mulchandani A (2005) Removal of estrogenic pollutants from contaminated water using molecularly imprinted polymers. Environ Sci Technol 39(22):8958–8962
Ng SM, Narayanaswamy R (2006) Fluorescence sensor using a molecularly imprinted polymer as a recognition receptor for the detection of aluminium ions in aqueous media. Analy Bioanal Chem 386(5):1235–1244
Nicholls IA, Andersson HS, Golker K et al (2011) Rational design of biomimetic molecularly imprinted materials: theoretical and computational strategies for guiding nanoscale structured polymer development. Anal Bioanal Chem 400(6):1771–1786
Oller I, Malato S, Sánchez-Pérez JA (2011) Combination of advanced oxidation processes and biological treatments for wastewater decontamination—a review. Sci Total Environ 409(20):4141–4166
Onesios KM, Jim TY, Bouwer EJ (2009) Biodegradation and removal of pharmaceuticals and personal care products in treatment systems: a review. Biodegradation 20(4):441–466
Ou JJ, Hu LH, Hu LG et al (2006) Determination of phenolic compounds in river water with on-line coupling bisphenol A imprinted monolithic precolumn with high performance liquid chromatography. Talanta 69(4):1001–1006
Pan GQ, Zhang Y, Ma Y et al (2011a) Efficient one-pot synthesis of water-compatible molecularly imprinted polymer microspheres by facile RAFT precipitation polymerization. Angew Chem Int Edit 50(49):11731–11734
Pan J, Xu LC, Dai JD et al (2011b) Magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers based on attapulgite/Fe3O4 particles for the selective recognition of 2, 4-dichlorophenol. Chem Eng J 174(1):68–75
Pan J, Yao H, Xu LC et al (2011c) Selective recognition of 2, 4, 6-trichlorophenol by molecularly imprinted polymers based on magnetic halloysite nanotubes composites. J Phys Chem C 115(13):5440–5449
Pauling L (1940) A Theory of the structure and process of formation of antibodies*. J Am Chem Soc 62(10):2643–2657
Pérez-Moral N, Mayes AG (2004) Comparative study of imprinted polymer particles prepared by different polymerisation methods. Anal Chim Acta 504(1):15–21
Piletska EV, Guerreiro AR, Romero-Guerra M et al (2008) Design of molecular imprinted polymers compatible with aqueous environment. Anal Chim Acta 607(1):54–60
Polyakov MV (1931) Adsorption properties and structure of silica gel. Zhur Fiz Khim 2:799–805
Poma A, Turner APF, Piletsky SA (2010) Advances in the manufacture of MIP nanoparticles. Trends Biotechnol 28(12):629–637
Rafatullah M, Sulaiman O, Hashim R et al (2010) Adsorption of methylene blue on low-cost adsorbents: a review. J Hazard Mater 177(1):70–80
Resmini M (2012) Molecularly imprinted polymers as biomimetic catalysts. Anal Bioanal Chem 402(10):3021–3026
Reungoat J, Macova M, Escher BI et al (2010) Removal of micropollutants and reduction of biological activity in a full scale reclamation plant using ozonation and activated carbon filtration. Water Res 44(2):625–637
Sambe H, Hoshina K, Haginaka J (2007) Molecularly imprinted polymers for triazine herbicides prepared by multi-step swelling and polymerization method: their application to the determination of methylthiotriazine herbicides in river water. J Chromatogr A 1152(1):130–137
Sánchez-Barragán I, Karim K, Costa-Fernández JM et al (2007) A molecularly imprinted polymer for carbaryl determination in water. Sensor Actuat B-Chem 123(2):798–804
Say R, Ersöz A, Türk H et al (2004) Selective separation and preconcentration of cyanide by a column packed with cyanide-imprinted polymeric microbeads. Sep Purif Technol 40(1):9–14
Sellergren B (2000) Molecularly imprinted polymers: man-made mimics of antibodies and their application in analytical chemistry. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Sharabi D, Paz Y (2010) Preferential photodegradation of contaminants by molecular imprinting on titanium dioxide. Appl Cata l B-Environ 95(1):169–178
Shen XT, Zhu LH, Liu GX et al (2008) Enhanced photocatalytic degradation and selective removal of nitrophenols by using surface molecular imprinted titania. Environ Sci Technol 42(5):1687–1692
Shen XT, Zhu LH, Wang N et al (2012) Molecular imprinting for removing highly toxic organic pollutants. Chem Commun 48(6):788–798
Snyder SA, Wert EC, Rexing DJ et al (2006) Ozone oxidation of endocrine disruptors and pharmaceuticals in surface water and wastewater. Ozone-Sci Eng 28(6):445–460
Snyder SA, Adham S, Redding AM et al (2007) Role of membranes and activated carbon in the removal of endocrine disruptors and pharmaceuticals. Desalination 202(1):156–181
Strikovsky A, Hradil J, Wulff G (2003) Catalytically active, molecularly imprinted polymers in bead form. React Funct Polym 54(1):49–61
Sueyoshi Y, Fukushima C, Yoshikawa M (2010) Molecularly imprinted nanofiber membranes from cellulose acetate aimed for chiral separation. J Membrane Sci 357(1):90–97
Sun H, Qiao F (2008) Recognition mechanism of water-compatible molecularly imprinted solid-phase extraction and determination of nine quinolones in urine by high performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr A 1212(1):1–9
Sun WQ, Tan R, Zheng WG et al (2013) Molecularly imprinted polymer containing Fe (III) catalysts for specific substrate recognition. Chin J Catal 34(8):1589–1598
Tamayo FG, Turiel E, Martín-Esteban A (2007) Molecularly imprinted polymers for solid-phase extraction and solid-phase microextraction: recent developments and future trends. J Chromatogr A 1152(1):32–40
Tan F, Sun D, Gao JS et al (2013) Preparation of molecularly imprinted polymer nanoparticles for selective removal of fluoroquinolone antibiotics in aqueous solution. J Hazard Mater 244:750–757
Tang HQ, Zhu LH, Yu C et al (2012) Selective photocatalysis mediated by magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers. Sep Purif Technol 95:165–171
Tarley CRT, Kubota LT (2005) Molecularly-imprinted solid phase extraction of catechol from aqueous effluents for its selective determination by differential pulse voltammetry. Anal Chim Acta 548(1):11–19
Ternes T, von Gunten U (2010) Editorial to special issue in water research: emerging contaminants in water. Water Res 44(2):351
Tong AJ, Dong H, Li LD (2002) Molecular imprinting-based fluorescent chemosensor for histamine using zinc (II)–protoporphyrin as a functional monomer. Anal Chim Acta 466(1):31–37
Turiel E, Martin-Esteban A (2004) Molecularly imprinted polymers: towards highly selective stationary phases in liquid chromatography and capillary electrophoresis. Anal Bioanal Chem 378(8):1876–1886
Turiel E, Martín-Esteban A (2010) Molecularly imprinted polymers for sample preparation: a review. Anal Chim Acta 668(2):87–99
Turkewitsch P, Wandelt B, Darling GD et al (1998) Fluorescent functional recognition sites through molecular imprinting. A polymer-based fluorescent chemosensor for aqueous cAMP. Anal Chem 70(10):2025–2030
Van Tilborg GAF, Mulder WJM, Chin PTK et al (2006) Annexin A5-conjugated quantum dots with a paramagnetic lipidic coating for the multimodal detection of apoptotic cells. Bioconjugate Chem 17(4):865–868
Vasapollo G, Sole RD, Mergola L et al (2011) Molecularly imprinted polymers: present and future prospective. Int J Mol Sci 12(9):5908–5945
Vlatakis G, Andersson LI, Müller R et al (1993) Drug assay using antibody mimics made by molecular imprinting. Nature 361:645–647
Wang HF, He Y, Ji TR et al (2009) Surface molecular imprinting on Mn-doped ZnS quantum dots for room-temperature phosphorescence optosensing of pentachlorophenol in water. Anal Chem 81(4):1615–1621
Wang S, Li Y, Ding MJ et al (2011) Self-assembly molecularly imprinted polymers of 17β-estradiol on the surface of magnetic nanoparticles for selective separation and detection of estrogenic hormones in feeds. J Chromatogr B 879(25):2595–2600
Wang H, Yuan XZ, Wu Y et al (2013) Graphene-based materials: fabrication, characterization and application for the decontamination of wastewater and wastegas and hydrogen storage/generation. Adv Colloid Interfac 195:19–40
Watabe Y, Kubo T, Nishikawa T et al (2006) Fully automated liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry determination of 17β-estradiol in river water. J Chromatogr A 1120(1):252–259
Wei FD, Liu XP, Zhai MJ et al (2013) Molecularly Imprinted Nanosilica Solid-Phase Extraction for Bisphenol A in Fish Samples. Food Anal Method 6(2):415–420
Whitcombe MJ, Vulfson EN (2001) Imprinted polymers. Adv Mater 13(7):467–478
Wulff G, Sarhan A (1972) Use of polymers with enzyme-analogous structures for resolution of racemates. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 11:341
Xia X, Lai EPC, Örmeci B (2013) Duo-molecularly imprinted polymer-coated magnetic particles for class-selective removal of endocrine-disrupting compounds from aqueous environment. Enviro Sci Pollut R 20(5):3331–3339
Xu X, Zhu L, Chen L (2004) Separation and screening of compounds of biological origin using molecularly imprinted polymers. J Chromatogr B 804(1):61–69
Xu ZX, Chen S, Huang W et al (2009) Study on an on-line molecularly imprinted solid-phase extraction coupled to high-performance liquid chromatography for separation and determination of trace estrone in environment. Anal Bioanal Chem 393(4):1273–1279
Xu P, Zeng GM, Huang DL et al (2012) Use of iron oxide nanomaterials in wastewater treatment: a review. Sci Total Environ 424:1–10
Xu GL, Yang LL, Zhong M et al (2013a) Selective recognition and electrochemical detection of p-nitrophenol based on a macroporous imprinted polymer containing gold nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 180:1461–1469
Xu SF, Lu HZ, Li JH et al (2013b) Dummy molecularly imprinted polymers-capped CdTe quantum dots for the fluorescent sensing of 2, 4, 6-Trinitrotoluene. ACS Appl Mater Inter 5(16):8146–8154
Xue JQ, Li DW, Qu LL et al (2013) Surface-imprinted core–shell Au nanoparticles for selective detection of bisphenol A based on surface-enhanced Raman scattering. Anal Chim Acta 777:57–62
Yan SL, Gao ZX, Fang YJ et al (2007) Characterization and quality assessment of binding properties of malachite green molecularly imprinted polymers prepared by precipitation polymerization in acetonitrile. Dyes Pigments 74(3):572–577
Yang WJ, Jiao FP, Zhou L et al (2013) Molecularly imprinted polymers coated on multi-walled carbon nanotubes through a simple indirect method for the determination of 2, 4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid in environmental water. Appl Surf Sci 284:692–699
Yin J, Meng Z, Du MJ et al (2010) Pseudo-template molecularly imprinted polymer for selective screening of trace β-lactam antibiotics in river and tap water. J Chromatogr A 1217(33):5420–5426
Yin YM, Chen YP, Wang XF et al (2012) Dummy molecularly imprinted polymers on silica particles for selective solid-phase extraction of tetrabromobisphenol A from water samples. J Chromatogr A 1220:7–13
Yoshimatsu K, Reimhult K, Krozer A et al (2007) Uniform molecularly imprinted microspheres and nanoparticles prepared by precipitation polymerization: the control of particle size suitable for different analytical applications. Anal Chim Acta 584(1):112–121
Yu CM, Gou LL, Zhou XH et al (2011) Chitosan–Fe3O4 nanocomposite based electrochemical sensors for the determination of bisphenol A. Electrochim Acta 56(25):9056–9063
Zeng GM, Huang DL, Huang GH et al (2007) Composting of lead-contaminated solid waste with inocula of white-rot fungus. Bioresource Technol 98(2):320–326
Zhan J, Fang GZ, Yan Z et al (2013) Preparation of a semicovalent, molecularly surface imprinted polymer for the rapid determination of trace acid orange II in food and environmental samples. Anal Bioanal Chem 405(19):6353–6363
Zhang W, He XW, Chen Y et al (2012) Molecularly imprinted polymer anchored on the surface of denatured bovine serum albumin modified CdTe quantum dots as fluorescent artificial receptor for recognition of target protein. Biosens Bioelectron 31(1):84–89
Zhang WL, Li Y, Wang Q et al (2013) Performance evaluation and application of surface-molecular-imprinted polymer-modified TiO2 nanotubes for the removal of estrogenic chemicals from secondary effluents. Environ Sci Pollut R 20(3):1431–1440
Zhao WH, Sheng N, Zhu R et al (2010) Preparation of dummy template imprinted polymers at surface of silica microparticles for the selective extraction of trace bisphenol A from water samples. J Hazard Mater 179(1–3):223–229
Zhao YY, Ma YX, Li H et al (2011) Composite QDs@ MIP nanospheres for specific recognition and direct fluorescent quantification of pesticides in aqueous media. Anal Chem 84(1):386–395
Zheng C, Huang YP, Liu ZS (2013) Synthesis and theoretical study of molecularly imprinted monoliths for HPLC. Anal Bioanal Chem 405(7):2147–2161
Zhongbo Z, Hu J (2008) Selective removal of estrogenic compounds by molecular imprinted polymer (MIP). Water Res 42(15):4101–4108
Zhou Y, Qu ZB, Zeng YB et al (2014) A novel composite of graphene quantum dots and molecularly imprinted polymer for fluorescent detection of paranitrophenol. Biosens Bioelectron 52:317–323
Zhu LL, Cao YH, Cao GQ (2013) Preparation and application of core-shell magnetic imprinted nanoparticles for bisphenol A. Chin J Anal Chem 41(11):1724–1728
Acknowledgments
The study was financially supported by the Program for the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51039001, 51278176, 51408206), the Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education of China (20100161110012), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, Hunan University Fund for Multidisciplinary Developing (531107040762), the Program for New Century Excellent Talents in University (NCET-13-0186).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, DL., Wang, RZ., Liu, YG. et al. Application of molecularly imprinted polymers in wastewater treatment: a review. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22, 963–977 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3599-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3599-8