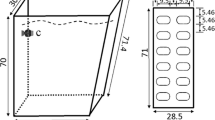
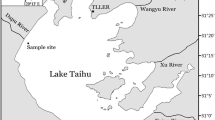
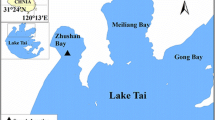
Abstract
Sediments play important roles, as nutrient reservoir, especially in shallow lake ecosystem. The water column of large shallow lakes is often stable but also disturbed by turbulence causing resuspension of sediments. While considerable research has been carried out to investigate the influence of sediment resuspension on nutrient release, fewer studies have been done to understand the contribution of alkaline phosphatase activity (APA) in water as a response to the two conditions (turbulence and stability). Also, effects of the two lake conditions on photosynthetic efficiency of phytoplankton are still poorly understood. This study will evaluate the effect of these two conditions on photosynthetic efficiency and APA. Sediments used in the indoor experiments were collected from Zhushan Bay in Lake Taihu. Turbulence was generated by rotors to simulate the strong wind-induced disturbance in Lake Taihu. Results of the experiments showed that TN and TP in the stable and episodically turbulent conditions were not significantly different, with TN ranging from 1.34 to 1.90 mg/L and TP from 0.08 to 0.18 mg/L. Whereas, the soluble reactive phosphorus in the episodically turbulent condition was significantly higher than in the stable condition. Episodic turbulence could enhance P cycling by resuspending sediment-associated P, which alleviated algal P limitation. In stable conditions, P deficiency induced the production of high APA, which enhanced the availability of P. Although episodic turbulence could also cause increased algal biomass, photosynthetic efficiency of the algae was also affected not only by the nutrients but also by many other factors, especially light availability. Our results suggest that episodic turbulence is an important driver of biogeochemical cycling in large shallow hypertrophic lake ecosystem.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berman T (1970) Alkaline phosphatases and phosphorus availability in Lake Kinneret. Limnol Oceanogr 15(5):663–674
Blom G, Duin EHS, Lijklema L (1994) Sediment resuspension and light conditions in some shallow Dutch lakes. Water Sci Technol 30:243–252
Cao X, Song C, Zhou Y (2009) Limitations of using extracellular alkaline phosphatase activities as a general indicator for describing P deficiency of phytoplankton in Chinese shallow lakes. J Appl Phycol 22(1):33–41
Carrick HJ, Aldridge FJ, Schelske CL (1993) Wind influences phytoplankton biomass and composition in a shallow, productive lake. Limnol Oceanogr 38:1179–1192
Cembella AD, Antia NJ, Harrison PJ (1984) The utilization of inorganic and organic phosphorus compounds as nutrients by eukaryotic microalgae—a multidisciplinary perspective. 1. CRC Crit Rev Microbiol 10:317–391
Chrost RJ, Overbeck J (1987) Kinetics of alkaline-phosphatase activity and phosphorus availability for phytoplankton and bacterioplankton in Lake Plusssee (North-German eutrophic lake). Microb Ecol 13:229–248
Davies JM, Nowlin WH, Mazumder A (2004) Variation in temporal C-14 plankton photosynthesis among warm monomictic lakes of coastal British Columbia. J Plankton Res 26:763–778
Ding YQ, Qin BQ, Zhu GW, Wu TF, Wang YP, Luo LC (2012) Effects of typhoon Morakot on a large shallow lake ecosystem, Lake Taihu, China. Ecohydrology 5(6):798–807
Duan HT, Ma RH, Hu CH (2012) Evaluation of remote sensing algorithms for cyanobacterial pigment retrievals during spring bloom formation in several lakes of East China. Remote Sens Environ 126(11):126–135
Dyhrman ST, Ruttenberg KC (2006) Presence and regulation of alkaline phosphatase activity in eukaryotic phytoplankton from the coastal ocean: implications for dissolved organic phosphorus remineralization. Limnol Oceanogr 51(3):1381–1390
Fan CX, Liu YB, Chen HS (2000) Approach on estimating storage sludge in Lake Taihu and its distributing characteristics. Shanghai Environ Sci 19:72–75 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Gao L, Zhou JM, Yang H, Chen J (2005) Phosphorus fractions in sediment profiles and their potential contributions to eutrophication in Dianchi Lake. Environ Geol 48:835–844
Gao G, Zhu GW, Qin BQ, Chen J, Wang K (2006) Alkaline phosphatase activity and the phosphorus mineralization rate of Lake Taihu. Sci China Ser D Earth Sci 49:176–185
Gervais F, Gervais D, Behrendt H (1996) Influence of small-scale turbulence and large-scale mixing on phytoplankton primary production. Hydrobiologia 342–343:95–105
Gikuma-Njuru P, Hecky RE, Guildford SJ (2010) Surficial sediment phosphorus fractions along a biogeochemical gradient in Nyanza (Winam) Gulf, northeastern Lake Victoria and their possible role in phosphorus recycling and internal loading. Biogeochemistry 97:247–261
Guo L (2007) Ecology—doing battle with the green monster of Taihu Lake. Science 317(5842):1166
Hallegraeff GM (1993) A review of harmful algal blooms and their apparent global increase. Phycologia 32(2):79–99
Havens KE (1991) Fish-induced sediment resuspension: effects on phytoplankton biomass and community structure in a shallow hypereutrophic lake. J Plankton Res 13(6):1163–1176
Hellstrom T (1991) The effect of resuspension on algal production in a shallow lake. Hydrobiologia 213:183–190
James RT, Chimney MJ, Sharfstein B, Engstrom DR, Schottler SP, East T et al (2008) Hurricane effects on a shallow lake ecosystem, Lake Okeechobee, Florida (USA). Fundam Appl Limnol 172:273–287
Jeppesen E, Jensen JP, Sondergaard M et al (2003) Does resuspension prevent a shift to a clear state in shallow lakes during reoligotrophication? Limnol Oceanogr 48:1913–1919
Jespersen AM, Christoffersen K (1987) Measurements of chlorophyll-a from phytoplankton using ethanol as extraction solvent. Archiv Fur Hydrobiologie 109(3):445–454
Jin XC, Tu QY (1990) Standard of Lake Eutrophication Survey of China. China Environmental Science Publishing House, Beijing (in Chinese)
Kauer T, Kutser T, Arst H, Danckaert T, Nõges T (2015) Modelling primary production in shallow well mixed lakes based on MERIS satellite data. Remote Sens Environ 163:253–261
Labry C, Delmas D, Herbland A (2005) Phytoplankton and bacterial alkaline phosphatase activities in relation to phosphate and DOP availability within the Gironde plume waters (Bay of Biscay). J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 318(2):213–225
Li G, Wu YP, Gao KSH (2009) Effects of Typhoon Kaemi on coastal phytoplankton assemblages in the South China Sea, with special reference to the effects of solar UV radiation. J Geophys Res Biogeosci 114(G4):213–213
Litchman E, Nguyen BLV (2008) Alkaline phosphatase activity as a function of internal phosphorus concentration in freshwater phytoplankton. J Phycol 44(6):1379–1383
Lin I, Liu WT, Wu CC, Wong GTF, Hu CM, Chen ZQ, Liang WD, Yang Y, Liu KK (2003) New evidence for enhanced ocean primary production triggered by tropical cyclone. Geophys Res Lett 30 (13), 1718, doi:10.1029/2003GL017141
Luettich RA, Harleman DRF, Somlyόdy L (1990) Dynamic behavior of suspended sediment concentrations in a shallow lake perturbed by episodic wind events. Limnol Oceanogr 35:1050–1067
Luo LC, Qin BQ, Zhu GW (2004) Sediment distribution pattern mapped from the combination of objective analysis and geostatistics in the large shallow Taihu Lake, China. J Environ Sci 16(6):908–911
Luo LC, Qin BQ, Zhu GW, Sun XJ, Hong DL, Gao YJ et al (2006) Nutrient fluxes induced by disturbance in Meiliang Bay of Lake Taihu. Sci China Ser D Earth Sci 49:186–192
Luo LC, Qin BQ, Yang LY, Song YZ (2007) Total inputs of phosphorus and nitrogen by wet deposition into Lake Taihu, China. Hydrobiologia 581:63–70
Macintyre S (1993) Vertical mixing in a shallow, eutrophic lake: possible consequences for the light climate of phytoplankton. Limnol Oceanogr 38(4):798–817
MacIntyre HL, Cullen JJ (1996) Primary production by suspended and benthic microalgae in a turbid estuary: time-scales of variability in San Antonio Bay, Texas. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 145:245–268
Nicholson D, Dyhrman S, Chavez F, Paytan A (2006) Alkaline phosphatase activity in the phytoplankton communities of Monterey Bay and San Francisco Bay. Limnol Oceanogr 51:874–883
Niemisto J, Holmroos H, Horppila J (2011) Water pH and sediment resuspension regulating internal phosphorus loading in a shallow lake—field experiment on diurnal variation. J Limnol 70:3–10
Nixdorf B, Deneke R (1997) Why ‘very shallow’ lakes are more successful opposing reduced nutrient loads. Hydrobiologia 342/343:269–284
Ogilvie BG, Mitchell SF (1998) Does sediment resuspension have persistent effects on phytoplankton? Experimental studies in three shallow lakes. Freshw Biol 40:51–63
Paerl HW (2009) Controlling eutrophication along the freshwater–marine continuum: dual nutrient (N and P) reductions are essential estuaries & coasts. Estuar Coasts 32(4):593–601
Paerl HW, Xu H, McCarthy MJ, Zhu GW, Qin BQ, Li YP, Gardner WS (2011) Controlling harmful cyanobacterial blooms in a hyper-eutrophic lake (Lake Taihu, China): the need for a dual nutrient (N & P) management strategy. Water Res 45(5):1973–1983
Palmer-Felgate EJ, Mortimer RJG, Krom MD, Jarvie HP, Williams RJ (2011) Internal loading of phosphorus in a sedimentation pond of a treatment wetland: effect of a phytoplankton crash. Sci Total Environ 409(2):292–298
Pedro C, Patricia E, Emilio M, Emilio F (2005) Maximum photo-synthetic efficiency of size-fractionated phytoplankton assessed by 14C uptake and fast repetition rate fluorometry. Limnol Oceanogr 50(5):1438–1446
Pitkanen H, Lehtoranta J, Raike A (2001) Internal nutrient fluxes counteract decreases in external load: the case of the estuarial eastern Gulf of Finland, Baltic Sea. Ambio 30:195–201
Qin BQ (2008) Lake Taihu, China. Springer, New York
Qin BQ, Hu WP, Gao G et al (2004) Dynamics of sediment resuspension and the conceptual schema of nutrient release in the large shallow Lake Taihu, China. Chin Sci Bull 49:54–64
Qin BQ, Yang LY, Chen FZ et al (2006) Mechanism and control of lake eutrophication. Chin Sci Bull 51:2401–2412
Qin BQ, Xu PZ, Wu QL et al (2007) Environmental issues of Lake Taihu, China. Hydrobiologia 581:3–14
Qin BQ, Zhu GW, Gao G, Zhang YL, Li W, Paerl HW, Carmichael WW (2010) A drinking water crisis in Lake Taihu, China: linkage to climatic variability and lake management. Environ Manage 45(1):105–112
Qin BQ, Gao G, Zhu GW, Zhang YL, Song YZ, Tang XM, Xu H, Deng JM (2013) Lake eutrophication and its ecosystem response. Chin Sci Bull 58(9):961–970
Robarts RD, Waiser MJ, Hadas O, Zohary T, MacIntyre S (1998) Relaxation of phosphorus limitation due to typhoon-induced mixing in two morphologically distinct basins of Lake Biwa, Japan. Limnol Oceanogr 43(6):1023–1036
Schallenberg M, Burns CW (2004) Effects of sediment resuspension on phytoplankton production: teasing apart the influences of light, nutrients and algal entrainment. Freshw Biol 49:143–159
Schelske CL (2009) Eutrophication: focus on phosphorus. Science 324:722–722
Schelske CL, Carrick HJ, Aldridge FJ (1995) Can wind-induced resuspension of meroplankton affect phytoplankton dynamics? J N American Benthol Soc 14:616–630
Schelske CL, Aldridge FJ, Carrick HJ, Coveney MF (2003) Phytoplankton community photosynthesis and primary production in a hypereutrophic lake, Lake Apopka, Florida. Archiv Fur Hydrobiologie 157:145–172
Shi K, Zhang YL, Xu H, Zhu GW, Qin BQ, Huang CC, Liu XH, Zhou YQ, Lv H (2015) Long-term satellite observations of microcystin concentrations in Lake Taihu during cyanobacterial bloom periods. Environ Sci Technol 49:6448–6456
Skoog AC, Arias-Esquivel VA (2009) The effect of induced anoxia and reoxygenation on benthic fluxes of organic carbon, phosphate, iron, and manganese. Sci Total Environ 407:6085–6092
Søndergaard M, Kristensen P, Jeppesen E (1992) Phosphorus release from resuspended sediment in the shallow and wind-exposed Lake Arreso, Denmark. Hydrobiologia 228:91–99
Søndergaard M, Jensen JP, Jeppesen E (2003) Role of sediment and internal loading of phosphorus in shallow lakes. Hydrobiologia 506–509:135–145
Sun XJ, Zhu GW, Luo LC, Qin BQ (2006) Experimental study on phosphorus release from sediments of shallow lake in wave flume. Sci China Ser D Earth Sci 49(Supplement 1):92–101
Tanaka T, Henriksen P, Lignell R, Olli K, Seppala J, Tamminen T, Thingstad TF (2006) Specific affinity for phosphate uptake and specific alkaline phosphatase activity as diagnostic tools for detecting phosphorus-limited phytoplankton and bacteria. Estuar Coasts 29:1226–1241
Tanaka T, Thingstad TF, Lovdal T, Gressart HP, Larsen A, Allgaier M, Meyerhofer M, Schulz KG, Wohlers J, Zollner E, Riebesell U (2008) Availability of phosphate for phytoplankton and bacteria and of labile organic carbon for bacteria at different pCO2 levels in a mesocosm study. Biogeosciences 5:669–678
Vanni MJ, Temte J (1990) Seasonal patterns of grazing and nutrient limitation of phytoplankton in a eutrophic lake. Limnol Oceanogr 35:697–709
Wang XD, Qin BQ, Gao G, Paerl HW (2010) Nutrient enrichment and selective predation by zooplankton promote Microcystis (Cyanobacteria) bloom formation. J Plankton Res 32:457–470
Xu H, Paerl HW, Qin BQ, Zhu GW, Gao G (2010) Nitrogen and phosphorus inputs control phytoplankton growth in eutrophic Lake Taihu. China Limnol Oceanogr 55:420–432
Zhang YL, Qin BQ, Zhu GW, Gao G, Luo LC, Chen WM (2006) Effect of sediment resuspension on underwater light field in shallow lakes in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River: a case study in Longgan Lake and Taihu Lake. Sci China Ser D Earth Sci 49:114–125
Zhang T, Wang X, Jin X (2007) Variations of alkaline phosphatase activity and P fractions in sediments of a shallow Chinese eutrophic lake (Lake Taihu). Environ Pollut 150(2):288–294
Zhang L, Shang J, He W, You B, Fan C (2014) The role of tubificid worms (Limnodrilus hoffmeisteri) in sediment resuspension: a microcosm study. Annales de Limnologie - International Journal of limnology 50(3):253–260
Zhou J, Qin BQ, Casenave C, Han XX (2015) Effects of turbulence on alkaline phosphatase activity of phytoplankton and bacterioplankton in Lake Taihu. Hydrobiologia 765(1):1–11
Zhu GW, Qin BQ, Gao G (2005) Direct evidence of phosphorus outbreak release from sediment to overlying water in a large shallow lake caused by strong wind wave disturbance. Chin Sci Bull 50:577–582
Zhu GW, Qin BQ, Gao G et al (2007) Effects of hydrodynamics on phosphorus concentrations in water of Lake Taihu, a large, shallow, eutrophic lake of China. Hydrobiologia 581:53–61
Zhu GW, Wang F, Gao G, Zhang YL (2008) Variability of phosphorus concentration in large, shallow and eutrophic Lake Taihu, China. Water Environ Res 80:832–839
Zhu MY, Zhu GW, Zhao LL, Yao X, Zhang YL, Gao G, Qin BQ (2013) Influence of algal bloom degradation on nutrient release at the sediment-water interface in Lake Taihu, China. Environ Pollut Res 20(3):1803–1811
Zhu MY, Paerl HW, Zhu GW, Wu TF, Li W, Shi K, Zhao LL, Zhang YL, Qin BQ, Caruso AM (2014) The role of tropical cyclones in stimulating cyanobacterial (Microcystis spp.) blooms in hypertrophic Lake Taihu, China. Harmful Algae 39:310–321
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to the Lake Taihu Laboratory for Lake Ecosystem Research (TLLER) which provided the experiment platform. Jingchen Xue and KeXu Chi assisted with laboratory analyses. This work was funded through the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 41501518) and the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (BK20140184). And it also was supported by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (2014QNA86) and A Project Funded by the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions . We also thank the anonymous reviewers for their constructive comments and helpful suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ding, Y., Qin, B., Xu, H. et al. Effects of sediment and turbulence on alkaline phosphatase activity and photosynthetic activity of phytoplankton in the shallow hyper-eutrophic Lake Taihu, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23, 16183–16193 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6786-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6786-y