Abstract
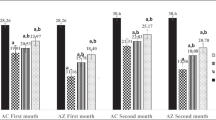
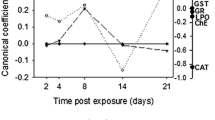
Important toxicological achievements have been made during the last decades using reptiles. We focus our investigation on gonadal reproductive health of the soil biosentinel Podarcis sicula which is very sensitive to endocrine-disrupting chemicals. The aim of this study is to quantitatively detect, by sensitive microassays, reactive oxygen species and the glutathione antioxidants in the testis and investigate if they are differentially expressed before and after remediation of a site of the “Land of Fires” (Campania, Italy) subject to illicit dumping of unknown material. The oxidative stress level was evaluated by electron spin resonance spectroscopy applying a spin-trapping procedure able to detect products of lipid peroxidation, DNA damage and repair by relative mobility shift, and poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase enzymatic activity, respectively, the expression of glutathione peroxidase 4 transcript by real-time quantitative PCR analysis, the antioxidant glutathione S-transferase, a well-assessed pollution index, by enzymatic assay and the total soluble antioxidant capacity. Experimental evidences from the different techniques qualitatively agree, thus confirming the robustness of the combined experimental approach. Collected data, compared to those from a reference unpolluted site constitute evidence that the reproductive health of this lizard is impacted by pollution exposure. Remediation caused significant reduction of reactive oxygen species and downregulation of glutathione peroxidase 4 mRNAs in correspondence of reduced levels of glutathione S-transferase, increase of antioxidant capacity, and repair of DNA integrity. Taken together, our results indicate directions to define new screening approaches in remediation assessment.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aitken RJ, Keith TJ, Robertson SA (2012) Reactive oxygen species and review sperm function—in sickness and in health. J Androl 33(6):1096–1106. https://doi.org/10.2164/jandrol.112.016535
Ashton T, Rowlands CC, Jones E, Young IS, Jackson SK, Davies B, Peters JR (1998) Electron spin resonance spectroscopic detection of oxygen-centred radicals in human serum following exhaustive exercise. Eur J Appl Physiol 77:498–502. https://doi.org/10.1007/s004210050366
Buettner GR (1987) Spin trapping: ESR parameters of spin adducts. Free Radic Biol Med 2:259–303 PMID:2826304
Campbell KR, Campbell TS (2002) A logical starting poınt for developing priorities for lizard and snake ecotoxicology: a review of available data. Environ Toxicol Chem 21(5):894–898. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.5620210502
Chaudhry AS, Jabeen F (2011) Assessing metal, protein, and DNA profiles in Labeo rohita from the Indus River in Mianwali. Pakistan Environ Monit Assess 174:665–679. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-010-1486-4
Ciarcia G, Angelini F, Polzonetti ZM, Botte V (1986a) Hormones and reproduction in the lizard Podarcis s. sicula Raf. In: Endocrine regulations and adaptive mechanisms to the environments. Eds I. Assenmacher & J. Boissin. CNRS, Paris, pp 95–100
Ciarcia G, Lancieri M, Suzuki H, Manzo C, Vitale L, Tornese B, Botte V (1986b) A specific nuclear protein and poly(ADPribose)transferase activity in lizard oviduct during the reproductive cycle. Mol Cell Endocrinol 47:235–241. https://doi.org/10.1016/0303-7207(86)90117-6
de Almeida EA, Miyamoto S, Celso Dias Bainy A, Gennari de Medeiros MH, Di Mascio P (2004) Protective effect of phospholipid hydroperoxide glutathione peroxidase (PHGPx) against lipid peroxidation in mussels Perna perna exposed to different metals. Mar Pollut Bull 49(5–6):386–392. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2004.02.020
De Maio A, Trocchia S, Guerriero G (2014) The amphibian Pelophylax bergeri (Günther, 1986) testis poly(ADP-ribose)polymerases: relationship to endocrine disruptors during spermatogenesis. Italian J Zool 81:256–263. https://doi.org/10.1080/11250003.2014.902124
Di Finizio A, Guerriero G, Russo GL, Ciarcia G (2007) Identification of gadoid species (Pisces, Gadidae) by sequencing and PCR-RFLP analysis of mitochondrial 12S and 16S rRNA gene fragments. Eur Food Res Technol 225:337–344. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00217-006-0420-z
Diamanti-Kandarakis E, Bourguignon JP, Giudice LC, Hauser R, Prins GS, Soto AM, Zoeller RT, Gore AC (2009) Endocrine-disrupting chemicals: an Endocrine Society scientific statement. Endocr Rev 30:293–342. https://doi.org/10.1210/er.2009-0002
Fasulo S, Guerriero G, Cappello S, Colasanti M, Schettino T, Leonzio C, Mancini G, Gornati R (2015) The “SYSTEMS BIOLOGY” in the study of xenobiotic effects on marine organisms for evaluation of the environmental health status: biotechnological applications for potential recovery. Rev Environ Sci Biotechnol 14(3):339–345. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11157-015-9373-7
Gachon C, Mingam A, Charrier B (2004) Real-time PCR: what relevance to plant studies? J Exp Bot 55:1445–1454. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erh181
Galatro A, Puntarulo S (2016) Measurement of nitric oxide (NO) generation rate by chloroplasts employing electron spin resonance (ESR). Methods Mol Biol 1424:103–112. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-3600-7_9
Gornati R, Papis E, Rimoldi S, Terova G, Saroglia M, Bernardini G (2004) Rearing density influences the expression of stress-related genes in sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax, L.) Gene 341:111–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2004.06.020
González PM, Aguiar MB, Malanga G, Puntarulo S (2013) Electronic paramagnetic resonance (EPR) for the study of ascorbyl radical and lipid radicals in marine organisms. Comp Biochem Physiol A-Mol Integr Physiol 165:439–447
Guerriero E, Capone F, Accardo M, Sorice A, Costantini M, Colonna G, Castello G, Costantini S (2015) GPX4 and GPX7 over-expression in human hepatocellular carcinoma tissues. Eur J Histochem 59(4):2540. https://doi.org/10.4081/ejh.2015.2540
Guerriero G & Ciarcia G (2006) Stress biomarkers and reproduction in fish. Fish endocrinology Vol.2. Edited by M Reinecke, G. Zaccone, & B. G. Kapoor Sci Publ Inc Enfield (NH). USA; Plymouth, U.K. pp:665–692. https://es.scribd.com/document/326780080/Manfred-Reinecke-Giacomo-Zaccone-B-G-Kapoor-F-BookZZ-org-pdf
Guerriero G, D’Errico G, Trocchia S, Ciarcia G (2013) Electron spin resonance (ESR) spectroscopy detection of oxygen-centred radical in frog. Free Radic Biol Med 65:S89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2013.10.609
Guerriero G, Trocchia S, Abdel-Gawad FK, Ciarcia G (2014) Roles of reactive oxygen species in the spermatogenesis regulation. Front Endocrin 5:56. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2014.00056
Guthrie HD, Welch GR (2012) Effects of reactive oxygen species on sperm function. Theriogenology 78(8):1700–1708. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.theriogenology.2012.05.002
Habig WH, Pabst MJ, Jakoby WB (1974) Glutathione S–transferases, the first enzymatic step in mercapturic acid formation. J Biol Chem 249:7130–7139 http://www.jbc.org/content/249/22/7130.long
Hall R J (1980) Effects of environmental contaminants on reptiles: a review Special scientific report. Wildlife 228 Publisher: U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service
Hawkins CL, Davies MJ (2014) Detection and characterisation of radicals in biological materials using EPR methodology. Biochem Biophys Acta 1840:708–721. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbagen.2013.03.034
Hopkins WA (2000) Reptile toxicology: challenges and opportunities on the last frontier in vertebrate ecotoxicology. Environ Toxicol Chem:19 (10): 2391–19 (10): 2393. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.5620191001
Hudson NJ, Lehner SA, Ingham AB, Symonds B, Franklin CE, Harper G (2006) Lessons from an estivating frog: sparing muscle protein despite starvation and disuse. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 290:R836–R843. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpregu.00380.2005
Huggett J, Bustin S (2011) Standardisation and reporting for nucleic acid quantification. Accred Qual Assur 16:399–405. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00769-011-0769-y
Koch-Nolte F, Kernstock S, Mueller-Dieckmann C, Weiss MS, Haag F (2008) Mammalian ADP ribosyltransferases and ADP-ribosylhydrolases. Front Biosci 13:6716–6729. https://doi.org/10.2741/3184
Labuschagne CF, Brenkman AB (2013) Current methods in quantifying ROS and oxidative damage in Caenorhabditis elegans and other model organism of aging. Utrecht
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(−delta deltaC(T)). Methods 25:402–40.8. https://doi.org/10.1006/meth.2001.1262
Maiorino M, Bosello V, Ursini F, Foresta C, Garolla A, Scapin M, Sztajer H, Flohé L (2003) Genetic variations of gpx-4 and male infertility in humans. Biol Reprod 68(4):1134–1141. https://doi.org/10.1095/biolreprod.102.007500
Marsili L, Casinia S, Moria G, Ancora S, Bianchia N, D'Agostino A, Ferraroc M, Fossia MC (2009) The Italian wall lizard (Podarcis sicula) as a bioindicator of oil field activity. Sci Total Environ 407(11):3597–3604. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2009.01.035
Monaco D, Riccio A, Chianese E, Adamo P, Di Rosa S, Fagnano M (2015) Chemical characterization and spatial distribution of PAHs and heavy hydrocarbons in rural sites of Campania region, South Italy. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:14993–15003. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4733-y
Munoz-Garcia AB, Sannino F, Vitiello G, Pirozzi D, Minieri L, Aronne A, Pernice P, Pavone M, D’Errico G (2015) Origin and electronic features of reactive oxygen species at hybrid zirconia-acetylacetonate interfaces. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7:21662–21667. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.5b06988
Nam SY, Baek IJ, Lee BJ, In CH, Jung EY, Yon JM, Ahn B, Kang JK, Yu WJ, Yun YW (2003) Effects of 17 β estradiol and tamoxifen on the Selenoprotein phospholipid hydroperoxide glutathione peroxidase (PHGPx) mRNA expression in male reproductive organs of rats. J Reprod Dev 49(5):389–396. https://doi.org/10.1262/jrd.49.389
Oliver AW, Ame JC, Roe SM, Good V, de Murcia G, Pearl LH (2004) Crystal structure of the catalytic fragment of murine poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-2. Nucleic Acids Res 32:456–464. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkh215
Perez AF, Boy CC, Calcagno J, Malanga G (2015) Reproduction and oxidative metabolism in the brooding sea star Anasterias antarctica (Lutken, 1957). J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 463:150–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jembe.2014.11.009
Pfeifer H, Conrad M, Roethlein D, Kyriakopoulos A, Brielmeier M, Bornkamm GW, Behne D (2001) Identification of a specific sperm nuclei selenoenzyme necessary for protamine thiol cross-linking during sperm maturation. FASEB J 15(7):1236–1238. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.00-0655fje
Pincheira-Donoso D, Bauer AM, Meiri S, Uetz P (2013) Global taxonomic diversity of living reptiles. PLoS ONE 3(8):e59741. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0059741
Prakash M, Gopalakrishnan N, Park SY, Choi J (2012) Characterization and expression analysis of phospholipid hydroperoxide glutathione peroxidase cDNA from Chironomus riparius on exposure to cadmium. Comp Biochem Physiol 163(1):37–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpb.2012.04.004
Prieto P, Pineda M, Aguilar M (1999) Spectrophotometric quantitation of antioxidant capacity through the formation of a phosphomolybdenum complex: specific application to the determination of vitamin E. Anal Biochem 269:337–341. https://doi.org/10.1006/abio.1999.4019. 10222007
Puglisi R, Tramer F, Carlomagno G, Gandini L, Panfili E, Stefanini M, Lenzi A, Mangia F, Boitani C (2005) PHGPx in spermatogenesis: how many functions? Contraception 72:291–293. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.contraception.2005.03.002
Rave N, Crkvenjakov R, Boedtker H (1979) Identification of procollagen mRNAs transferred to diazobenzyloxymethyl paper from formaldehyde agarose gels. Nucleic Acids Res 6:3559–3567. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/6.11.3559
Rocco C, Duro I, Di Rosa S, Fagnano M, Fiorentino N, Vetromile A, Adamo P (2016) Composite vs. discrete soil sampling in assessing soil pollution of agricultural sites affected by solid waste disposal. J Geochem Explor 170:30–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2016.08.004
Rudneva II, Kuzminova NS, Skuratovskaya EN (2010) Glutathione S-transferase activity in tissues of Black Sea fish species. Asian J Exp Biol Sci 1(1):141–150 http://www.ajebs.com/vol1/21.pdf
Samanta L, Paital B (2016) Effects of seasonal variation on oxidative stress physiology in natural population of toad Bufo melanostictus; clues for analysis of environmental pollution. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23(22):22819–22831. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7481-8
Schreiber V, Dantzer F, Ame JC, de Murcia G (2006) Poly(ADP-ribose): novel functions for an old molecule. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 7:517–528. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm1963
Schug TT, Janesick A, Blumberg B, Heindel JJ (2011) Endocrine disrupting chemicals and disease susceptibility. J Steroid Biochem 127(3-5:204–215. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsbmb.2011.08.007
Shi Y, Buffenstein R, Pulliam DA, Van Remmen H (2010) Comparative studies of oxidative stress and mitochondrial function in aging. Integr Comp Biol 50:869–879. https://doi.org/10.1093/icb/icq079
Simoniello P, Filosa S, Scudiero R, Trinchella F, Motta CM (2013) Cadmium impairment of reproduction in the female wall lizard Podarcis sicula. Environ Toxicol 28(10):553–562. https://doi.org/10.1002/tox.20749
Stahlschmidt-Allner P, Allner B, Römbke J, Knacker T (1997) Endocrine disrupters in the aquatic environment. Environ Sci & Pollut Res 4(3):155. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02986325
Valko M, Rhodes CJ, Moncol J, Izakovic M, Mazur M (2006) Free radicals, metals and antioxidants in oxidative stress-induced cancer. Chem Biol Interact 160(1):1–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbi.2005.12.009
Verderame M, Limatola E (2015) Interferences of an environmental pollutant with estrogen-like action in the male reproductive system of the terrestrial vertebrate Podarcis sicula. Gen Comp Endocrinol 213:9–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygcen.2015.01.027
Acknowledgements
This paper gives part of the results of the action C2 of the LIFE11/ENV/IT/275 ECOREMED: Implementation of eco-compatible protocols for agricultural soil remediation in Litorale Domizio-Agro Aversano NIPS (Coordinator Prof. M. Fagnano). The authors thank the Interdepartmental Research Center for Environment (I.R.C.Env.), Federico II University, Naples, Italy, the coworkers Anna Rita Bianchi, Martina Caressa, Francesca Castaldo, Rosa D’Angelo, and Giulia Pastore for their logistics help and technical support and the colleague Dr. Anna De Maio for the helpful scientific collaboration.
Funding
Supported by LIFE11 ENV/IT/275 (CUP E69E12000590006).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to conception and design of the experiments. All the authors have given their approval to the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
This study was conducted in strict accordance with European (Directive 2010/63) and Italian (Decreto Legislativo no. 116/1992) legislation on the care and use of animals for scientific purpose.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Electronic supplementary material
Fig. A1
EPR spectrum of PBN adduct of radicals deriving from Podarcis sicula testis (GIF 98 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guerriero, G., D’Errico, G., Di Giaimo, R. et al. Reactive oxygen species and glutathione antioxidants in the testis of the soil biosentinel Podarcis sicula (Rafinesque 1810). Environ Sci Pollut Res 25, 18286–18296 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0098-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0098-8