Abstract
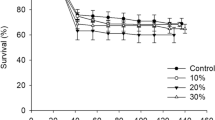
Treating municipal sewage sludge (MSS) sustainably and economically in China remains a challenge because of risks associated with the heavy metals it contains. In this study, black solider fly larvae (BSFL) were used for MSS treatment. The resistance of larvae to combined heavy metals and their potential use in conversion of MSS were investigated. The results indicated that seven MSS samples contained large amounts of heavy metals, with the lead and nickel contents of several samples exceeding Chinese national discharge standards. BSFL were highly tolerant to an artificial diet spiked with combined heavy metals. Principal component analysis revealed that high concentrations of lead, nickel, boron, and mercury potentially interfered with larval weight gain, while zinc, copper, chromium, cadmium, and mercury slightly reduced larval survival. The addition of chicken manure and wheat bran as co-substrates improved the conversion process, which was influenced by the nature and amount of added co-substrate and especially the quantity of nitrogen added. With the amended substrate, the BSFL accumulated heavy metals into their bodies but not into extracted larval oil. The heavy metal content of the treatment residue was lower than that considered safe for organic-inorganic compound fertilizers standards in China and the harvested larvae could be used as a source of oil for industrial application.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ajeej A, Thanikal JV, Narayanan CM, Senthil Kumar R (2015) An overview of bio augmentation of methane by anaerobic co-digestion of municipal sludge along with microalgae and waste paper. Renew Sust Energ Rev 50:270–276
Borowska J, Sulima B, Nilińska M, Pyza E (2004) Heavy metal accumulation and its effects on development, survival and immuno-competent cells of the housefly Musca domestica from closed laboratory populations as model organism. Fresenius Environ Bull 13:1402–1409
Budych-Gorzna M, Smoczynski M, Oleskowicz-Popiel P (2016) Enhancement of biogas production at the municipal wastewater treatment plant by co-digestion with poultry industry waste. Appl Energ 161:387–394
Chen M, Li X-m, Yang Q, Zeng G-m, Zhang Y, Liao D-x, Liu J-j, Hu J-m, Guo L (2008) Total concentrations and speciation of heavy metals in municipal sludge from Changsha, Zhuzhou and Xiangtan in middle-south region of China. J Hazard Mater 160:324–329
Čičková H, Newton GL, Lacy RC, Kozánek M (2015) The use of fly larvae for organic waste treatment. Waste Manag 35:68–80
Dede G, Ozdemir S (2016) Effects of elemental sulphur on heavy metal uptake by plants growing on municipal sewage sludge. J Environ Manag 166:103–108
Diener S, Zurbrügg C, Tocknera K (2009) Conversion of organic material by black soldier fly larvae—establishing optimal feeding rates. Waste Manag Res 27:603–610
Diener S, Studt Solano NM, Roa Gutiérrez F, Zurbrügg C, Tockner K (2011) Biological treatment of municipal organic waste using black soldier fly larvae. Waste Biomass Valori 2:357–363
Diener S, Zurbrügg C, Tockner K (2015) Bioaccumulation of heavy metals in the black soldier fly, Hermetia illucens and effects on its life cycle. J Insects Food Feed 1:261–270
Dzulkurnain Z, Hassan MA, Zakaria MR, Wahab PEM, Hasan MY, Shirai Y (2017) Co-composting of municipal sewage sludge and landscaping waste: a pilot scale study. Waste Biomass Valori 8:695–705
Gao M, Liang F, Yu A, Li B, Yang L (2009) Evaluation of stability and maturity during forced-aeration composting of chicken manure and sawdust at different C/N ratios. Chemosphere 78:614–619
Hsu L-C, Huang C-Y, Chuang Y-H, Chen H-W, Chan Y-T, Teah HY, Chen T-Y, Chang C-F, Liu Y-T, Tzou Y-M (2016) Accumulation of heavy metals and trace elements in fluvial sediments received effluents from traditional and semiconductor industries. Sci Rep-UK 6:34250
Hung CV, Cam BD, Mai PTN, Dzung BQ (2015) Heavy metals and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in municipal sewage sludge from a river in highly urbanized metropolitan area in Hanoi, Vietnam: levels, accumulation pattern and assessment of land application. Environ Geochem Health 37:133–146
Lalander C, Diener S, Magri ME, Zurbrügg C, Lindström A, Vinnerås B (2013) Faecal sludge management with the larvae of the black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens)—from a hygiene aspect. Sci Total Environ 458–460:312–318
Lalander CH, Fidjeland J, Diener S, Eriksson S, Vinnerås B (2014) High waste-to-biomass conversion and efficient salmonella spp. reduction using black soldier fly for waste recycling. Agron Sustain Dev 35:261–271
Li Q, Zheng L, Qiu N, Cai H, Tomberlin JK, Yu Z (2011) Bioconversion of dairy manure by black soldier fly (Diptera: Stratiomyidae) for biodiesel and sugar production. Waste Manag 31:1316–1320
Li W, Li Q, Zheng L, Wang Y, Zhang J, Yu Z, Zhang Y (2015) Potential biodiesel and biogas production from corncob by anaerobic fermentation and black soldier fly. Bioresour Technol 194:276–282
Liu J, Chen J, Huang L (2015) Heavy metal removal from MSS fly ash by thermal and chlorination treatments. Sci Rep-UK 5:17270
Milinovic J, Vidal M, Lacorte S, Rigol A (2014) Leaching of heavy metals and alkylphenolic compounds from fresh and dried sewage sludge. Environ Sci Pollut R 21:2009–2017
Nakamura S, Ichiki TR, Shimoda M, Morioka S (2016) Small-scale rearing of the black soldier fly, Hermetia illucens (Diptera: Stratiomyidae), in the laboratory: low-cost and year-round rearing. Appl Entomol Zool 51:161–166
Ogunwande GA, Osunade JA, Adekalu KO, Ogunjimi LA (2008) Nitrogen loss in chicken litter compost as affected by carbon to nitrogen ratio and turning frequency. Bioresour Technol 99:7495–7503
Parra Paz AS, Carrejo NS, Gómez Rodríguez CH (2015) Effects of larval density and feeding rates on the bioconversion of vegetable waste using black soldier fly larvae Hermetia illucens (L.), (Diptera: Stratiomyidae). Waste Biomass Valori 6:1059–1065
Peng C, Cai Y, Wang T, Xiao R, Chen W (2016) Regional probabilistic risk assessment of heavy metals in different environmental media and land uses: an urbanization-affected drinking water supply area. Sci Rep-UK 6:37084
Popa R, Green TR (2012) Using black soldier fly larvae for processing organic leachates. J Econ Entomol 105:374–378
Ščančar J, Milačič R, Stražar M, Burica O (2000) Total metal concentrations and partitioning of Cd, Cr, Cu, Fe, Ni and Zn in sewage sludge. Sci Total Environ 250:9–19
Shamuyarira KK, Gumbo JR (2014) Assessment of heavy metals in municipal sewage sludge: a case study of Limpopo province, South Africa. Int J Environ Res Public Health 11:2569–2579
Sheppard DC, Tomberlin JK, Joyce JA, Kiser BC, Sumner SM (2002) Rearing methods for the black soldier fly (Diptera: Stratiomyidae). J Med Entomol 39:695–698
Tandukar M, Pavlostathis SG (2015) Co-digestion of municipal sludge and external organic wastes for enhanced biogas production under realistic plant constraints. Water Res 87:432–445
Wang C, Hu X, Chen M-L, Y-H W (2005) Total concentrations and fractions of Cd, Cr, Pb, Cu, Ni and Zn in sewage sludge from municipal and industrial wastewater treatment plants. J Hazard Mater 119:245–249
Weng H-X, Ma X-W, F-X F, Zhang J-J, Liu Z, Tian L-X, Liu C (2014) Transformation of heavy metal speciation during sludge drying: mechanistic insights. J Hazard Mater 265:96–103
Xiao Z, Yuan X, Jiang L, Chen X, Li H, Zeng G, Leng L, Wang H, Huang H (2015) Energy recovery and secondary pollutant emission from the combustion of co-pelletized fuel from municipal sewage sludge and wood sawdust. Energy 91:441–450
Zheng L, Hou Y, Li W, Yang S, Li Q, Yu Z (2012a) Biodiesel production from rice straw and restaurant waste employing black soldier fly assisted by microbes. Energy 47:225–229
Zheng L, Li Q, Zhang J, Yu Z (2012b) Double the biodiesel yield: rearing black soldier fly larvae, Hermetia illucens, on solid residual fraction of restaurant waste after grease extraction for biodiesel production. Renew Energ 41:75–79
Zheng L, Crippen TL, Holmes L, Singh B, Pimsler ML, Benbow ME, Tarone AM, Dowd S, Yu Z, Vanlaerhoven SL, Wood TK, Tomberlin JK (2013) Bacteria mediate oviposition by the black soldier fly, Hermetia illucens (L.), (Diptera: Stratiomyidae). Sci Rep-UK 3:2563
Zhou F, Tomberlin JK, Zheng L, Yu Z, Zhang J (2013) Developmental and waste reduction plasticity of three black soldier fly strains (Diptera: Stratiomyidae) raised on different livestock manures. J Med Entomol 50:1224–1230
Acknowledgements
The authors kindly acknowledge Dr. Linda S. Thomashow from the USDA-ARS (in USA) for the manuscript revision.
Funding
This work is supported in part by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41603110), The Special Fund for Agro-scientific Research in the Public Interest from the Ministry of Agriculture, China (201303094), and Postdoctoral Science Foundation of China (2015M572165).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical statement
The work has not been published previously and is not under consideration for publication elsewhere.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interest.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 15 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cai, M., Hu, R., Zhang, K. et al. Resistance of black soldier fly (Diptera: Stratiomyidae) larvae to combined heavy metals and potential application in municipal sewage sludge treatment. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25, 1559–1567 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0541-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0541-x