Abstract
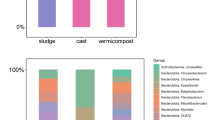
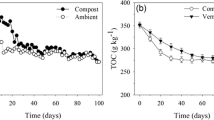
This study aims to reveal the effects of earthworms (Eisenia fetida) on bacterial profiles during the vermicomposting process of sewage sludge and cattle dung with the high-throughput sequencing technology. The earthworms could accelerate organic degradation and improve the stabilization process. Moreover, the addition of earthworms not only affected the bacterial numbers, but also increased the bacterial community diversity. The activity of earthworms had significant effects on the bacterial community structure as the bacterial community was clearly different between the vermicomposting and the control treatment. Furthermore, the earthworms affected the physical and chemical properties of substrates, thus promoting the growth of some microorganisms, such as Flavobacteria, Acidbacteria, and Planctomycetes. Earthworms largely inhibited the growth of various human pathogenic bacteria. In summary, earthworms significantly affected the bacterial community in vermicomposting and it could be applied as an authentically effective technique for the stabilization of organic wastes.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aira M, Bybee S, Pérez-Losada M, Domínguez J (2015) Feeding on microbiomes: effects of detritivory on the taxonomic and phylogenetic bacterial composition of animal manures. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 91:817–822
Arora S, Rajpal A, Bhargava R, Pruthi V, Bhatia A, Kazmi AA (2014) Antibacterial and enzymatic activity of microbial community during wastewater treatment by pilot scale vermifiltration system. Bioresour Technol 166:132–141
Arora S, Kazmi AA (2015) The effect of seasonal temperature on pathogen removal efficacy of vermifilter for wastewater treatment. Water Res 74:88–99
Benitez E, Nogales R, Elvira C, Masciandaro G, Ceccanti B (1999) Enzyme activities as indicators of the stabilization of sewage sludges composting with Eisenia foetida. Bioresour Technol 67:297–303
Bernard L, Chapuis-Lardy L, Razafimbelo T, Razafindrakoto M, Pablo AL, Legname E, Poulain J, Brüls T, O'Donohue M, Brauman A, Chotte JL, Blanchart E (2012) Endogeic earthworms shape bacterial functional communities and affect organic matter mineralization in a tropical soil. ISME J 6:213–222
Brown BA, Mitchell MJ (1981) Role of the earthworm, Eisenia foetida, in affecting the survival of Salmonella enteritidis ser. Typhimurium. Pedobiologia 22:434–438
Byzov BA, Nechitaylo TY, Bumazhkin BK, Kurakov AV, Golyshin PN, Zvyagintsev DG (2009) Culturable microorganisms from the earthworm digestive tract. Microbiology 78:360–368
Cai L, Zhang T (2013) Detecting human bacterial pathogens in wastewater treatment plants by a high-throughput shotgun sequencing technique. Environ Sci Technol 47:5433–5441
Chen YX, Chang SKC, Chen J, Zhang Q, Yu HY (2018) Characterization of microbial community succession during vermicomposting of medicinal herbal residues. Bioresour Technol 249:542–549
Eastman BR, Kane PN, Edwards CA, Trytek L, Gunadi B, Stermer AL, Mobley JR (2001) The effectiveness of vermiculture in human pathogen reduction for USEPA biosolids stabilization. Compost Sci Util 9:38–49
Fernández-Gómez MJ, Nogales R, Insam H, Romero E, Goberna M (2010) Continuous-feeding vermicomposting as a recycling management method to revalue tomato-fruit wastes from greenhouse crops. Waste Manag 30:2461–2468
Fernández-Gómez MJ, Nogales R, Insam H, Romero E, Goberna M (2012) Use of DGGE and COMPOCHIP for investigating bacterial communities of various vermicomposts produced from different wastes under dissimilar conditions. Sci Total Environ 414:664–671
Fracchia L, Dohrmann AB, Martinotti MG, Tebbe CC (2006) Bacterial diversity in a finished compost and vermicompost: differences revealed by cultivation-independent analyses of PCR-amplified 16S rRNA genes. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 71:942–952
Fu XY, Cui GY, Huang K, Chen XM, Li FS, Zhang XY, Li F (2016) Earthworms facilitate the stabilization of pelletized dewatered sludge through shaping microbial biomass and activity and community. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:4522–4530
Gómez-Brandón M, Aira M, Lores M, Domínguez J (2011) Changes in microbial community structure and function during vermicomposting of pig slurry. Bioresour Technol 102:4171–4178
Hamady M, Lozupone C, Knight R (2010) Fast UniFrac: facilitating high-throughput phylogenetic analyses of microbial communities including analysis of pyrosequencing and PhyloChip data. ISME J 4:17–27
Hill GB, Baldwin SA (2012) Vermicomposting toilets, an alternative to latrine style microbial composting toilets, prove far superior in mass reduction, pathogen destruction, compost quality, and operational cost. Waste Manag 32:1811–1820
Huang K, Li FS, Wei YF, Chen XM, Fu XY (2013) Changes of bacterial and fungal community compositions during vermicomposting of vegetable wastes by Eisenia foetida. Bioresour Technol 150:35–241
Huang K, Li FS, Wei YF, Fu XY, Chen XM (2014) Effects of earthworms on physicochemical properties and microbial profiles during vermicomposting of fresh fruit and vegetable wastes. Bioresour Technol 170:45–52
Karsten GR, Drake HL (1995) Comparative assessment of the aerobic and anaerobic microfloras of earthworm guts and forest soils. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 61:1039–1044
Khwairakpam M, Bhargava R (2009) Vermitechnology for sewage sludge recycling. J Hazard Mater 161:948–954
Lazcano C, Gómez-Brandón M, Domínguez J (2008) Comparison of the effectiveness of composting and vermicomposting for the biological stabilization of cattle manure. Chemosphere 72:1013–1019
Li B, Ju F, Cai L, Zhang T (2015) Profile and fate of bacterial pathogens in sewage treatment plants revealed by high-throughput metagenomic approach. Environ Sci Technol 49:10492–10502
Liu J, Lu ZB, Yang J, Xing MY, Yu F, Guo MT (2012) Effect of earthworms on the performance and microbial communities of excess sludge treatment process in vermifilter. Bioresour Technol 117:214–221
Lores M, Gómez-Brandón M, Pérez-Díaz D, Domínguez J (2006) Using FAME profiles for the characterization of animal wastes and vermicomposts. Soil Biol Biochem 38:2993–2996
Lv BY, Xing MY, Yang J, Zhang LB (2015) Pyrosequencing reveals bacterial community differences in composting and vermicomposting on the stabilization of mixed sewage sludge and cattle dung. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol 99:10703–10712
Monroy F, Aira M, Domínguez J (2009) Reduction of total coliform numbers during vermicomposting is caused by short-term direct effects of earthworms on microorganisms and depends on the dose of application of pig slurry. Sci Total Environ 407:5411–5416
Nebert LD, Bloem J, Lubbers IM, van Groenigen JW (2011) Association of earthworm-denitrifier interactions with increased emission of nitrous oxide from soil mesocosms amended with crop residue. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 77:4097–4104
Pepper IL, Gerba CP, Brendecke JW (1995) Environmental microbiology: a laboratory manual. Academic Press, New York
Potts DA, Görres JH, Nicosia EL, Amador JA (2004) Effects of aeration on water quality from septic system leachfields. J Environ Qual 33:1828–1838
Rodríguez-Canché LG, Vigueros LC, Maldonado-Montiel T, Martinez-Sanmiguel M (2010) Pathogen reduction in septic tank sludge through vermicomposting using Eisenia fetida. Bioresour Technol 101:3548–3553
Sen B, Chandra TS (2009) Do earthworms affect dynamics of functional response and genetic structure of microbial community in a lab-scale composting system? Bioresour Technol 100:804–811
Singh D, Suthar S (2012) Vermicomposting of herbal pharmaceutical industry solid wastes. Ecol Eng 39:1–6
Soobhany N, Mohee R, Garg VK (2017) Inactivation of bacterial pathogenic load in compost against vermicompost of organic solid waste aiming to achieve sanitation goals: a review. Waste Manag 64:54–62
State Environmental Protection Administration of China (SEPA) (2002) Monitor and analysis method of water and wastewater. Chinese Environmental Science Publication Press, Beijing (in Chinese)
Toyota K, Kimura M (2000) Microbial community indigenous to the earthworm Eisenia foetida. Biol. Fertil. Soils 31:187–190
Vargas-García MC, Suárez-Estrella F, López MJ, Moreno J (2010) Microbial population dynamics and enzyme activities in composting processes with different starting materials. Waste Manag 30:771–778
Vivas A, Moreno B, Garcia-Rodriguez S, Benitez E (2009) Assessing the impact of composting and vermicomposting on bacterial community size and structure, and microbial functional diversity of an olive-mill waste. Bioresour Technol 100:1319–1326
Wang H, Li HY, Gilbert JA, Li HB, Wu LH, Liu M, Wang LL, Zhou QS, Yuan JX, Zhang ZJ (2015) Housefly larva vermicomposting efficiently attenuates antibiotic resistance genes in swine manure, with concomitant bacterial population changes. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 81:7668–7679
Woolhouse M, Gowtage-Sequeria S, Evans B (2006) T16: quantitative analysis of the characteristics of emerging and re-emerging human pathogens. University of Edinburgh, Centre for Infectious Diseases
Yadav A, Garg VK (2011) Recycling of organic wastes by employing Eisenia fetida. Bioresour Technol 102:2874–2880
Yang J, Lv BY, Zhang J, Xing MY (2014) Insight into the roles of earthworm in vermicomposting of sewage sludge by determining the water-extracts through chemical and spectroscopic methods. Bioresour Technol 154:94–100
Yasir M, Aslam Z, Kim SW, Lee SW, Jeon CO, Chung YR (2009) Bacterial community composition and chitinase gene diversity of vermicompost with antifungal activity. Bioresour Technol 100:4396–4403
Zhao LM, Wang YY, Yang J, Xing MY, Li XW, Yi DH, Deng DH (2010) Earthworm-microorganism interactions: a strategy to stabilize domestic wastewater sludge. Water Res 44:2572–2582
Zhu WQ, Yao W, Zhang Z, Wu Y (2014) Heavy metal behavior and dissolved organic matter (DOM) characterization of vermicomposted pig manure amended with rice straw. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21:12684–12692
Funding
The research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51508318; 51679168), the “Chenguang Program” (15CG53) of Shanghai Education Development Foundation, and Shanghai Municipal Education Commission.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lv, B., Xing, M. & Yang, J. Exploring the effects of earthworms on bacterial profiles during vermicomposting process of sewage sludge and cattle dung with high-throughput sequencing. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25, 12528–12537 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-1520-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-1520-6