Abstract
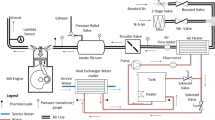
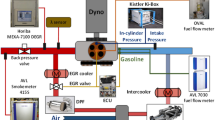
The present study describes the experimental and numerical analysis of the combustion and emission characteristics of CI engine operated with diesel-butanol blends. Experiments were carried with neat diesel fuel (i.e., Bu00) and its blends of n-butanol, 10%, 20% and 30% by volume (Bu10, Bu20 and Bu30) at a constant speed and rated load. From the experimental results, it is observed that CO, NOx and smoke emissions decreased, whereas the unburned hydrocarbon (UBHC) emission increased with increasing butanol content, as compared to Bu00. From the experimental analysis, it is also observed that Bu20 blend gives higher brake thermal efficiency (BTE) and lower brake specific energy consumption (BSEC) as compared to Bu00, Bu10 and Bu30, but produces higher UBHC. In order to decrease the UBHC emission, different piston bowl geometries were analysed using simulation studies. The combustion and emission characteristics of the CI engine operating with Bu20 blend for three different piston bowl geometries viz., hemispherical combustion chamber (HCC), shallow combustion chamber (SCC) and toroidal combustion chamber (TCC), were studied using CONVERGE CFD code. The simulation model was validated with experimental results of the baseline engine configuration (HCC) for diesel fuel as well as Bu20 blend. The results showed that there is a significant reduction in UBHC and improvement of performance for SCC and TCC piston geometry compared to HCC piston geometry. However, a slight increment of NOx emissions was observed.

























Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Buxy:
-
Diesel-butanol blend, with (xy) percentage by volume of butanol
- HCC:
-
Hemi spherical Combustion Chamber
- BSEC:
-
Brake specific energy consumption (J/kWh)
- bTDC:
-
Before top dead centre
- LHV:
-
latent heat of vaporisation (kJ/kg)
- BTE:
-
Brake thermal efficiency (%)
- NOx:
-
Nitrogen oxides (g/kWh)
- CI:
-
Compression ignition
- OCC:
-
Omega combustion chamber
- CO:
-
Carbon monoxide (g/kWh)
- SI:
-
Spark ignition
- CFD:
-
Computational fluid dynamics
- SCC:
-
Shallow combustion chamber
- DI:
-
Direct injection
- TCC:
-
Toroidal combustion chamber
- EGR:
-
Exhaust gas recirculation
- UBHC:
-
Unburned hydrocarbon (g/kWh)
- HRR:
-
Heat release rate (J/CAD)
References
Chen Z, Wu Z, Liu J, Lee C (2014) Combustion and emissions characteristics of high n-butanol/diesel ratio blend in a heavy-duty diesel engine and EGR impact. Energy Convers Manag 78:787–795. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2013.11.037
Doǧan O (2011) The influence of n-butanol/diesel fuel blends utilization on a small diesel engine performance and emissions. Fuel 90:2467–2472. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2011.02.033
Ganji PRAO, Singh RN, Raju VRK, Rao SS (2018) Design of piston bowl geometry for better combustion in direct-injection compression ignition engine. Sādhanā 43:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12046-018-0907-x
Han Z, Uludogan A, Hampson GJ, Reitz RD (1996) Mechanism of soot and NOx emission reduction using multiple-injection in a diesel engine. SAE transactions 105:837–852
Imran A, Varman M, Masjuki HH, Kalam MA (2013) Review on alcohol fumigation on diesel engine: a viable alternative dual fuel technology for satisfactory engine performance and reduction of environment concerning emission. Renew Sust Energ Rev 26:739–751. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2013.05.070
Jaichandar S, Annamalai K (2012) Influences of re-entrant combustion chamber geometry on the performance of Pongamia biodiesel in a DI diesel engine. Energy 44:633–640. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2012.05.029
Jaichandar S, Annamalai K (2013) Combined impact of injection pressure and combustion chamber geometry on the performance of a biodiesel fueled diesel engine. Energy 55:330–339. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2013.04.019
Jaichandar S, Senthil Kumar P, Annamalai K (2012) Combined effect of injection timing and combustion chamber geometry on the performance of a biodiesel fueled diesel engine. Energy 47:388–394. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2012.09.059
Karabektas M, Hosoz M (2009) Performance and emission characteristics of a diesel engine using isobutanol-diesel fuel blends. Renew Energy 34:1554–1559. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2008.11.003
Kennedy IM (1997) Models of soot formation and oxidation. Prog Energy Combust Sci 23:95–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0360-1285(97)00007-5
Lapuerta M, García-Contreras R, Campos-Fernández J, Dorado MP (2010) Stability, lubricity, viscosity, and cold-flow properties of alcohol-diesel blends. Energy Fuel 24:4497–4502. https://doi.org/10.1021/ef100498u
Li J, Yang WM, An H, Maghbouli A, Chou SK (2014) Effects of piston bowl geometry on combustion and emission characteristics of biodiesel fueled diesel engines. Fuel 120:66–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2013.12.005
Nalgundwar A, Paul B, Sharma SK (2016) Comparison of performance and emissions characteristics of di CI engine fueled with dual biodiesel blends of palm and jatropha. Fuel 173:172–179. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2016.01.022
Park S (2012) Optimization of combustion chamber geometry and engine operating conditions for compression ignition engines fueled with dimethyl ether. Fuel 97:61–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2012.03.004
Ra Y, Reitz RD (2009) A vaporization model for discrete multi-component fuel sprays. Int J Multiphase Flow 35:101–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmultiphaseflow.2008.10.006
Rajesh Kumar B, Saravanan S (2016a) Use of higher alcohol biofuels in diesel engines: a review. Renew Sust Energ Rev 60:84–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2016.01.085
Rajesh Kumar B, Saravanan S (2016b) Effects of iso-butanol/diesel and n-pentanol/diesel blends on performance and emissions of a di diesel engine under premixed LTC (low temperature combustion) mode. Fuel 170:49–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2015.12.029
Rajesh Kumar B, Saravanan S, Rana D, Nagendran A (2016) A comparative analysis on combustion and emissions of some next generation higher-alcohol/diesel blends in a direct-injection diesel engine. Energy Convers Manag 119:246–256. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2016.04.053
Rakopoulos CD, Antonopoulos KA, Rakopoulos DC (2007) Experimental heat release analysis and emissions of a HSDI diesel engine fueled with ethanol-diesel fuel blends. Energy 32:1791–1808. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2007.03.005
Rakopoulos DC, Rakopoulos CD, Giakoumis EG, Dimaratos AM, Kyritsis DC (2010a) Effects of butanol-diesel fuel blends on the performance and emissions of a high-speed di diesel engine. Energy Convers Manag 51:1989–1997. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2010.02.032
Rakopoulos DC, Rakopoulos CD, Hountalas DT, Kakaras EC, Giakoumis EG, Papagiannakis RG (2010b) Investigation of the performance and emissions of bus engine operating on butanol/diesel fuel blends. Fuel 89:2781–2790. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2010.03.047
Reitz RD, Beale JC (1999) Modeling spray atomization with the kelvin-Helmholtz/Rayleigh-Taylor hybrid model. At Sprays 9:623–650. https://doi.org/10.1615/AtomizSpr.v9.i6.40
Şahin Z, Aksu ON (2015) Experimental investigation of the effects of using low ratio n-butanol/diesel fuel blends on engine performance and exhaust emissions in a turbocharged DI diesel engine. Renew Energy 77:279–290. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2014.11.093
Saravanan S, Rajesh Kumar B, Varadharajan A, Rana D, Sethuramasamyraja B, Lakshmi Narayana rao G (2017) Optimization of DI diesel engine parameters fueled with iso-butanol/diesel blends – response surface methodology approach. Fuel 203:658–670. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2017.04.083
Siwale L, Kristóf L, Adam T, Bereczky A, Mbarawa M, Penninger A, Kolesnikov A (2013) Combustion and emission characteristics of n-butanol / diesel fuel blend in a turbo-charged compression ignition engine. Fuel 107:409–418. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2012.11.083
Taylor P, Han Z, Reitz RD (2007) Combustion Science and Technology Turbulence Modeling of Internal Combustion Engines Using RNG κ - ε Models Turbulence Modeling of Internal Combustion Engines Using RNG k-E Models. 37–41
Wang H, Deneys Reitz R, Yao M, Yang B, Jiao Q, Qiu L (2013) Development of an n-heptane-n-butanol-PAH mechanism and its application for combustion and soot prediction. Combust Flame 160:504–519. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.combustflame.2012.11.017
Zhang ZH, Chua SM, Balasubramanian R (2016) Comparative evaluation of the effect of butanol-diesel and pentanol-diesel blends on carbonaceous particulate composition and particle number emissions from a diesel engine. Fuel 176:40–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2016.02.061
Funding
This work was supported by Centre for sustainable energy studies, NITW of Technical Education Quality Improvement Programme (TEQIP-II), India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kattela, S.P., Vysyaraju, R.K.R., Surapaneni, S.R. et al. Effect of n-butanol/diesel blends and piston bowl geometry on combustion and emission characteristics of CI engine. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26, 1661–1674 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-3704-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-3704-5