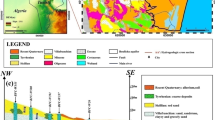
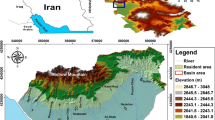
Abstract
Effects of pollution caused by seawater intrusion into groundwater in coastal aquifers cannot be ignored. Identification of areas exposed to this pollution by preparing vulnerability maps is one way of preventing aquifer pollution. In its primary section, the present study compared three different index ranking methods of DRASTIC, GALDIT, and SINTACS to select an optimal model for determining vulnerability of the Gharesoo-Gorgan Rood coastal aquifer. Initial results led to selection of the GALDIT model for vulnerability assessment of the selected coastal aquifer. Since this type of models use a rating system, the model must be modified and optimized in various regions to show the vulnerable areas more accurately. In the next step, and for the first time, the ratings in this index were modified using the Wilcoxon nonparametric statistical method and its weights were optimized employing particle swarm optimization (PSO) and single-parameter sensitivity analysis (SPSA) methods. Finally, in order to select the best hybrid model, the total dissolved solids (TDS) parameter was used to determine correlation coefficients. Results indicated that the GALDT model modified by the Wilcoxon-PSO method has the strongest correlation (0.77) with the TDS parameter. Moreover, the correlations of the Wilcoxon-GALDIT and Wilcoxon-SPSA models were 0.66 and 0.73, respectively. Final results of the Wilcoxon-PSO model revealed that the northwestern and western areas of the study region needed considerable protection against pollution. In general, we can conclude that by combining statistical, mathematical, and metaheuristic methods, we can obtain more accurate results for preparing vulnerability maps.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aller L, Bennett T, Lehar JH, Petty RJ, Hackett G (1987) DRASTIC: a standardized system for evaluating ground water pollution potential using hydrogeologic settings, EPA 600/2–87-035. U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Ada
Allouche N, Brahim FB, Gontara M, Khanfir H, Bouri S (2015) Validation of two applied methods of groundwater vulnerability mapping: application to the coastal aquifer system of southern Sfax (Tunisia). J Water Supply Res Technol 64(6):719–737. https://doi.org/10.2166/aqua.2015.105
Allouche N, Maanan M, Gontara M, Rollo N, Jmal I, Bouri S (2017) A global risk approach to assessing groundwater vulnerability. Environ Model Softw 88:168–182. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envsoft.2016.11.023
Arauzo M (2017) Vulnerability of groundwater resources to nitrate pollution: a simple and effective procedure for delimiting nitrate vulnerable zones. Sci Total Environ 575:799–812. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.09.139
Asadi P, Ataie-Ashtiani B, Beheshti A (2017) Vulnerability assessment of urban groundwater resources to nitrate: the case study of Mashhad, Iran. Environ Earth Sci 76(1):41. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-6357-z
Babiker IS, Mohamed MAA, Hiyama T, Kato K (2005) A GIS-based DRASTIC model for assessing aquifer vulnerability in Kakamigahara Heights, Gifu Prefecture, central Japan. Sci Total Environ 345(1–3):127–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv
Barzegar R, Moghaddam AA, Deo R, Fijani E, Tziritis E (2018) Mapping groundwater contamination risk of multiple aquifers using multi-model ensemble of machine learning algorithms. Sci Total Environ 621:697–712. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv
Bouderbala A, Remini B, Hamoudi S, Pulido-Bosch A (2016) Assessment of groundwater vulnerability and quality in coastal aquifers: a case study (Tipaza, North Algeria). Arab J Geosci 9:181. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-015-21516
Chachadi AG (2005) Seawater intrusion mapping using modified GALDIT indicator model-case study in Goa. Jalvigyan Sameeksha 20:29–45
Chachadi AG, and Lobo Ferreira JPC (2001) Sea water intrusion vulnerability mapping of aquifers using the GALDIT method. Proc. Workshop on modeling in hydrogeology. Anna University, CHENNAI 143--156
Civita M (1994) Aquifer vulnerability maps to pollution. Pitagora Ed, Bologna
Civita M, De Maio M (1997) SINTACS. Un sistema parametrico per la valutazione e la cartografia della vulnerabilita‘ degli acquiferi all’inquinamento. Metodologia and Automatizzazione, vol. 60. Pitagora Editrice, Bologna. 191
Civita M, De Maio M (2004) Assessing and mapping groundwater vulnerability to contamination: the Italian combined approach. Geofis Int 43(4):513–532
Daly D, Drew D (1999) Irish methodologies for karst aquifer protection. Hydrogeology and engineering geology of sinkholes and karst. Balkema, Rotterdam, pp 267–272
Dhar A, Datta B (2009) Saltwater intrusion management of coastal aquifers. I: linked simulation-optimization. J Hydrol Eng 14(12):1263–1272. https://doi.org/10.1061/ASCE_HE.1943-5584.0000097
Foster SSD (1987) Fundamental concepts in aquifer vulnerability, pollution risk and protection strategy. In: Van Duijvenbooden W, Waegeningh HG (eds) TNO Committee on Hydrological Research, the Hague. Vulnerability of Soil and Groundwater to Pollutants, Proc Inf 38:69–86
Gaur S, Chahar BR, Graillot D (2011) Analytic elements method and particle swarm optimization based simulation–optimization model for groundwater management. J Hydrol 402(3–4):217–227. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2011.03.016
Gaur S, Ch S, Graillot D, Chahar BR, Kumar DN (2013) Application of artificial neural networks and particle swarm optimization for the management of groundwater resources. Water Resour Manag 27(3):927–941
Gontara M, Allouche N, Jmal I, Bouri S (2016) Sensitivity analysis for the GALDIT method based on the assessment of vulnerability to pollution in the northern Sfax coastal aquifer, Tunisia. Environ. Earth Sci 75:669. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-5459-y
Gorgij AD, Moghaddam AA (2016) Vulnerability assessment of saltwater intrusion using simplified GAPDIT method: a case study of Azarshahr Plain Aquifer, East Azerbaijan, Iran. Arab J Geosci 9(2):106. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-015-2200-1
Guneshwor L, Eldho TI, Kumar AV (2018) Identification of groundwater contamination sources using Meshfree RPCM Simulation and Particle Swarm Optimization. Water Resour Manag 32(4):1517–1538. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-017-1885-1
Huan H, Wang J, Teng Y (2012) Assessment and validation of groundwater vulnerability to nitrate based on a modified DRASTIC model: a case study in Jilin City of Northeast China. Sci Total Environ 440:14–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2012.08.037
Iqbal J, Pathak G, Gorai AK (2014) Development of hierarchical fuzzy model for groundwater vulnerability to pollution assessment. Arab J Geosci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-014-1417-8
Jafari SM, Nikoo MR (2016) Groundwater risk assessment based on optimization framework using DRASTIC method. Arab J Geosci 9:742. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-016-2756-4
Kardan Moghaddam H, Jafari F, Javadi S (2017) Vulnerability evaluation of a coastal aquifer via GALDIT model and comparison with DRASTIC index using quality parameters. Hydrol Sci J 62(1):137–146
Kazakis N, Spiliotis M, Voudouris K, Pliakas FK, Papadopoulos B (2018) A fuzzy multicriteria categorization of the GALDIT method to assess seawater intrusion vulnerability of coastal aquifers. Sci Total Environ 621:524–534. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.11.235
Kennedy J, Eberhart RC (1995) Particle swarm optimization. Proc. IEEE int'l conf. on neural networks. 1942–1948. IEEE service center, Piscataway
Khosravi K, Sartaj M, Tsai FTC, Singh VP, Kazakis N, Melesse AM, Prakash I, Bui DT, Pham BT (2018) A comparison study of DRASTIC methods with various objective methods for groundwater vulnerability assessment. Sci Total Environ 642:1032–1049. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.06.130
Kumar S, Thirumalaivasan D, Radhakrishnan N, Mathew S (2013) Groundwater vulnerability assessment using SINTACS model. Geomat Nat Haz Risk 4(4):339–354. https://doi.org/10.1080/433935419475705.2012.732119
Luchian H, Breaban ME, Bautu A (2015) On meta-heuristics in optimization and data analysis. Application to geosciences. In: Artificial intelligent approaches in petroleum geosciences, pp 53–100. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-16531-8_2
Luoma S, Okkonen J, Korkka-Niemi K (2017) Comparison of the AVI, modified SINTACS and GALDIT vulnerability methods under future climate-change scenarios for a shallow low-lying coastal aquifer in southern Finland. Hydrogeol J 25:203–222. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10040-016-1471-2
Mahi M, Baykan OK, Kodaz H (2018) A new approach based on particle swarm optimization algorithm for solving data allocation problem. Appl Soft Comput 62:571–578. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2017.11.019
Mahrez B, Klebingat S, Houha B, Houria B (2018) GIS-based GALDIT method for vulnerability assessment to seawater intrusion of the Quaternary coastal Collo aquifer (NE-Algeria). Arab J Geosci 11(4):71. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-018-3400-2
Majandang J, Sarapirome S (2013) Groundwater vulnerability assessment and sensitivity analysis in nong Rua, Khon Kaen, Thailand, using a GIS-based SINTACS model. Environ Earth Sci 68(7):2025–2039. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-012-1890-x
Motevalli A, Moradi HR, Javadi S (2018) A comprehensive evaluation of groundwater vulnerability to saltwater up-coning and sea water intrusion in a coastal aquifer (case study: Ghaemshahr-juybar aquifer). J Hydrol 557:753–773. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2017.12.047
Nadiri AA, Gharekhani M, Khatibi R, Sadeghfam S, Asghari Moghaddam A (2017a) Groundwater vulnerability indices conditioned by supervised intelligence committee machine (SICM). Sci Total Environ 574:691–706. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.09.093
Nadiri AA, Sedghi Z, Khatibi R, Gharekhani M (2017b) Mapping vulnerability of multiple aquifers using multiple models and fuzzy logic to objectively derive model structures. Sci Total Environ 593:75–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.03.109
Nadiri AA, Gharekhani M, Khatibi R (2018) Mapping aquifer vulnerability indices using artificial intelligence-running multiple frameworks (AIMF) with supervised and unsupervised learning. Water Resour Manag 32(9):3023–3040. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-018-1971-z
Napolitano P, Fabbri AG (1996) Single-parameter sensitivity analysis for aquifer vulnerability assessment using DRASTIC and SINTACS. Proceedings of the Vienna conference on Hydro GIS 96: application of geographic information systems in hydrology and water resources management IAHS. 235:559–566
Neshat A, Pradhan B (2015a) An integrated DRASTIC model using frequency ratio and two new hybrid methods for groundwater vulnerability assessment. Nat Hazards 76(1):543–563. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-014-1503-y
Neshat A, Pradhan B (2015b) Risk assessment of groundwater pollution with a new methodological framework: application of Dempster–Shafer theory and GIS. Nat Hazards 78(3):1565–1585. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-015-1788-5
Neshat A, Pradhan B (2017) Evaluation of groundwater vulnerability to pollution using DRASTIC framework and GIS. Arab J Geosci 10(22):501. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-017-3292-6
Neshat A, Pradhan B, Pirasteh S, Shafri HZM (2014a) Estimating groundwater vulnerability to pollution using a modified DRASTIC model in the Kerman agricultural area, Iran. Environ Earth Sci 71(7):3119–3131. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-013-2690-7
Neshat A, Pradhan B, Shafri HZM (2014b) An integrated GIS based statistical model to compute groundwater vulnerability index for decision maker in agricultural area. J Indian Soc Remote Sens 42(4):777–788. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12524-014-0376-6
Neshat A, Pradhan B, Dadras M (2014c) Groundwater vulnerability assessment using an improved DRASTIC method in GIS. Resour Conserv Recycl 86:74–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2014.02.008
Pacheco FA, Fernandes LFS (2013) The multivariate statistical structure of DRASTIC model. J Hydrol 476:442–459. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2012.11.020
Pacheco FAL, Pires LMGR, Santos RMB, Fernandes LS (2015) Factor weighting in DRASTIC modeling. Sci Total Environ 505:474–486. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.09.092
Recinos N, Kallioras A, Pliakas F, Schuth C (2015) Application of GALDIT index to assess the intrinsic vulnerability to seawater intrusion of coastal granular aquifers. Environ Earth Sci 73(3):1017–1032. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-014-3452-x
Ribeiro L, Pindo JC, Dominguez-Granda L (2017) Assessment of groundwater vulnerability in the Daule aquifer, Ecuador, using the susceptibility index method. Sci Total Environ 574:1674–1683. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.09.004
Saidi S, Bouri S, Dhia HB (2013) Groundwater management based on GIS techniques, chemical indicators and vulnerability to seawater intrusion modelling: application to the Mahdia–Ksour Essaf aquifer, Tunisia. Environ Earth Sci 70(4):1551–1568. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-013-2241-2
Trabelsi N, Triki I, Hentati I, Zairi M (2016) Aquifer vulnerability and seawater intrusion risk using GALDIT, GQISWI and GIS: case of a coastal aquifer in Tunisia. Environ Earth Sci 75:669. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-5459-y
Wilcoxon F (1945) Individual comparisons by ranking methods. Biom Bull 1:80–83
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Marcus Schulz
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Highlights
- Comparison of various vulnerability methods
- Considerable improvement of the introduced method compared to the previous ones
- Development of a road map for sea water management based on vulnerability classification
- Development of modified and optimized methods for assessment of groundwater vulnerability
- Presentation of a more accurate estimate of groundwater vulnerability using Wilcoxon-PSO method
- Employment of a new framework to study groundwater vulnerability
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bordbar, M., Neshat, A. & Javadi, S. A new hybrid framework for optimization and modification of groundwater vulnerability in coastal aquifer. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26, 21808–21827 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-04853-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-04853-4