Abstract
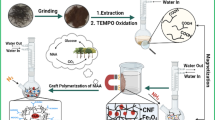
The present study describes preparation of cellulose incorporated magnetic nano-biocomposites (CNPs) by using cellulose as base material. The prepared CNPs were characterised by SEM, EDAX, TEM, XRD, and FT-IR and found to exhibit an intrinsic peroxidase-like activity with a Km and Vmax of 550 μM and 3.8 μM/ml/min, respectively. The CNPs exhibited higher pH and thermal stability compared to commercial peroxidase. These nanocomposites were able to completely remove (i) a persistent azo dye, methyl orange at a concentration of 50 ppm, within 60 min under acidic conditions (pH 3.0) and also (ii) decolourize commercial textile dye mixture under acidic conditions within 30 min. CNP-mediated degradation of dyes into simple products was further confirmed by UV-Vis and AT-IR spectroscopy The added advantage of CNPs separation after decolourization by simple magnet due to their magnetic properties and consequent reusability makes them fairy attractive system for dye remediation from environmental samples or textile industries effluents.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Attallah OA, Al-Ghobashy MA, Nebsen M, Salem MY (2016) Removal of cationic and anionic dyes from aqueous solution with magnetite/pectin and magnetite/silica/pectin hybrid nanocomposites: kinetic, isotherm and mechanism analysis. RSC Adv 6:11461–11480
Beyki MH, Bayat M, Shemirani F (2016) Fabrication of core–shell structured magnetic nanocellulose base polymeric ionic liquid for effective biosorption of Congo red dye. Bioresour Technol 218:326–334
Bilgi S, Demir C (2005) Identification of photooxidation degradation products of C.I. Reactive Orange 16 dye by gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. Dyes Pigm 66:69–76
Bodirlau R, Teaca C (2009) Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy and thermal analysis of lignocellulose fillers treated with organic anhydrides. Rom J Phys 54:93–104
Cai Y, Zheng L, Fang Z (2015) Selective adsorption of Cu (II) from an aqueous solution by ion imprinted magnetic chitosan microspheres prepared from steel pickling waste liquor. RSC Adv 5:97435–97445
Cao J, Wei L, Huang Q, Wang L, Han S (1999) Reducing degradation of azo dye by zero-valent iron in aqueous solution. Chemosphere 38:565–571
Dai R, Chen X, Xiang X, Wang Y, Wang F (2018) Understanding azo dye anaerobic bio-decolorization with artificial redox mediator supplement: considering the methane production. Bioresour Technol 249:799–808
Darabdhara G, Sharma B, Das MR, Boukherroub R, Szunerits S (2017) Cu-Ag bimetallic nanoparticles on reduced graphene oxide nanosheets as peroxidase mimic for glucose and ascorbic acid detection. Sens Actuators B Chem 238:842–851
dos Santos AB, Bisschops IAE, Cervantes FJ, van Lier JB (2005) The transformation and toxicity of anthraquinone dyes during thermophilic (55 °C) and mesophilic (30 °C) anaerobic treatments. J Biotechnol 115:345–353
Duan D, Fan K, Zhang D, Tan S, Liang M, Liu Y, Zhang J, Zhang P, Liu W, Qiu X, Kobinger GP, Fu Gao G, Yan X (2015) Nanozyme-strip for rapid local diagnosis of Ebola. Biosens Bioelectron 74:134–141
Fan J, Guo Y, Wang J, Fan M (2009) Rapid decolorization of azo dye methyl orange in aqueous solution by nanoscale zerovalent iron particles. J Hazard Mater 166:904–910
Gao L, Zhuang J, Nie L, Zhang J, Zhang Y, Gu N, Wang T, Feng J, Yang D, Perrett S (2007) Intrinsic peroxidase-like activity of ferromagnetic nanoparticles. Nat Nanotechnol 2:577–583
Gao L, Fan K, Yan X (2017) Iron oxide nanozyme: a multifunctional enzyme mimetic for biomedical applications. Theranostics 7:3207–3227
Hameed BB, Ismail ZZ (2018) Decolorization, biodegradation and detoxification of reactive red azo dye using non-adapted immobilized mixed cells. Biochem Eng J 137:71–77
Korschelt K, Tahir MN, Tremel W (2018) A step into the future: applications of nanoparticle enzyme mimics. Chem Eur J 24:9703–9713
Kyzas G, Fu J, Matis K (2013) The change from past to future for adsorbent materials in treatment of dyeing wastewaters. Materials 6:5131–5158
Lamba R, Umar A, Mehta S, Kansal SK (2015) ZnO doped SnO2 nanoparticles heterojunction photo-catalyst for environmental remediation. J Alloy Compd 653:327–333
Li F, Zhang L, Hu C, Xing X, Yan B, Gao Y, Zhou L (2019) Enhanced azo dye decolorization through charge transmission by σ-Sb3+-azo complexes on amorphous Sb2S3 under visible light irradiation. Appl Catal B 240:132–140
Liu B, Han X, Liu J (2016) Iron oxide nanozyme catalyzed synthesis of fluorescent polydopamine for light-up Zn2+ detection. Nanoscale 8:13620–13626
Liu J, Meng L, Fei Z, Dyson PJ, Jing X, Liu X (2017) MnO2 nanosheets as an artificial enzyme to mimic oxidase for rapid and sensitive detection of glutathione. Biosens Bioelectron 90:69–74
Liu XD, Chen H, Liu SS, Ye LQ, Li YP (2015) Hydrothermal synthesis of superparamagnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles with ionic liquids as stabilizer. Mater Res Bull 62:217–221
Liu X, Chen Z, Chen Z, Megharaj M, Naidu R (2013) Remediation of Direct Black G in wastewater using kaolin-supported bimetallic Fe/Ni nanoparticles. Chem Eng J 223:764–771
Lu P, Hsieh YL (2010) Preparation and properties of cellulose nanocrystals: rods, spheres, and network. Carbohydr Polym 82:329–336
Mateen F, Javed I, Rafique U, Tabassum N, Sarfraz M, Safi SZ, Yusoff I, Ashraf MA (2016) New method for the adsorption of organic pollutants using natural zeolite incinerator ash (ZIA) and its application as an environmentally friendly and cost-effective adsorbent. Desalin Water Treat 57:6230–6238
Mishra A, Ahmad R, Sardar M (2015) Biosynthesized iron oxide nanoparticles mimicking peroxidase activity: application for biocatalysis and biosensing. J Nanoeng Nanomanuf 5:37–42
Mishra A, Ahmad R, Perwez M, Sardar M (2016) Reusable green synthesized biomimetic magnetic nanoparticles for glucose and H2O2 detection. Bionanoscience 6:93–102
Musa A, Ahmad MB, Hussein MZ, Mohd Izham S, Shameli K, Abubakar Sani H (2016) Synthesis of nanocrystalline cellulose stabilized copper nanoparticles. J Nanomater 2016:1–7
Oh S, Kim J, Tran VT, Lee DK, Ahmed SR, Hong JC, Lee J, Park EY, Lee J (2018) Magnetic nanozyme-linked immunosorbent assay for ultrasensitive influenza A virus detection. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 10:12534–12543
Pine L, Hoffman P, Malcolm G, Benson R, Keen M (1984) Determination of catalase, peroxidase, and superoxide dismutase within the genus Legionella. J Clin Microbiol 20:421–429
Pratsinis A, Kelesidis GA, Zuercher S, Krumeich F, Bolisetty S, Mezzenga R, Leroux J-C, Sotiriou GA (2017) Enzyme-mimetic antioxidant luminescent nanoparticles for highly sensitive hydrogen peroxide biosensing. ACS Nano 11:12210–12218
Ren G, Sun M, Sun Y, Li Y, Wang C, Lu A, Ding H (2017) A cost-effective birnessite–silicon solar cell hybrid system with enhanced performance for dye decolorization. RSC Adv 7:47975–47982
Sahoo B, Sahu SK, Nayak S, Dhara D, Pramanik P (2012) Fabrication of magnetic mesoporous manganese ferrite nanocomposites as efficient catalyst for degradation of dye pollutants. Catal Sci Technol 2:1367–1374
Sha Y, Mathew I, Cui Q, Clay M, Gao F, Zhang XJ, Gu Z (2016) Rapid degradation of azo dye methyl orange using hollow cobalt nanoparticles. Chemosphere 144:1530–1535
Sharma JK, Srivastava P, Ameen S, Akhtar MS, Sengupta S, Singh G (2017) Phytoconstituents assisted green synthesis of cerium oxide nanoparticles for thermal decomposition and dye remediation. Mater Res Bull 91:98–107
Sun R, Hughes S (1998) Fractional extraction and physico-chemical characterization of hemicelluloses and cellulose from sugar beet pulp. Carbohydr Polym 36:293–299
Taha M, Adetutu EM, Shahsavari E, Smith AT, Ball AS (2014) Azo and anthraquinone dye mixture decolourization at elevated temperature and concentration by a newly isolated thermophilic fungus, Thermomucor indicae-seudaticae. J Environ Chem Eng 2:415–423
Truskewycz A, Shukla R, Ball AS (2016) Iron nanoparticles synthesized using green tea extracts for the fenton-like degradation of concentrated dye mixtures at elevated temperatures. J Environ Chem Eng 4:4409–4417
Vallabani NS, Karakoti AS, Singh S (2017) ATP-mediated intrinsic peroxidase-like activity of Fe3O4-based nanozyme: one step detection of blood glucose at physiological pH. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 153:52–60
Wang N, Zhu L, Wang M, Wang D, Tang H (2010) Sono-enhanced degradation of dye pollutants with the use of H2O2 activated by Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles as peroxidase mimetic. Ultrason Sonochem 17:78–83
Wang Q, Wei H, Zhang Z, Wang E, Dong S (2018) Nanozyme: an emerging alternative to natural enzyme for biosensing and immunoassay. Trends Anal Chem 105:218–224
Wu W, Xiao X, Zhang S, Peng T, Zhou J, Ren F, Jiang C (2010) Synthesis and magnetic properties of maghemite (γ-Fe2O3) short-nanotubes. Nanoscale Res Lett 5:1474–1479
Xie S, Huang P, Kruzic JJ, Zeng X, Qian H (2016) A highly efficient degradation mechanism of methyl orange using Fe-based metallic glass powders. Sci Rep 6:1–10
Yousefinejad S, Rasti H, Hajebi M, Kowsari M, Sadravi S, Honarasa F (2017) Design of C-dots/Fe3O4 magnetic nanocomposite as an efficient new nanozyme and its application for determination of H2O2 in nanomolar level. Sens Actuators B Chem 247:691–696
Zhang S, Li H, Wang Z, Liu J, Zhang H, Wang B, Yang Z (2015) A strongly coupled Au/Fe3 O4/GO hybrid material with enhanced nanozyme activity for highly sensitive colorimetric detection, and rapid and efficient removal of Hg2+ in aqueous solutions. Nanoscale 7:8495–8502
Zhang J, Ma J, Fan X, Peng W, Zhang G, Zhang F, Li Y (2017a) Graphene supported Au-Pd-Fe3O4 alloy trimetallic nanoparticles with peroxidase-like activities as mimic enzyme. Catal Commun 89:148–151
Zhang Z, Zhang X, Liu B, Liu J (2017b) Molecular imprinting on inorganic nanozymes for hundred-fold enzyme specificity. J Am Chem Soc 139:5412–5419
Zhao H, Kwak JH, Conrad Zhang Z, Brown HM, Arey BW, Holladay JE (2007) Studying cellulose fiber structure by SEM, XRD, NMR and acid hydrolysis. Carbohydr Polym 68:235–241
Zhao J, Dong W, Zhang X, Chai H, Huang Y (2018) FeNPs@Co3O4 hollow nanocages hybrids as effective peroxidase mimics for glucose biosensing. Sens Actuators B Chem 263:575–584
Zhou Y, Liu B, Yang R, Liu J (2017) Filling in the gaps between nanozymes and enzymes: challenges and opportunities. Bioconjugate Chem 28:2903–2909
Acknowledgements
AS and SKK gratefully acknowledge DST for the financial assistance and IIT Delhi for providing infrastructure and the required facilities.
Funding
The work was supported by the grant provided by the Department of Science and Technology, India (DST/INT/TUNISIA/P07/2017).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sadaf, A., Ahmad, R., Ghorbal, A. et al. Synthesis of cost-effective magnetic nano-biocomposites mimicking peroxidase activity for remediation of dyes. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27, 27211–27220 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05270-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05270-3