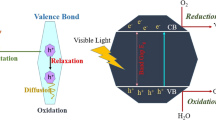
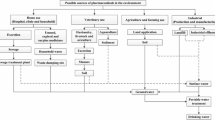
Abstract
The following work provides a perspective on the degradation of cytostatic pollutants through TiO2 heterogeneous photocatalysis. Cytostatic drugs are emerging pollutants used for cancer treatment found in hospital and domestic wastewater. Small amounts of cytostatic pollutants may pose severe health problems in human beings, animals, and plants after prolonged contact. This research presents a general review of some water treatment methods, such as aerobic activated sludge, enzymatic degradation, nanofiltration and chlorination, that have been used for the degradation or elimination of cytostatic drugs in wastewater. In recent years, photocatalysis has become important to solve this problem; these advanced oxidation process uses pure and modified TiO2 to degrade cytostatic contaminants and convert them into non-harmful substances or to eliminate them completely. This work contains a comprehensive review of the heterogeneous photocatalysis process and mechanism, and its application on the removal of cytostatic pollutants. Even if research on the topic is still scarce, this literature review provides interesting highlights on the scope of the research field, and the path such research could follow.

Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Adityosulindro S, Barthe L, González-Labrada K, Jáuregui-Haza UJ, Julcour C (2017) Sonolysis and sono-Fenton oxidation for removal of ibuprofen in (waste)water. Ultrason Sonochem 39:889–896. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2017.06.008
Ahmadpour N, Sayadi MH, Sobhani S, Hajiani M (2020) Photocatalytic degradation of model pharmaceutical pollutant by novel magnetic TiO2@ZnFe2O4/Pd nanocomposite with enhanced photocatalytic activity and stability under solar light irradiation. J Environ Manage 271:110964. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.110964
Ahmed S, Rasul MG, Brown R, Hashib MA (2011) Influence of parameters on the heterogeneous photocatalytic degradation of pesticides and phenolic contaminants in wastewater: a short review. J Environ Manage 92:311–330. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2010.08.028
Ahmed SN, Haider W (2018) Heterogeneous photocatalysis and its potential applications in water and wastewater treatment: a review. Nanotechnology 29:342001. https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6528/aac6ea
Alharbi SK, Price WE, Kang J, Fujioka T, Nghiem LD (2016) Ozonation of carbamazepine, diclofenac, sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim and formation of major oxidation products. Desalin Water Treat 57:29340–29351. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2016.1172986
Aliofkhazraei M, Ali N (2014) 70.4 - PVD Technology in Fabrication of Micro- and Nanostructured Coatings. Elsevier, Netherlands. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-08-096532-1.00705-6
Almomani F, Bhosale R, Kumar A, Khraisheh M (2018) Potential use of solar photocatalytic oxidation in removing emerging pharmaceuticals from wastewater: a pilot plant study. Sol Energy 172:128–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solener.2018.07.041
Almomani FA, Shawaqfah M, Bhosale RR, Kumar A (2016) Removal of emerging pharmaceuticals from wastewater by ozone-based advanced oxidation processes. Environ Prog Sustain Energy 35:982–995. https://doi.org/10.1002/ep.12306
Alotaibi A, Sathasivam S, Williamson B, Kafizas A, Sotelo-Vázquez C, Taylor A, Scanlon D, Parkin I (2018) Chemical vapor deposition of photocatalytically active pure Brookite TiO2 thin films. Chem Mater 30:1353–1361. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemmater.7b04944
Alotaibi A, Williamson B, Sathasivam S, Kafizas A, Alqahtani M, Sotelo-Vázquez C, Buckeridge J, Wu J, Nair S, Scanlon D, Parkin I (2020) Enhanced photocatalytic and antibacterial ability of Cu – doped Anatase TiO2 thin films: Theory and experiment. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 12:15348–15361. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.9b22056
Arcanjo GS, Mounteer AH, Bellato CR, Silva LMMD, Brant-Dias SH, Silva PRD (2018) Heterogeneous photocatalysis using TiO2 modified with hydrotalcite and iron oxide under UV–visible irradiation for color and toxicity reduction in secondary textile mill effluent. J Environ Manage 211:154–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2018.01.033
Asghar A, Raman AAA, Daud WMAW (2015) Advanced oxidation processes for in-situ production of hydrogen peroxide/hydroxyl radical for textile wastewater treatment: a review. J Clean Prod 87:826–838. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2014.09.010
Augugliaro V, Bellardita M, Loddo V, Palmisano G, Palmisano L, Yurdakal S (2012) Overview on oxidation mechanisms of organic compounds by TiO2 in heterogeneous photocatalysis. J Photochem Photobiol C 13:224–245. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotochemrev.2012.04.003
Avei A, Eker A, Eker B (2018) Chapter 3.5 - Microstructure and oxidation behavior of atmospheric plasma-sprayed thermal barrier coatings. In: Press Academic (ed) Exergetic, Energetic and Environmental Dimensions. Elsevier, Netherlands, pp 793–814. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-813734-5.00045-7
Aziz NAA, Palaniandy P, Aziz HA, Dahlan I (2016) Review of the mechanism and operational factors influencing the degradation process of contaminants in heterogenous photocatalysis. J Chem Res 40:704–712. https://doi.org/10.3184/174751916X14769685673665
Baba Y, Yatagai T, Harada T, Kawase Y (2015) Hydroxyl radical generation in the photo-Fenton process: effects of carboxylic acids on iron redox cycling. Chem Eng J 277:229–241. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2015.04.103
Babuponnusami A, Muthukumar K (2014) A review on Fenton and improvements to the Fenton process for wastewater treatment. J Environ Chem Eng 2:557–572. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2013.10.011
Baeza C, Knappe DRU (2011) Transformation kinetics of biochemically active compounds in low-pressure UV Photolysis and UV/H2O2 advanced oxidation processes. Water Res 45:4531–4543. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2011.05.039
Barrientos L, Allende P, Laguna-Bercero M, Pastrián J, Rodríguez-Becerra J, Cáceres-Jensen L (2018) Controlled Ag-TiO2 heterojunction obtained by combining physical vapor deposition and bifunctional surface modifiers. J Phys Chem Solids 119:147–156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpcs.2018.03.046
Bernabeu A, Vercher RF, Santos-Juanes L, Simón PJ, Lardín C, Martínez MA, Vicente JA, González R, Llosá C, Arques A, Amat AM (2011) Solar photocatalysis as a tertiary treatment to remove emerging pollutants from wastewater treatment plant effluents. Catal Today 161:235–240. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cattod.2010.09.025
Bokare AD, Choi W (2014) Review of iron-free Fenton-like systems for activating H2O2 in advanced oxidation processes. J Hazard Mater 275:121–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2014.04.054
Bouanimba N, Zouaghi R, Laid N, Sehili T (2011) Factors influencing the photocatalytic decolorization of bromophenol blue in aqueous solution with different types of TiO2 as photocatalysts. Desalination 275:224–230. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2011.03.005
Byun J, Zhang KAI (2020) Designing conjugated porous polymers for visible light-driven photocatalytic chemical transformations. Mater Horiz 7:15–31. https://doi.org/10.1039/C9MH01071H
Calza P, Medana C, Sarro M, Rosato V, Aigotti R, Baiocchi C, Minero C (2014) Photocatalytic degradation of selected anticancer drugs and identification of their transformation products in water by liquid chromatography–high resolution mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 1362:135–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2014.08.035
Cao M, Wang P, Ao Y, Wang C, Hou J, Qian J (2015) Photocatalytic degradation of tetrabromobisphenol A by a magnetically separable graphene–TiO2 composite photocatalyst: mechanism and intermediates analysis. Chem Eng Sci 264:113–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2014.10.011
Carvalho H, Batista A, Hammer P, Ramalho T (2010) Photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue by TiO2 – Cu thin films: theoretical and experimental study. J Hazard Mater 184:273–280. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.08.033
Castellet-Rovira F, Lucas D, Villagrasa M, Rodríguez-Mozaz S, Barceló D, Sarrà M (2018) Stropharia rugosoannulata and Gymnopilus luteofolius: promising fungal species for pharmaceutical biodegradation in contaminated water. J Environ Manage 207:396–404. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2017.07.052
Cheshme-Khavar AH, Moussavi G, Mahjoub AR (2018) The preparation of TiO2@rGO nanocomposite efficiently activated with UVA/LED and H2O2 for high rate oxidation of acetaminophen: catalyst characterization and acetaminophen degradation and mineralization. Appl Surf Sci 440:963–973. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.01.238
Constantin LA, Constantin MA, Nitoi I, Chiriac FL, Galaon T, Cristea NI (2018) Possible pathway for ifosfamide degradation via Fe-TiO2 assisted photo catalysis. Rev Chim 69:3234–3237. https://doi.org/10.37358/RC.18.11.6720
Cristea IN, Sobetkii A, Constantin LA, Constantin MA, Nitoi I (2020) Ag-TiO2 assisted photocatalytic degradation of cytostatic drug cyclophosphamide under UV-VIS light. Rev Chim 71:347–355. https://doi.org/10.37358/RC.20.4.8074
Cristóvão MB, Janssens R, Yadav A, Pandey S, Luis P, Van der Bruggen B, Dubey KK, Mandal MK, Crespo JG, Pereira VJ (2020) Predicted concentrations of anticancer drugs in the aquatic environment: what should we monitor and where should we treat? J Hazard Mater 392:122330. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122330
Cristóvão MB, Torrejais J, Janssens R, Luis P, Van der Bruggen B, Dubey KK, Mandal MK, Bronze MR, Crespo JG, Pereira VJ (2019) Treatment of anticancer drugs in hospital and wastewater effluents using nanofiltration. Sep Purif Technol 224:273–280. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2019.05.016
Daghrir R, Drogui P, Robert D (2013) Modified TiO2 for environmental photocatalytic applications: a review. Ind Eng Chem Res 52:3581–3599. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie303468t
De Greef N, Zhang L, Magrez A, Forró L, Loquet J, Verpoest I, Seo J (2015) Direct growth of carbon nanotubes on carbon fibers: effect of CVD parameters on the degradation of mechanical properties of carbon fibers. Diam Relat Mater 51:39–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diamond.2014.11.002
De Oliveira KM, Serrano SV, Santos-Neto Á, da Cruz C, Brunetti IA, Lebre D, Gimenez MP, Reis RM, Silveira HCS (2021) Detection of anti-cancer drugs and metabolites in the effluents from a large Brazilian cancer hospital and an evaluation of ecotoxicology. Environ Pollut 268:115857. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.115857
Delgado LF, Faucet-Marquis V, Pfohl-Leszkowicz A, Dorandeu C, Marion B, Schetrite S, Albasi C (2011) Cytotoxicity micropollutant removal in a crossflow membrane bioreactor. Bioresour Technol 102:4395–4401. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2010.12.107
Dimpe KM, Nomngongo PN (2016) Current sample preparation methodologies for analysis of emerging pollutants in different environmental matrices. Trends Anal Chem 82:199–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2016.05.023
DrugBank – Capecitabine. https://go.drugbank.com/drugs/DB01101 Accessed Jan 11 2021
DrugBank – Cyclophosphamide. https://go.drugbank.com/drugs/DB00531 Accessed Jan 1 2021
DrugBank – Cytarabine. https://go.drugbank.com/drugs/DB00987 Accessed Jan 11 2021
DrugBank – Fluorouracil. https://go.drugbank.com/drugs/DB00544 Accessed Jan 11 2021
DrugBank – Gemcitabine. https://go.drugbank.com/drugs/DB00441 Accessed Jan 11 2021
DrugBank – Ifosfamide. https://go.drugbank.com/drugs/DB01181 Accessed Jan 11 2021
DrugBank – Irinotecan. https://go.drugbank.com/drugs/DB00762 Accessed Jan 11 2021
DrugBank – Methotrexate. https://go.drugbank.com/drugs/DB00563 Accessed Jan 11 2021
DrugBank – Tamoxifen. https://go.drugbank.com/drugs/DB00675 Accessed Jan 11 2021
Ebrahiem EE, Al-Maghrabi MN, Mobarki AR (2017) Removal of organic pollutants from industrial wastewater by applying photo-Fenton oxidation technology. Arab J Chem 10:S1674–S1679. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2013.06.012
Elmolla ES, Chaudhuri M (2010) Photocatalytic degradation of amoxicillin, ampicillin and cloxacillin antibiotics in aqueous solution using UV/TiO2 and UV/H2O2/TiO2 photocatalysis. Desalination 252:46–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2009.11.003
Evgenidou E, Ofrydopoulou A, Malesic-Eleftheriadou N, Nannou C, Ainali NM, Christodoulou E, Bikiaris DN, Kyzas GZ, Lambropoulou DA (2020) New insights into transformation pathways of a mixture of cytostatic drugs using polyester-TiO2 films: identification of intermediates and toxicity assessment. Sci Total Environ 741:140394. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.140394
Farahi G, Kim H, Kashi H (2018) Introduction. In: Elsevier (ed) Severe Plastic deformation. Elsevier, Netherlands, pp 1–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-813518-1.00020-5
Ferrando-Climent L, Cruz-Morató C, Marco-Urrea E, Vicent T, Sarrà M, Rodriguez-Mozaz S, Barceló D (2015) Non conventional biological treatment based on Trametes versicolor for the elimination of recalcitrant anticancer drugs in hospital wastewater. Chemosphere 136:9–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.03.051
Finčur NL, Krstić JB, Šibul FS, Šojić DV, Despotović VN, Banić ND, Agbaba JR, Abramović BF (2017) Removal of alprazolam from aqueous solutions by heterogeneous photocatalysis: influencing factors, intermediates, and products. Chem Eng J 307:1105–1115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.09.008
Fiszka Borzyszkowska A, Pieczyńska A, Ofiarska A, Stepnowski P, Siedlecka EM (2016) Bi-B-TiO2-based photocatalytic decomposition of cytostatic drugs under simulated sunlight treatments. Sep Purif Technol 169:113–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2016.06.012
Fouda A (2020) Influence of deposition temperature on the structural and dispersion parameters of TiO2 thin films. Appl Phys A 126:48. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-019-3226-0
Franquet-Griell H, Medina A, Sans C, Lacorte S (2017) Biological and photochemical degradation of cytostatic drugs under laboratory conditions. J Hazard Mater 323:319–328. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.06.057
Gajski G, Gerić M, Žegura B, Novak M, Nunić J, Bajrektarević D, Garaj-Vrhovac V, Filipič M (2016) Genotoxic potential of selected cytostatic drugs in human and zebrafish cells. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:14739–14750. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4592-6
Gar Alalm M, Tawfik A, Ookawara S (2015) Degradation of four pharmaceuticals by solar photo-Fenton process: kinetics and costs estimation. J Environ Chem Eng 3:46–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2014.12.009
Garrido-Cardenas JA, Esteban-García B, Agüera A, Sánchez-Pérez JA, Manzano-Agugliaro F (2020) Wastewater treatment by advanced oxidation process and their worldwide research trends. Int J Environ Res Public Health 17:170. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17010170
Gavrilescu M, Demnerová K, Aamand J, Agathos S, Fava F (2015) Emerging pollutants in the environment: present and future challenges in biomonitoring, ecological risks and bioremediation. New Biotechnol 32:147–156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbt.2014.01.001
Geissen V, Mol H, Klumpp E, Umlauf G, Nadal M, van der Ploeg M, van de Zee SEATM, Ritsema CJ (2015) Emerging pollutants in the environment: a challenge for water resource management. Int Soil Water Conserv Res 3:57–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iswcr.2015.03.002
González-Burciaga LA, Núñez-Núñez CM, Morones-Esquivel MM, Avila-Santos M, Lemus-Santana A, Proal-Nájera JB (2020) Characterization and comparative performance of TiO2 photocatalysts on 6-mercaptopurine degradation by solar heterogeneous photocatalysis. Catalysts 10:118. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10010118
Gouveia TIA, Silva AMT, Ribeiro AR, Alves A, Santos MSF (2020) Liquid-liquid extraction as a simple tool to quickly quantify fourteen cytostatics in urban wastewaters and access their impact in aquatic biota. Sci Total Environ 740:139995. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.139995
Guo F, Liu J, Zhang W, Yu Z, Liu Y, Liang W (2019) Synthesis of Cu, N – doped TiO2 nanotube by a novel magnetron sputtering method and its photoelectric property. Vacuum 165:223–231. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vacuum.2019.04.032
Güyer GT, Ince NH (2011) Degradation of diclofenac in water by homogeneous and heterogeneous sonolysis. Ultrason Sonochem 18:114–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2010.03.008
Haroune L, Salaun M, Ménard A, Legault CY, Bellenger J-P (2014) Photocatalytic degradation of carbamazepine and three derivatives using TiO2 and ZnO: effect of pH, ionic strength, and natural organic matter. Sci Total Environ 475:16–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.12.104
Hassan I, Parkin I, Nair S, Carmalt C (2014) Antimicrobial activity of copper and copper (I) oxide thin films deposited via aerosol – assisted cvd. J Mater Chem B 2:2855–2860. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4TB00196F
Hassan M, Zhao Y, Xie B (2016) Employing TiO2 photocatalysis to deal with landfill leachate: current status and development. Chem Eng J 285:264–275. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2015.09.093
Xiao Hong (2012) Chemical Vapor Deposition and Dielectric Thin Films. SPIE, USA. https://doi.org/10.1117/3.924283.ch10
Horikoshi S, Serpone N (2020) Can the photocatalyst TiO2 be incorporated into a wastewater treatment method? Background and prospects. Catal Today 340:334–346. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cattod.2018.10.020
Hu D, Ye C, Wang X, Zhao X, Kang L, Liu J, Duan R, Cao X, He Y, Hu J, Li S, Zeng Q, Deng Y, Yin P, Ariando A, Huang Y, Zhang H, Wang X, Liu Z (2021) Chemical vapor deposition of superconducting FeTe1-xSex nanosheets. ACS Nano Lett 21:5338–5344. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.nanolett.1c01577
Huang H, Yang W, Chen X, Wu Z (2010) Metal semiconductor – metal ultraviolet photo reactors based on TiO2 films deposited by radio – frequency magnetron sputtering. IEEE Electron Device Lett 31:588–590. https://doi.org/10.1109/LED.2010.2045876
Ibhadon AO, Fitzpatrick P (2013) Heterogeneous photocatalysis: recent advances and applications. Catalysts 3:189–218. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal3010189
Iervolino G, Zammit I, Vaiano V, Rizzo L (2020) Limitations and prospects for wastewater treatment by uv and visible-light-active heterogeneous photocatalysis: a critical review. Top Curr Chem 2020:378. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41061-019-0272-1
Ikram M, Hassan J, Raza A, Haider A, Naz S, Ul-Hamid A, Haider J, Shahzadi I, Qamar U, Ali S (2020) Photocatalytical and bactericidal properties and molecular docking analysis of TiO2 nanoparticles conjugated with Zr for environmental remediation. RSC Adv. 10:30007–30024. https://doi.org/10.1039/D0RA05862A
Ince NH (2018) Ultrasound-assisted advanced oxidation processes for water decontamination. Ultrason Sonochem 40:97–103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2017.04.009
Isidori M, Lavorgna M, Russo C, Kundi M, Žegura B, Novak M, Filipič M, Mišík M, Knasmueller S, López de Alda M, Barceló D, Žonja B, Česen M, Ščančar J, Kosjek T, Heath E (2016) Chemical and toxicological characterization of anticancer drugs in hospital and municipal wastewaters from Slovenia and Spain. Environ Pollut 219:275–287. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2016.10.039
Jabra Z, Berbezier I, Michon A, Koudia M, Assaf E, Ronda A, Castrucci P, De Crescenzi M, Vach H, Abel M (2021) Hydrogen – mediated CVD epitaxy of graphene on SIC: implications for microelectronic applications. ACS Appl Nano Mater 4:4462–4473. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsanm.1c00082
Carlsson Jan-Otto, Martin Peter (2010) Chapter 7 - Chemical vapor deposition. In: Andrew William (ed) Handbook of Deposition Technologies for Films and Coatings, 3rd edn. Elsevier, Netherlands, pp 314–363. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-8155-2031-3.00007-7
Javid A, Kumar M, Ashraf M, Lee H, Han J (2019) Photocatalytic antibacterial study of N - doped TiO2 films synthetized by ICP assisted plasma sputtering method. PHYSICA E 106:187–193. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physe.2018.10.034
Karaolia P, Michael-Kordatou I, Hapeshi E, Drosou C, Bertakis Y, Christofilos D, Armatas GS, Sygellou L, Schwartz T, Xekoukoulotakis NP, Fatta-Kassinos D (2018) Removal of antibiotics, antibiotic-resistant bacteria and their associated genes by graphene-based TiO2 composite photocatalysts under solar radiation in urban wastewaters. Appl Catal B 224:810–824. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2017.11.020
Karunakaran C, Vijayabalan A, Manikandan G (2012) Photocatalytic bacteria inactivation by polyethylene glycol-assisted sol–gel synthesized Cd-doped TiO2 under visible light. Res Chem Intermed 39:1437–1446. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11164-012-0700-0
Khan NA, Khan SU, Ahmed S, Farooqi IH, Yousefi M, Mohammadi AA, Changani F (2020) Recent trends in disposal and treatment technologies of emerging-pollutants- a critical review. Trends Anal Chem 122:115744. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2019.115744
Kitsiou V, Zachariadis GA, Lambropoulou DA, Tsiplakides D, Poulios I (2018) Mineralization of the antineoplastic drug carboplatin by heterogeneous photocatalysis with simultaneous synthesis of platinum-modified TiO2 catalysts. J Environ Chem Eng 6:2409–2416. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2018.03.036
Koltsakidou A, Antonopoulou M, Evgenidou E, Konstantinou I, Giannakas AE, Papadaki M, Bikiaris D, Lambropoulou DA (2017a) Photocatalytical removal of fluorouracil using TiO2-P25 and N/S doped TiO2 catalysts: a kinetic and mechanistic study. Sci Total Environ 578:257–267. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.08.208
Koltsakidou Α, Antonopoulou M, Evgenidou E, Konstantinou I, Lambropoulou DA (2017b) Cytarabine degradation by simulated solar assisted photocatalysis using TiO2. Chem Eng J 316:823–831. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.01.132
Kosjek T, Negreira N, Heath E, López de Alda M, Barceló D (2018) Aerobic activated sludge transformation of vincristine and identification of the transformation products. Sci Total Environ 610–611:892–904. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.08.061
Kovalova L, Siegrist H, Singer H, Wittmer A, McArdell CS (2012) Hospital wastewater treatment by membrane bioreactor: performance and efficiency for organic micropollutant elimination. Environ Sci Technol 46:1536–1545. https://doi.org/10.1021/es203495d
Kumar A, Hitkari G, Singh S, Gautam M, Pandey G (2015) Synthesis of Ni-TiO2 Nanocomposites and photocatalytic degradation of oxalic acid in waste water. Int J Innov Res Sci Eng Technol 4:12721–12731. https://doi.org/10.15680/IJIRSET.2015.0412097
Kumar R, Kumar V (2019) Effect of high energy Ti9+ ion beam induced modifications in titanium dioxide and tinoxide nanocomposite thin films and detailed analysis of optical, structural and morphological properties. Opt Mat 88:320–332. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optmat.2018.11.040
Kumar V, Chauhan V, Ram J, Gupta R, Kumar S, Chaudary P, Yadav B, Ojha S, Sulania I, Kumar R (2020) Study of humidity sensing properties and ion beam induced modifications in SnO2 – TiO2 nanocomposite thin films. Surf Coat Technol 392:125768. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2020.125768
Lai WW-P, Hsu M-H, Lin AY-C (2017) The role of bicarbonate anions in methotrexate degradation via UV/TiO2: mechanisms, reactivity and increased toxicity. Water Res 112:157–166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2017.01.040
Lang F, Gluba M, Albrecht S, Rappich J, Korte L, Rech B, Nickel N (2015) Perovskite solar cells with large area CVD – graphene for tandem solar cells. J Phys Chem Lett 6:2745–2750. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpclett.5b01177
Lee HU, Lee SC, Choi SH, Son B, Lee SJ, Kim HJ, Lee J (2013) Highly visible-light active nanoporous TiO2 photocatalysts for efficient solar photocatalytic applications. Appl Catal B 129:106–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2012.09.010
Li C-J, Wang J-N, Wang B, Gong JR, Lin Z (2012) A novel magnetically separable TiO2/CoFe2O4 nanofiber with high photocatalytic activity under UV–vis light. Mater Res Bull 47:333–337. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2011.11.012
Li Z, Khor K (2019) Preparation and properties of coatings and thin films on metal implants. In: Elsevier (ed) Encyclopedia of Biomedical Engineering. Elsevier, Netherlands, pp 203–212. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-801238-3.11025-6
Liang R, Hu A, Li W, Zhou YN (2013) Enhanced degradation of persistent pharmaceuticals found in wastewater treatment effluents using TiO2 nanobelt photocatalysts. J Nanopart Res 15:1990. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-013-1990-x
Lin HH-H, Lin AY-C (2014) Photocatalytic oxidation of 5-fluorouracil and cyclophosphamide via UV/TiO2 in an aqueous environment. Water Res 48:559–568. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2013.10.011
Lin HH-H, Lin AY-C, Hung C-L (2015) Photocatalytic oxidation of cytostatic drugs by microwave-treated N-doped TiO2 under visible light. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 90:1345–1354. https://doi.org/10.1002/jctb.4503
Llewellyn N, Lloyd P, Jürgens MD, Johnson AC (2011) Determination of cyclophosphamide and ifosfamide in sewage effluent by stable isotope-dilution liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 1218:8519–8528. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2011.09.061
Loo R, Arimura H, Cott D, Witters L, Pourtois G, Schulze A, Douhard B, Vanherle W, Eneman G, Richard O, Favia P, Mitard J, Mocuta D, Langer R, Collaert N (2018) Epitaxial CVD growth of ultra – thin Si passivation layers on strained Ge Fin structures. ECS J Solid State Sci Technol 7:66–72. https://doi.org/10.1149/2.0191802jss
Lu H, Fang S, Hu J, Chen B, Zhao R, Li H, Ming C, Ye J (2020) Fabrication of a TiO2/Fe2O3 core/shell nanostructure by pulse laser deposition toward stable and visible light photoelectrochemical water splitting. ACS Omega 5:19861–19867. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.0c02838
Lumbaque EC, Sitori C, Vilar VJP (2020) Heterogeneous photocatalytic degradation of pharmaceuticals in synthetic and real matrices using a tube-in-tube membrane reactor with radial addition of H2O2. Sci Total Environ 743:140629. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.140629
Lutterbeck CA, Baginska E, Machado ÊL, Kümmerer K (2015a) Removal of the anti-cancer drug methotrexate from water by advanced oxidation processes: Aerobic biodegradation and toxicity studies after treatment. Chemosphere 141:290–296. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.07.069
Lutterbeck CA, Machado ÊL, Kümmerer K (2015b) Photodegradation of the antineoplastic cyclophosphamide: a comparative study of the efficiencies of UV/H2O2, UV/Fe2+/H2O2 and UV/TiO2 processes. Chemosphere 120:538–546. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2014.08.076
Lutterbeck CA, Wilde ML, Baginska E, Leder C, Machado ÊL, Kümmerer K (2015c) Degradation of 5-FU by means of advanced (photo)oxidation processes: UV/H2O2, UV/Fe2+/H2O2 and UV/TiO2-comparison of transformation products, ready biodegradability and toxicity. Sci Total Environ 527–528:232–245. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.04.111
Maeng SK, Cho K, Jeong B, Lee J, Lee Y, Lee C, Choi KJ, Hong SW (2015) Substrate-immobilized electrospun TiO2 nanofibers for photocatalytic degradation of pharmaceuticals: the effects of pH and dissolved organic matter characteristics. Water Res 86:25–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2015.05.032
Mahlambi MM, Ngila CJ, Mamba BB (2015) Recent developments in environmental photocatalytic degradation of organic pollutants: the case of titanium dioxide nanoparticles-a review. J Nanomater 2015:29. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/790173
Makhouf ASH (2011) 1 - Current and advanced coating technologies for industrial applications. In: Woodhead (ed) Nanocoatings and Ultra-Thin Films. Elsevier, Netherlands, pp 3–23. https://doi.org/10.1533/9780857094902.1.3
Martín J, Camacho-Muñoz D, Santos JL, Aparicio I, Alonso E (2011) Simultaneous determination of a selected group of cytostatic drugs in water using high-performance liquid chromatography–triple-quadrupole mass spectrometry. J Sep Sci 34:3166–3177. https://doi.org/10.1002/jssc.201100461
Martínez C, Canle M, Fernández MI, Santaballa JA, Faria J (2011) Kinetics and mechanism of aqueous degradation of carbamazepine by heterogeneous photocatalysis using nanocrystalline TiO2, ZnO and multi-walled carbon nanotubes–anatase composites. Appl Catal B 102:563–571. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2010.12.039
Martín-Lancharro P, De Castro-Acuña N, González-Barcala FJ, Moure-González JD (2016) Evidence of exposure to cytostatic drugs in healthcare staff: a review of recent literature. Farm Hosp 40:604–621. https://doi.org/10.7399/fh.2016.40.6.9103
Merisalu M, Kahro T, Kozlova J, Niilisk A, Nikolajev A, Marandi M, Floren A, Alles H, Sammelselg V (2015) Graphene – polypyrrole thin hybrid corrosion resistant coatings for copper. Synth Met 200:16–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.synthmet.2014.12.024
Miklos DB, Remy C, Jekel M, Linden KG, Drewes JE, Hübner U (2018) Evaluation of advanced oxidation processes for water and wastewater treatment – a critical review. Water Res 139:119–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2018.03.042
Molinari R, Caruso A, Argurio P, Poerio T (2008) Degradation of the drugs Gemfibrozil and Tamoxifen in pressurized and de-pressurized membrane photoreactors using suspended polycrystalline TiO2 as catalyst. J Membr Sci 319:54–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2008.03.033
Moreira NFF, Narciso-da-Rocha C, Polo-López MI, Pastrana-Martínez LM, Faria JL, Manaia CM, Fernández-Ibáñez P, Nunes OC, Silva AMT (2018) Solar treatment (H2O2, TiO2-P25 and GO-TiO2 photocatalysis, photo-Fenton) of organic micropollutants, human pathogen indicators, antibiotic resistant bacteria and related genes in urban wastewater. Water Res 135:195–206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2018.01.064
Moretti E, Cattaruzza E, Flora C, Talon A, Casini E, Vomiero A (2021) Photocatalytic performance of Cu – doped titania thin films under UV light irradiation. App Surf Sci 553:149535. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2021.149535
Mukherjee S, Mehta D, Dhangar K, Kumar M (2021) Environmental fate, distribution and state-of-the-art removal of antineoplastic drugs: a comprehensive insight. Chem Eng J 407:127184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.127184
Murcia JJ, Ávila-Martínez EG, Rojas H, Navío JA, Hidalgo MC (2017) Study of the E. coli elimination from urban wastewater over photocatalysts based on metallized TiO2. Appl Catal B 200:469–476. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2016.07.045
Nadimi M, Ziarati Saravani A, Aroon MA, Ebrahimian Pirbazari A (2019) Photodegradation of methylene blue by a ternary magnetic TiO2/Fe3O4/graphene oxide nanocomposite under visible light. Mater Chem Phys 225:464–474. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2018.11.029
Negreira N, Regueiro J, López de Alda M, Barceló D (2015) Degradation of the anticancer drug erlotinib during water chlorination: non-targeted approach for the identification of transformation products. Water Res 85:103–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2015.08.005
Nipane SV, Lee SW, Gokavi GS, Kadam AN (2018) In situ one pot synthesis of nanoscale TiO2-anchored reduced graphene oxide (RGO) for improved photodegradation of 5-fluorouracil drug. J Mater Sci Mater Electron 29:16553–16564. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-018-9749-x
Noh M, Arzaee N, Safaei J, Mohamed N, Kim H, Yussoff A, Jang J, Teridi M (2019) Eliminating oxygen vacancies in SiO2 films via aerosol – assisted chemical vapor deposition for perovskite solar cells and photoelectrochemical cells. J Alloys Compd 773:997–1008. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.09.273
Nosaka Y, Nosaka AY (2017) Generation and detection of reactive oxygen species in photocatalysis. Chem Rev 117:11302–11336. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrev.7b00161
Núñez-Núñez CM, Chairez-Hernández I, García-Roig M, García-Prieto JC, Melgoza-Alemán RM, Proal-Nájera JP (2018) UV-C/H2O2 heterogeneous photocatalytic inactivation of coliforms in municipal wastewater in a TiO2/SiO2 fixed bed reactor: a kinetic and statistical approach. React Kinet Mech Catal 125:1159–1177. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal3010189
Ofiarska A, Pieczyńska A, Fiszka Borzyszkowska A, Stepnowski P, Siedlecka EM (2016) Pt–TiO2-assisted photocatalytic degradation of the cytostatic drugs ifosfamide and cyclophosphamide under artificial sunlight. Chem Eng J 285:417–427. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2015.09.109
Olalla A, Negreira N, López de Alda M, Barceló D, Valcárcel Y (2018) A case study to identify priority cytostatic contaminants in hospital effluents. Chemosphere 190:417–430. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.09.129
Pablos C, Marugán J, Grieken RV, Serrano E (2013) Emerging micropollutant oxidation during disinfection processes using UV-C, UV-C/H2O2, UV-A/TiO2 and UV-A/TiO2/H2O2. Water Res 47:1237–1245. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2012.11.041
Pałaszewska-Tkacz A, Czerczak S, Konieczko K, Kupczewska-Dobecka M (2019) Cytostatics as hazardous chemicals in healthcare workers’ environment. Int J Occup Med Environ Health 32:141–159. https://doi.org/10.13075/ijomeh.1896.01248
Pantoja-Espinoza JC, Proal-Nájera JB, García-Roig M, Cháirez-Hernández I, Osorio-Revilla GI (2015) Comparative efficiencies of inactivation of coliform bacteria in municipal effluents by photolysis (UV) and by photocatalysis (UV/TiO2/SiO2). Case: Salamanca water treatment plant. Spain Rev Mex Ing Quím 14:119–135 (in Spanish)
Papageorgiou M, Zioris I, Danis T, Bikiaris D, Lambropoulou D (2019) Comprehensive investigation of a wide range of pharmaceuticals and personal care products in urban and hospital wastewaters in Greece. Sci Total Environ 694:133565. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.07.371
Pattanaik P, Sahoo MK (2014) TiO2 photocatalysis: progress from fundamentals to modification technology. Desalination Water Treat 52:6567–6590. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2013.822187
Pazoki M, Parsa M, Farhadpour R (2016) Removal of the hormones dexamethasone (DXM) by Ag doped on TiO2 photocatalysis. J Environ Chem Eng 4:4426–4434. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2016.09.034
Pedroza-Herrera G, Medina-Ramírez IE, Lozano-Álvarez JA, Rodil SE (2018) Evaluation of the photocatalytic activity of copper doped TiO2 nanoparticles for the purification and/or disinfection of industrial effluents. Catal Today 341:37–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cattod.2018.09.017
Peña-Guzmán C, Ulloa-Sánchez S, Mora K, Helena-Bustos R, López-Barrera E, Alvarez J, Rodriguez-Pinzón M (2019) Emerging pollutants in the urban water cycle in Latin America: a review of the current literature. J Environ Manage 237:408–423. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.02.100
Pereira CS, Kelbert M, Daronch NA, Michels C, de Oliveira D, Soares HM (2020) Potential of enzymatic process as an innovative technology to remove anticancer drugs in wastewater. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 104:23–31. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-019-10229-y
Potter D, Bhachu D, Powell M, Darr J, Parkin I, Carmalt C (2016) Al-, Ga-, and In – doped ZnO thin films via aerosol assisted CVD for use as transparent conducting oxides. Phys Status Solidi A 213:1346–1352. https://doi.org/10.1002/pssa.201532996
Pradhan SR, Nair V, Giannakoudakis DA, Lisovytskiy D, Colmenares JC (2020) Design and development of TiO2 coated microflow reactor for photocatalytic partial oxidation of benzyl alcohol. Mol Catal 486:110884. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mcat.2020.110884
Pu J, Tang L, Li C, Li T, Ling L, Zhang K, Li Q, Yao Y (2015) Chemical vapor deposition growth of few – layer graphene for transparent conductive films. RSC Adv 5:44142–44148. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5RA03919C
Quesada HB, Baptista ATA, Cusioli LF, Seibert D, de Oliveira BC, Bergamasco R (2019) Surface water pollution by pharmaceuticals and an alternative of removal by low-cost adsorbents: a review. Chemosphere 222:766–780. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.02.009
Rane A, Kanny K, Abitha V, Thomas S (2018) Chapter 5 - Methods for synthesis of nanoparticles and fabrication of nanocomposites. In: Woodhead (ed) Micro and Nano Technologies, Synthesis of Inorganic Nanomaterials. Elsevier, Netherlands, pp 121–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-08-101975-7.00005-1
Rivera-Utrilla J, Sánchez-Polo M, Ferro-García MA, Prados-Joya G, Ocampo-Pérez R (2013) Pharmaceuticals as emerging contaminants and their removal from water. A Review Chemosphere 93:1268–1287. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.07.059
Sacco O, Vaiano V, Rizzo L, Sannino D (2018) Photocatalytic activity of a visible light active structured photocatalyst developed for municipal wastewater treatment. J Clean Prod 175:38–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.11.088
Samélor D, Turgambaeva A, Krisyuk V, Miquelot A, Cure J, Sysoev S, Trubin S, Stabnikov P, Esvan J, Constandoudis V, Vahlas C (2021) Engineering structure and functionalities of chemical vapor deposited photocatalytic titanium dioxide films through different types of precursors. Crys Eng Comm 23:3681–3692. https://doi.org/10.1039/D1CE00081K
Sangpour P, Hashemi F, Moshfegh A (2010) Photoenhanced degradation of methylene blue on cosputtered M:TiO2 (M=Au, Ag, Cu) nanocomposite systems: a comparative study. J Phys Chem C 114:13955–13961. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp910454r
Santana-Viera S, Montesdeoca-Esponda S, Sosa-Ferrera Z, Santana-Rodríguez JJ (2016) Cytostatic drugs in environmental samples: an update on the extraction and determination procedures. Trends Anal Chem 80:373–386. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2015.08.016
Saravani AZMN, Aroon MA, Pirbazari AE (2019) Magnetic TiO2/NiFe2O4/reduced graphene oxide nanocomposite as a recyclable photocatalyst for photocatalytic removal of methylene blue under visible light. J Alloys Compd 803:291–306. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.06.245
Sarkar M, Mondal A, Choudhuri B (2016) Presence of capacitive memory in Indium doped TiO2 alloy thin film. J Alloys Compd 654:529–533. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2015.09.129
Sarkar S, Das R, Choi H, Bhattacharjee C (2014) Involvement of process parameters and various modes of application of TiO2 nanoparticles in heterogeneous photocatalysis of pharmaceutical wastes – a short review. RSC Adv 4:57250–57266. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4RA09582K
Sedov V, Martyanov A, Altakhov A, Popovich A, Shevchenko M, Savin S, Zavedeev E, Zanaveskin M, Sinogeykin A, Ralchenko V, Konov V (2020) Effect of substrate holder design on stress and uniformity of large – area polycrystalline diamond films grown by microwave plasma – assisted CVD. Coatings 10:939. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings10100939
Seira J, Sablayrolles C, Montréjaud-Vignoles M, Albasi C, Joannis-Cassan C (2016) Elimination of an anticancer drug (cyclophosphamide) by a membrane bioreactor: Comprehensive study of mechanisms. Biochem Eng J 114:155–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bej.2016.07.001
Shang S, Zeng W (2013) 4 - Conductive nanofibres and nanocoatings for smart textiles. In: Woodhead (ed) Multidisciplinary know-how for smart-textiles developers. Elsevier, Netherlands, pp 92–128. https://doi.org/10.1533/9780857093530.1.92
Shih Y-J, Su C-C, Chen C-W, Dong C-D (2015) Synthesis of magnetically recoverable ferrite (MFe2O4, MCo, Ni and Fe)-supported TiO2 photocatalysts for decolorization of methylene blue. Catal Commun 72:127–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catcom.2015.09.017
Shinde SS, Bhosale CH, Rajpure KY (2013) Kinetic Analysis of Heterogeneous Photocatalysis: Role of Hydroxyl Radicals. Catal Rev 55:79–133. https://doi.org/10.1080/01614940.2012.734202
Singh J, Khan S, Shah J, Kotnala R, Mohapatra S (2017) Nanostructured TiO2 thin films prepared by RF magnetron sputtering for photocatalytic applications. Appl Surf Sc 422:953–961. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.06.068
Sirés I, Brillas E, Oturan MA, Rodrigo MA, Panizza M (2014) Electrochemical advanced oxidation processes: today and tomorrow. a review. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21:8336–8367. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-2783-1
Suwannaruang T, Kidkhunthod P, Chanlek N, Soontaranon S, Wantala K (2019) High anatase purity of nitrogen-doped TiO2 nanorice particles for the photocatalytic treatment activity of pharmaceutical wastewater. Appl Surf Sci 478:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.01.158
Talwar S, Verma AK, Sangal VK (2021) Synergistic degradation employing photocatalysis and photo-Fenton process of real industrial pharmaceutical effluent utilizing the Iron-Titanium dioxide composite. Process Saf Environ Prot 146:564–576. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2020.11.029
Tayade RJ, Surolia PK, Kulkarni RG, Jasra RV (2007) Photocatalytic degradation of dyes and organic contaminants in water using nanocrystalline anatase and rutile TiO2. Sci Technol Adv Mater 8:455–462. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.stam.2007.05.006
Teodosiu C, Gilca AF, Barjoveanu G, Fiore S (2018) Emerging pollutants removal through advanced drinking water treatment: a review on processes and environmental performances assessment. J Clean Prod 197:1210–1221. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.06.247
Thapa R, Maiti S, Rana T, Maiti U, Chattopadhyay K (2012) Anatase TiO2 nanoparticles synthesis via simple hydrothermal route: degradation of orange II, methyl orange and rhodamine B. J Mol Catal A Chem 363:223–229. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcata.2012.06.013
Tobajas M, Belver C, Rodríguez JJ (2017) Degradation of emerging pollutants in water under solar irradiation using novel TiO2-ZnO/clay nanoarchitectures. Chem Eng J 309:596–606. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.10.002
Vandreuil MA, Vo Duy S, Munoz G, Furtos A, Sauvé S (2020) A framework for the analysis of polar anticancer drugs in wastewater: On-line extraction coupled to HILIC or reverse phase LC-MS/MS. Talanta 220:121407. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2020.121407
Verlicchi P, Al Aukidy M, Galletti A, Petrovic M, Barceló D (2012) Hospital effluent: investigation of the concentrations and distribution of pharmaceuticals and environmental. risk assessment. Sci Total Environ 430:109–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2012.04.055
Wang J, Wang S (2016) Removal of pharmaceuticals and personal care products (PPCPs) from wastewater: a review. J Environ Manage 182:620–640. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2016.07.049
Wang J, Wang S (2020) Reactive species in advanced oxidation processes: formation, identification and reaction mechanism. Chem Eng J 401:126158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.126158
Wang W, Yangues-Gil A, Yang Y (2014) Chemical vapor deposition of TiO2 thin films from a new halogen free precursor. J Vac Sci Technol A 32:061502. https://doi.org/10.1116/1.4894454
Wang X, Lim T-T (2010) Solvothermal synthesis of C-N codoped TiO2 and photocatalytic evaluation for bisphenol A degradation using a visible-light irradiated LED photoreactor. Appl Catal B 100:355–364. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2010.08.012
Wu X-P, Choudhuri I, Truhlar DG (2019) Computational Studies of photocatalysis with metal–organic frameworks. Energy Environ Mater 2:251–263. https://doi.org/10.1002/eem2.12051
Xekoukoulotakis NP, Drosou C, Brebou C, Chatzisymeon E, Hapeshi E, Fatta-Kassinos D, Mantzavinos D (2011) Kinetics of UV-A/TiO2 photocatalytic degradation and mineralization of the antibiotic sulfamethoxazole in aqueous matrices. Catalysis 161:163–168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cattod.2010.09.027
Xiang Q, Yu J, Wong PK (2011) Quantitative characterization of hydroxyl radicals produced by various photocatalysts. J Colloid Interface Sci 357:163–167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2011.01.093
Yang S, Wang P, Yang X, Wei G, Zhang W, Shan L (2009) A novel advanced oxidation process to degrade organic pollutants in wastewater: microwave-activated persulfate oxidation. J Environ Sci 21:1175–1180. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1001-0742(08)62399-2
Yang Y, Ok YS, Kim KH, Kwon EE, Tsang YF (2017) Occurrences and removal of pharmaceuticals and personal care products (PPCPs) in drinking water and water/sewage treatment plants: a review. Sci Total Environ 596–597:303–320. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.04.102
Yasmina M, Mourad K, Mohammed SH, Khaoula C (2014) Treatment heterogeneous photocatalysis; factors influencing the photocatalytic degradation by TiO2. Energy Procedia 50:559–566. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egypro.2014.06.068
Yin J, Shao B, Zhang J, Li K (2010) A preliminary study on the occurrence of cytostatic drugs in hospital effluents in Beijing, China. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 84:39–45. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-009-9884-4
Younis SA, Kim K-H (2020) Heterogeneous photocatalysis scalability for environmental remediation: opportunities and challenges. Catalysts 10:1109. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10101109
Yu D, Bai J, Liang H, Wang J, Li C (2015) Fabrication of a novel visible-light-driven photocatalyst Ag-AgI-TiO2 nanoparticles supported on carbon nanofibers. Appl Surf Sci 349:241–250. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2015.05.019
Zhang J, Zhou P, Liu J, Yu J (2014) New understanding of the difference of photocatalytic activity among anatase, rutile and brookite TiO2. Phys Chem Chem Phys 16:20382–20386. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4CP02201G
Zhang L, Hu X, Wang C, Tai Y (2018) Water-dispersible and recyclable magnetic TiO2/graphene nanocomposites in wastewater treatment. Mater Lett 231:80–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2018.08.011
Zhang M, Dong H, Zhao L, Wang D, Meng D (2019) A review on Fenton process for organic wastewater treatment based on optimization perspective. Sci Total Environ 670:110–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.03.180
Zhang W, Li Y, Wang C, Wang P (2011) Kinetics of heterogeneous photocatalytic degradation of rhodamine B by TiO2-coated activated carbon: Roles of TiO2 content and light intensity. Desalination 266:40–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2010.07.066
Zhao Z, Sun J, Zhang G, Bai L (2015) The study of microstructure, optical and photocatalytic properties of nanoparticles (NPs) – Cu/TiO2 films deposited by magnetron sputtering. J Alloys Compd 652:307–312. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2015.08.117
Zúñiga-Benítez H, Peñuela GA (2016) Methylparaben removal using heterogeneous photocatalysis: effect of operational parameters and mineralization/biodegradability studies. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:6022–6030. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6468-9
Acknowledgements
A sincere gratitude is extended to the Consejo Nacional de Ciencia y Tecnología (CONACyT) for the scholarship provided for the first author’s PhD program in Sciences in Biotechnology, as well as to the Instituto Politécnico Nacional for the support, through Project SIP: 20210507.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Luis A. González-Burciaga performed the literature search, data analysis, and drafted the article. Cynthia M. Núñez-Núñez analyzed the work critically and checked the spelling and grammar of the English language and José B. Proal-Nájera had the idea, proposed the structure of the article, and analyzed the work critically. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
All authors have consented the manuscript content for publication.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Sami Rtimi
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
González-Burciaga, L.A., Núñez-Núñez, C.M. & Proal-Nájera, J.B. Challenges of TiO2 heterogeneous photocatalysis on cytostatic compounds degradation: state of the art. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 42251–42274 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-17241-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-17241-8