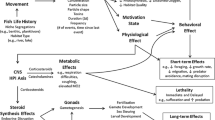
Abstract
Purpose
Sediments serve as integral and dynamic parts of our aquatic systems. Within the last 15 to 20 years, however, the scientific community has begun noticing deterioration of sediment quality at an alarming rate worldwide. Sediments are now harboring hazardous pollutants that can directly influence water quality, thereby creating very stressful conditions for aquatic life. As a consequence, global efforts were initiated in the early 1970s, to find ways to assess sediment quality. Because of their obvious ecological and economic significance, fish have remained a major taxonomic group for appraising the general quality of aquatic systems. However, for sediment risk assessment, fish have lagged behind invertebrates due to their mobility and generally, pelagic lifestyle. To our knowledge, this is the first paper that comprehensively presents and reviews the versatile role of fish in assessing the state of health of aquatic sediments.
Main features
Through a literature search of the more relevant and/or more recent studies, this review attempted to trace the development of the various approaches as well as to describe the future prospects of using fish as sentinels for sediment quality assessment. Initially, the use of whole fish (juveniles or adults) bioassays contributed immensely to our understanding of sediment contamination and ecotoxicology. But due to economic as well as ethical issues linked to the use of live vertebrates for toxicity testing, the approach has shifted to using fish cell cultures and fish embryos. Much newer approaches involving receptors and gene arrays in fish cells to elucidate the mode of action of sediment-borne contaminants are very promising. The review paper also lists and explores some of the issues associated with the use of juvenile or adult fish, fish cell cultures, fish embryos, and fish gene expression profiles in sediment toxicity evaluations to stimulate further discussions, and hopefully, to serve as benchmark for future handling of similar or related aspects of fish utilization in sediment risk assessment.
Conclusions and perspectives
Overall, the present review has comprehensively explored the changing and progressing roles of fish in sediment toxicity evaluation. Indeed the usefulness of this taxon as test organisms has provided a significant contribution to the advancement of sediment toxicology. However, despite the quite optimistic and bright future for these current procedures, a number of issues and problems remain. Therefore, efforts to develop new technologies and to refine current methods and approaches continue to challenge many laboratories worldwide.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ali F, Lazar R, Haffner D, Adeli K (1993) Development of a rapid and simple genotoxicity assay using a brown bullhead fish cell line: application to toxicological surveys of sediments in the Huron–Erie corridor. J Great Lakes Res 19:324–351
Almeida JS, Meletti PC, Martinez CBR (2005) Acute effects of sediments taken from an urban stream on physiological and biochemical parameters of the neotropical fish Prochilodus lineatus. Comp Biochem Physiol Part C 140:356–363
Ankley GT (1991) Predicting the toxicity of bulk sediments to aquatic organisms with aqueous test fractions: pore water vs. elutriate. Environ Toxicol Chem 10:1359–1366
Ankley GT, Katko A, Arthur JW (1990) Identification of ammonia as an important sediment-associated toxicant in the lower Fox River and Green Bay, Wisconsin. Environ Toxicol Chem 9:313–322
Ankley GT, Lodge K, Call DJ, Balcer MD, Brooke LT, Cook PM, Kreis RG Jr, Carlson AR, Johnson RD, Niemi GJ, Hoke RA, West CW, Giesy JP, Jones PD, Fuying ZC (1992) Integrated assessment of contaminated sediments in the Lower Fox and Green Bay, Wisconsin. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 23:46–63
ASTM E1688-00a (2007) Standard guide for determination of the bioaccumulation of sediment-associated contaminants by Benthic Invertebrates
ASTM E1367-03 (2008) Standard test method for measuring the toxicity of sediment-associated contaminants with estuarine and marine invertebrates
Baksi SM, Frazier JM (1990) Review—isolated fish hepatocytes—model systems for toxicology research. Aquat Toxicol 16:229–256
Barbee GC, Barich J, Duncan B, Bickham JW, Hintze MCW, CJ ARL, Zhou GD, McDonald TJ, Cizmas L, Norton D, Donnely KC (2008) In situ biomonitoring of PAH-contaminated sediments using juvenile coho salmon (Oncorhynchus kisutch). Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 71:454–464
Barcelo D, Petrovic M (eds) (2007) Sustainable management of sediment resources: sediment quality and impact assessment of pollutants. SedNet, Elsevier, Amsterdam
Barra R, Sanchez-Hernandez JC, Orrego R, Parra O, Gavilan JF (2001) Bioavailability of PAHs in the Biobio river (Chile): MFO activity and biliary fluorescence in juvenile Oncorhynchus mykiss. Chemosphere 45:439–444
Bat L (2005) A review of sediment toxicity bioassays using the amphipods and polychaetes. Turk J Fish Aquat Sci 5:119–139
Baudo R, Beltrami M, Rossi D (1999) In situ tests to assess the potential toxicity of aquatic sediments. Aquat Ecosyst Health Manag 2:361–365
Belfiore NM, Anderson SL (2001) Effects of contaminants on genetic patterns in aquatic organisms: a review. Mutat Res 489:97–122
Besselink HT, Flipsen E, Eggens ML, Vethaak AD, Koeman JH, Brouwer A (1998) Alterations in plasma and hepatic retinoid levels in flounder (Platichthys flesus) after chronic exposure to contaminated harbor sludge in a mesocosm study. Aquat Toxicol 42:271–285
Beyer J, Sandvikb M, Hylland K, Fjeld E, Egaas E, Aas E, Utne Skfueb J, Gokssyr A (1996) Contaminant accumulation and biomarker responses in flounder (Platichthys ilesus L.) exposed by caging to polluted sediments in Sarrfjorden, Norway. Aquat Toxicol 36:75–98
Black JJ (1983) Field and laboratory studies of environmental carcinogenesis in Niagara River fish. J Great Lakes Res 9:326–334
Bols NC, Boliska SA, Dixon DG, Hodson PV, Kaiser KLE (1985) The use of fish cell cultures as an indication of contaminant toxicity to fish. Aquat Toxicol 6:147–155
Brack W, Schirmer K (2003) Effect-directed identification of oxygen and sulfur heterocycles as major polycyclic aromatic cytcohrome P4501A-inducers in a contaminated sediment. Environ Sci Technol 37:3062–3070
Brack W, Schirmer K, Erdinger L, Hollert H (2005) Effect-directed analysis of mutagens and ethoxyresorufin-o-deethylase inducers in aquatic sediments. Environ Toxicol Chem 24:2445–2458
Braunbeck T (1998) Cytological alterations in fish hepatocytes – in vivo and in vitro biomarkers of environmental contamination. In: Braunbeck T, Hinton DE, Streit B (eds) Fish ecotoxicology, Experientia, Suppl. Birkhaüser, Basel, pp 61–140
Braunbeck T, Strmac M (2001) Assessment of water and sediment contamination in small streams by means of cytological and biochemical alterations in isolated rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) hepatocytes. J Aquat Ecosyst Stress Recovery 8:337–354
Braunbeck T, Böttcher M, Hollert H, Kosmehl T, Lammer E, Leist E, Rudolf M, Seitz N (2005) Towards an alternative for the acute fish LC50 test in chemical assessment: the fish embryotoxicity test goes multispecies—an update. ALTEX 22:87–102
Bucke D, Dixon PF, Feist SW, Law RJ (1989) The measurement of disease susceptibility in dab, Limanda limanda L. following long-term exposure to contaminated sediments: preliminary studies. Mar Environ Res 28:363–367
Burgess RM, Scott KJ (1992) The significance of in-place contaminated marine sediments on the water column: processes and effects. In: Burton GA (ed) Sediment toxicity assessment. Lewis, Ann Arbor, p 129
Burton GA Jr (1991) Assessing the toxicity of freshwater sediments: annual review. Environ Toxicol Chem 10:1585–1627
Burton GA Jr, Scott KJ (1992) Sediment toxicity evaluations their niche in ecological assessments. Environ Sci Technol 26(11):2069–2075
Cachot J, Law M, Pottier D, Peluhet L, Norris M, Budzinski H, Winn R (2007) Characterization of toxic effects of sediment-associated organic pollutants using the lambda transgenic medaka. Environ Sci Technol 41:7820–7836
Castano A, Gomez-Lechon M (2005) Comparison of basal cytotoxicity data between mammalian and fish cell lines: a literature survey. Toxicol in Vitro 19:695–705
Castano A, Cantarino MJ, Catillo P, Tarazona JV (1996) Correlation between the RTG-2 cytotoxicity test EC50 and in vivo LC50 rainbow trout bioassay. Chemosphere 32:2141–2157
Champ WST, Kelly FL, King JJ (2009) The water framework directive: using fish as a management tool. Biol Environ: Proc Royal Irish Acad 109:191–206
Chapman PM, Hollert H (2006) Should the sediment quality triad become a tetrad, a pentad, or possibly even a hexad? J Soils Sediments 6:4–8
Chapman PM, Wang F (2001) Assessing sediment contamination in estuaries. Environ Toxicol Chem 20:3–22
Chapman PM, Vigers GA, Farrell MA, Dexter RN, Quinlan EA, Kocan RM, Landolt M (1982) Survey of biological effects of toxicants upon puget sound biota. I. Broad-scale toxicity study. U.S. Dept. of Commerce, NOAA Tech. Memo OMPA-25, 98 pp
Chapman PM, Wang F, Germano J, Batley G (2002) Pore water testing and analysis: the good, the bad, and the ugly. Mar Pollut Bull 44:359–366
Chappie DJ, Burton GA Jr (2000) Applications of aquatic and sediment toxicity testing in situ. Soil Sediment Contam 9:219–245
Cheung YH, Neller A, Chu KH, Tam NFY, Wong CK, Wong YS, Wong MH (1997) Assessment of sediment toxicity using different trophic organisms. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 32:260–267
Costa PM, Lobo J, Caeiro S, Martins M, Ferreira AM, Caetano M, Vale C, DelValls TA, Costa MH (2008) Genotoxic damage in Solea senegalensis exposed to sediments from the Sado Estuary (Portugal): effects of metallic and organic contaminants. Mutat Res/Gen Toxicol Environ Mutat 654:29–37
Cunha I, Neuparth T, Caeiro S, Costa MH, Guilhermino L (2007) Toxicity ranking of estuarine sediments on the basis of Sparus aurata biomarkers. Environ Toxicol Chem 26:444–453
Dave G, Xiu R (1991) Toxicity of mercury, copper, nickel, lead, and cobalt to embryo and larvae of zebrafish, Brachydanio rerio. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 21:126–34
Davoren M, Ni Shuilleabhain S, Hartl MGJ, Sheehan D, O’Brien NM, Halloran JO, Van Pelt FNAM, Mothersill C (2005) Assessing the potential of fish cell lines as tools for the cytotoxicity testing of estuarine sediment aqueous elutriates. Toxicol in Vitro 19:421–431
Dawe CJ, Stanton ME, Schwartz FJ (1964) Hepatic neoplasms in native bottom feeding fish of Deep Creek Lake, Maryland. Cancer Res 24:1194–1201
Dawson DA, Stebler EF, Burks SL, Bantle JA (1988) Evaluation of the developmental toxicity of metal-contaminated sediments using short-term fathead minnow and frog embryo-larval assays. Environ Toxicol Chem 7:27–34
DeFlora S, Vigano L, D’Agostini F, Camoirano A, Bagnasco M, Bennicelli C, Melodia F, Arillo A (1993) Multiple genotoxicity biomarkers in fish exposed in situ to polluted river water. Mutat Res 319:167–177
Delfino JJ (1979) Toxic substances in the Great Lakes. Environ Sci Technol 13:1462–1468
DelValls TA, Blasco J, Sarasquete MC, Forja JM, Gomez-Parra A (1998) Evaluation of heavy metal sediment toxicity in littoral ecosystems using juveniles of the fish Sparus aurata. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 41:157–167
Denslow ND, Garcia-Reyero N, Barber DS (2007) Fish ‘n’ chips: the use of microarrays for aquatic toxicology. Mol BioSyst 3:172–177
Di Giulio RT, Habig C, Gallagher EP (1993) Effects of black rock harbour sediments on indices of biotransformation, oxidative stress, and DNA integrity in channel catfish. Aquat Toxicol 26:1–22
DIN (2001) German standard methods for the examination of water, waste water and sludge—Subanimal testing (group T)—Part 6: Toxicity to fish. Determination of the Non-acute-Poisonous Effect of Waste Water to Fish Eggs by Dilution Limits (T 6). DIN 38415-6. German Standardization Organization.Berlin, Germany
DiPinto LM (1996) Trophic transfer of a sediment-associated organophosphate pesticide from meiobenthos to bottom feeding fish. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 30:459–466
Dipple A, Bigger CAH (1983) Metabolic properties of in vitro systems In: Williams GM, Dunkel VC, Ray VA. (eds) Cellular systems for toxicity testing. Ann NY Acad Sci 407:26–33
Ekwall B (1983) Screening of toxic compounds in mammalian cell cultures. In: Williams GM, Dunkel VC, Ray VA (eds) Cellular systems for toxicity testing. Ann NY Acad Sci 407:64–77
Ensenbach U (1998) Embryonic development of fish—a model to assess the toxicity of sediments to vertebrates. Fresenius Environ Bull 7:531–538
Ensenbach U, Nagel R (1997) Toxicity of binary chemical mixtures: effects on reproduction of zebrafish (Brachydanio rerio). Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 32:204–210
Environment Canada (1990) Biological test method: acute lethality test using rainbow trout, EPS 1/RM/9, 1990, Cat. No. EN 49-24/1-9E, ISBN 0-662-18074-7
Eriksson-Wiklund A-K, Sundelin B, Broman D (2005) Toxicity evaluation by using intact sediments and sediment extracts. Mar Pollut Bull 50:660–667
Fabacher DL, Besser JM, Schmitt CJ, Harshbarger JC, Peterman PH, Lebo JA (1991) Contaminated sediments from tributaries of the Great Lakes: chemical characterization and carcinogenic effects in medaka (Oryzias latipes). Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 20:17–34
Feiler U, Ahlf W, Hoess S, Hollert H, Neumann-Hensel H, Meller M, Weber J, Heininger P (2005) The SeKT joint research project: definition of reference conditions, control sediments and toxicity thresholds for limnic sediment contact tests. Environ Sci Pollut Res 12:257–258
Fent K (2001) Fish cell lines as versatile tools in ecotoxicology: assessment of cytotoxicity, cytochrome P4501A induction potential and estrogenic activity of chemicals and environmental samples. Toxicol in Vitro 15:477–488
Foekema EM, Deerenberg CM, Murk AJ (2008) Prolonged ELS test with the marine flatfish sole (Solea solea) shows delayed toxic effects of previous exposure to PCB 126. Aquat Toxicol 90:187–203
Förstner U, Heise S, Schwartz R, Westrich B, Ahlf W (2004) Historical contaminated sediments and soils at the river basin scale. J Soils Sediments 4:247–260
Förstner U, Heise S, Ahlf W, Westrich B (2008) Data quality assurance of sediment monitoring. In: Quevauviller Ph, Borchers U, Thompson C, Simonat T (eds) The water framework directive—ecological and chemical monitoring. Chapter 8.2. Wiley, London, pp 375–390
Fragoso N, Hodson PV, Zambon S (2006) Evaluation of an exposure assay to measure uptake of sediment PAH by fish. Environ Monit Assess 116:481–511
Francis PC, Birge WJ, Black JA (1984) Effects of cadmium-enriched sediment on fish and amphibian embryo larvale stages. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 8:378–387
French BL, Reichert WL, Horn T, Nishimoto M, Sanborn HR, Stein JE (1996) Accumulation and dose–response of hepatic DNA adducts in English sole (Pleuronectes vetulus) exposed to a gradient of contaminated sediments. Aquat Toxicol 36:1–16
Friccius T, Schulte C, Ensenbach U et al (1995) Der Embryotest mit dem Zebrabärbling—eine neue Möglichkeit zur Prüfung und Bewertung der Toxizität von Abwasserproben. Vom Wasser 84:407–418
Gagné F, Blaise C (1995) Evaluation of the genotoxicity of environmental contaminants in sediments to rainbow trout hepatocytes. Environ Toxicol Water Qual 10:217–229
Gagne F, Trottiera S, Blaise C, Sproull J, Ernst B (1995) Genotoxicity of sediment extracts obtained in the vicinity of creosote-treated wharf to rainbow trout hepatocytes. Toxicol Lett 78:175–182
Gagne F, Blaise C, Bermingham N (1996) Lethal and sublethal effects of marine sediment extracts on rainbow trout hepatocytes. Toxicol Lett 87:85–92
George S, Gubbins M, MacIntosh A, Reynolds W, Sabine V, Scott A, Thain J (2004) A comparison of pollutant biomarker responses with transcriptional responses in European flounders (Platichthyes flesus) subjected to estuarine pollution. Mar Environ Res 58:571–575
Giesy JP, Hoke RA (1989) Freshwater sediment toxicity bioassessment—rationale for species selection and test design. J Great Lakes 15:539–569
Guy CP, Pinkney AE, Taylor MH (2006) Effects of sediment-bound zinc contamination on early life stages of the mummichog (Fundulus heteroclitus L.) in the Christina Watershed, Delaware, USA. Environ Toxicol Chem 25:1305–1311
Haasch ML, Prince R, Wejksnora PJ, Cooper KR, Lech JJ (1993) Caged and wild fish: induction of hepatic cytochrome P-450 (CYP1A1) as an environmental biomonitor. Environ Toxicol Chem 12:885–895
Hallare AV, Köhler H-R, Triebskorn R (2004) Developmental toxicity and stress protein responses in zebrafish embryos after exposure to diclofenac and its solvent, DMSO. Chemosphere 56:659–666
Hallare AV, Schirling M, Luckenbach T, Köhler H-R, Triebskorn R (2005a) Combined effects of temperature and cadmium on developmental parameters and biomarker responses in zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryos. J Therm Biol 30:7–17
Hallare AV, Pagulayan R, Lacdan N, Köhler H-R, Triebskorn R (2005b) Assessing water quality in a tropical lake using biomarkers in zebrafish embryos: developmental toxicity and stress protein responses. Environ Monit Assess 104:171–187
Hallare AV, Kosmehl T, Schulze T, Hollert H, Köhler H-R, Triebskorn R (2005c) Assessing contamination levels of Laguna Lake sediments (Philippines) using a contact assay with zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryos. Sci Total Environ 347:254–271
Hallare AV, Factor P, Santos E, Hollert H (2009) Assessing impact of fish cage culture on Taal Lake (Philippines) water and sediment quality using the zebrafish embryo assay. Philipp J Sci 138:91–104
Hansen PD, Blasco J, DelValls TA, Poulsen V, van den Heuvel-Greve M (2007) Biological analaysis (Bioassays, biomarkers, biosensors). In: Barcelo D, Petrovic M (eds) Sustainable management of sediment resources: sediment quality and impact assessment of pollutants. SedNet, Elsevier, Amsterdam
Hargis WJ, Roberts MH, Zwerner DE (1984) Effects of contaminated sediments and sediment-exposed effluent water on an estuarine fish: acute toxicity. Mar Environ Res 14:337–354
Hayes MA, Smith IR, Rushmore TH, Crane TL, Thorn C, Kocal TE, Ferguson HW (1990) Pathogenesis of skin and liver neoplasms in white suckers from industrially polluted areas in Lake Ontario. Sci Total Environ 94:105–123
Hecker M, Hollert H (2009) Effect-directed analysis (EDA) in aquatic ecotoxicology: state of the art and future challenges. Environ Sci Pollut Res 16:607–613
Hilscherova K, Kannan K, Kang YS, Holoubek I, Machala M, Masunaga S, Nakanishi J, Giesy JP (2001) Characterization of dioxin-like activity of sediments from a Czech river basin. Environ Toxicol Chem 20:2768–2777
Hinkle-Conn C, Fleeger JW, Gregg JC, Carman KR (1998) Effects of sediment-bound polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons on feeding behavior in juvenile spot (Leiostomus xanthurus Lacepede: Pisces). J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 227:113–132
Hoess S, Ahlf W, Fahnenstich C, Gilberg D, Hollert H, Melbye K, Meller M, Hammers-Wirtz M, Heininger P, Neumann-Hensel H, Ottermanns R, Ratte HT, Seiler TB, Spira D, Weber J, Feiler U (2010) Variability of sediment-contact tests in freshwater sediments with low-level anthropogenic contamination—determination of toxicity thresholds. Environ Pollut 158:2999–3010
Hoke RA, Prater BL (1980) Relationship of percent mortality of four species of aquatic biota from 96-hour sediment bioassays of five Lake Michigan harbors and elutriate chemistry of the sediments. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 25:394–399
Hollert H, Dürr M, Erdinger L, Braunbeck T (2000) Cytotoxicity of settling particulate matter and sediments of the Neckar river (Germany) during a winter flood. Environ Toxicol Chem 19:528–534
Hollert H, Dürr M, Olsman H, Halldin K, Bavel VB, Brack W, Tysklind M, Engwall M, Braunbeck T (2002) Biological and chemical determination of dioxin-like compounds in sediments by means of a sediment triad approach in the catchment area of the river Neckar. Ecotoxicology 11:323–336
Hollert H, Keiter S, Konig N, Rudolf M, Ulrich M, Braunbeck T (2003) A new sediment contact assay to assess particle-bound pollutants using zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryos. J Soils Sediments 3(3):197–207
Hollert H, Dürr M, Holtey-Weber R, Islinger M, Brack W, Färber H, Erdinger L, Braunbeck T (2005) Endocrine disruption of water and sediment extracts in a non-radioactive dot blot/RNAse protection assay using isolated hepatocytes of rainbow trout—deficiencies between bioanalytical effectiveness and chemically determined concentrations and how to explain them. Environ Sci Pollut Res 12:347–360
Hopkins WA, Snodgrass JW, Staub BP, Jackson BP, Congdon JD (2003) Altered swimming performance of a benthic fish (Erimyzon sucetta) exposed to contaminated sediments. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 44:383–389
Husøy A, Myers MS, Goksøyr A (1996) Cellular localization of cytochrome P450 (CYPl A) induction and histology in Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua L.) and European flounder (Platichthys flesus) after environmental exposure to contaminants by caging in Sørfjorden, Norway. Aquat Toxicol 36:53374
Huuskonen SE, Ristola TE, Tuvikene A, Hahn ME, Kukkonen JVK, Lindström-Seppa P (1998) Comparison of two bioassays, a fish liver cell line (PLHC-1) and a midge (Chironomus riparius), in monitoring freshwater sediments. Aquat Toxicol 44:47–67
Huuskonen SE, Tuvikene A, Trapido M, Fent K, Hahn ME (2000) Cytochrome P4501A induction and porphyrin accumulation in PLHC-1 fish cells exposed to sediment and oil shale extracts. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 38:59–69
Ingersoll CG, Ankley GT, Benoit DA, Brunson EL, Burton GA, Dwyer FJ (1995) Toxicity and bioaccumulation of sediment-associated contaminants using freshwater invertebrates: a review of methods and applications. Environ Toxicol Chem 14:1885–1194
Inzunza B, Orrego R, Penalosa M, Gavilan JF, Barra R (2006) Analysis of CYP4501A1, PAHs metabolites in bile, and genotoxic damage in Oncorhynchus mykiss exposed to Biobio river sediments, Central Chile. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 65:242–251
Jimenez-Tenorio N, Morales-Caselles C, Kalman J, Salamanca MJ, de Canales MLG, Sarasquete C, Del Valls TA (2007) Determining sediment quality for regulatory purposes using fish chronic bioassays. Environ Int 33:474–480
Kammann U (2007) PAH metabolites in bile fluids of Dab (Limanda limanda) and flounder (Platichthys flesus): spatial distribution and seasonal changes. Environ Sci Pollut Res 14:102–108
Kammann U, Riggers JC, Theobald N, Steinhart H (2000) Genotoxic potential of marine sediments from the North Sea. Mutat Res 467:161–168
Kammann U, Bunke M, Steinhart H, Theobold N (2001) A permanent fish cell line (EPC) for genotoxicity testing of marine sediments with the comet assay. Mutat Res 498:67–77
Kammann U, Biselli S, Hühnerfuss H, Reineke N, Theobald N, Vobach M, Wosniok W (2004) Genotoxic and teratogenic potential of marine sediment extracts investigated with comet assay and zebrafish test. Environ Pollut 132:279–287
Kammann U, Biselli S, Reineke N, Wosniok W, Danischewski D, Hühnerfuss H, Kinder A, Sierts-Herrmann A, Theobald N, Vahl H-H, Vobach M, Westendorf J, Steinhart H (2005) Bioassay-directed fractionation of organic extracts of marine surface sediments from the North and Baltic Sea. J Soils Sediments 5:225–232
Kammann U, Lang T, Berkau AJ, Klempt M (2008) Biological effect monitoring in dab (Limanda limanda) using gene transcript of CYP1A1 or EROD—a comparison. Environ Sci Pollut Res 15:600–605
Karlsson J, Sundberg AG, Grunder K, Eklund B, Breitholtz M (2008) Hazard identification of contaminated sites—ranking potential toxicity of organic sediment extracts in crustacean and fish. J Soils Sediments 8:263–274
Keiter S, Rastall A, Kosmehl T, Wurm K, Erdinger L, Braunbeck T, Hollert H (2006) Ecotoxicological assessment of sediment, suspended matter, and water samples in the Upper Danube river. A pilot study in search for the causes for the decline of fish catches. Environ Sci Pollut Res 13:308–319
Keiter S, Grund S, van Bavel B, Hagberg J, Engwall M, Kammann U, Klempt M, Manz W, Olsman H, Braunbeck T, Hollert H (2008) Activities and identification of aryl hydrocarbon receptor agonists in sediments from the Danube River. Anal Bioanal Chem 390:2009–2019
Keiter S, Peddinghaus S, Feiler U, von der Goltz B, Hafner C, Ho NY, Rastegar S, Otte JC, Ottermanns R, Reifferscheid G, Strähle U, Braunbeck T, Hammers-Wirtz M, Hollert H (2010) DanTox – a novel joint research project using zebrafish (Danio rerio) to identify specific toxicity and molecular modes of action of sediment-bound pollutants. J Soils Sediments 10(4):714–717
Kemble NE, Brumbaugh WG, Brunson EL, Dwyer FJ, Ingersoll CG, Monda DP, Woodward DF (1994) Toxicity of metal-contaminated sediments from the Upper Clark Fork River, Montana, to aquatic invertebrates and fish in laboratory exposures. Environ Toxicol Chem 13:1985–1997
Kilemade MF, Hartl MGJ, Sheehan D, Mothersill C, vanPelt F, O’Halloran J, O’Brien N (2004) Genotoxicity of field-collected inter-tidal sediments from Cork Harbour, Ireland to juvenile turbot (Scophthalmus maximus). Environ Mol Mutagen 44:56–64
Kilemade M, Hartl MF, O’Halloran J, O’Brien NM, Sheehan D, Mothersill C, vanPelt FNAM (2009) Effects of contaminated sediment from Cork Harbour, Ireland on the cytochrome P450 system of turbot. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 72:747–755
Kimmel C, Ballard W, Kimmel SR et al (1995) Stages of embryonic development of the zebrafish. Dev Dyn 203:253–310
Kinani S, Bouchonnet S, Creusot N, Bourcier S, Balaguer P, Porcher J-M, Ait-Aissa S (2010) Bioanalytical characterization of multiple endocrine- and dioxin-like activities in sediments from reference and impacted small rivers. Environ Pollut 158:74–83
Kinder A, Sierts-Herrmann A, Biselli S, Heinzel N, Hühnerfuss H, Kammann U, Reineke N, Theobald N, Steinhart H (2007) Expression of heat shock protein 70 in a permanent cell line (EPC) exposed to sediment extracts from the North Sea and the Baltic Sea. Mar Environ Res 63:506–515
Klobucar GIV, Stambuk A, Pavlica M, Peric MS, Hackenberger BK, Hylland K (2010) Genotoxicity monitoring of freshwater environments using caged carp (Cyprinus carpio). Ecotoxicology 19:77–84
Klumpp DW, Humphrey C, Huasheng H, Tao F (2002) Toxic contaminants and their biological effects in coastal waters of Xiamen, China. II. Biomarkers and embryo malformation rates as indicators of pollution stress in fish. Mar Pollut Bull 44:761–769
Kocan RM, Sabo KM, Landolt ML (1985) Cytotoxicity/genotoxicity: the application of cell culture techniques to the measurement of marine sediment pollution. Aquat Toxicol 6:165–177
Kosmehl T (2007) Molecular biomarkers in zebrafish embryos: towards a more realistic approach in sediment assessment. Inaugural dissertation. University of Heidelberg, 271 pp
Kosmehl T, Krebs F, Manz W, Erdinger L, Braunbeck T, Hollert H (2004) Comparative genotoxicity testing of Rhine river sediment extracts using the permanent cell lines RTG-2 and RTL-W1 in the comet assay and Ames assay. J Soils Sediments 4:84–94
Kosmehl T, Krebs F, Manz W, Braunbeck T, Hollert H (2007) Differentiation between bioavailable and total hazard potential of sediment induced DNA fragmentation as measured by the comet assay with zebrafish embryos. J Soils Sediments 7:377–387
Kosmehl T, Hallare AV, Braunbeck T, Hollert H (2008) DNA damage induced by genotoxicants in zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryos after contact exposure to freeze-dried sediment and sediment extracts from Laguna Lake (The Philippines) as measured by the comet assay. Mutat Res 650:1–14
Krasnov A, Afanasyev S, Oikari A (2007) Hepatic responses of gene expression in juvenile brown trout (Salmo trutta lacustris) exposed to three model contaminants applied singly and in combination. Environ Toxicol Chem 26:100–109
Kristensen P (1995) Sensitivity of embryos and larvae in relation to other stages in the life cycle of fish: a literature review. In: Müller R, Lloyd R (eds) Sublethal and chronic effects of pollutants on freshwater fish. FAO, Oxford, pp 155–166
Küster E, Altenburger R (2008) Oxygen decline in biotesting of environmental samples—is there a need for consideration in the acute zebrafish embryo assay? Environ Toxicol 23:745–750
Laale HW (1977) The biology and use of zebrafish, Brachydanio rerio, in fisheries research: a literature review. J Fish Biol 10:121–173
Lammer E, Carr GJ, Wendler K, Rawlings JM, Belanger SE, Braunbeck Th (2009) Is the fish embryo toxicity test (FET) with the zebrafish (Danio rerio) a potential alternative for the fish acute toxicity test? Comp Biochem Physiol Part C 149:196–209
Landolt ML, Kocan RM (1984) Lethal and sublethal effects of marine sediment extracts on fish cells and chromosomes. Helgol Meersunters 37:479–491
Lange M, Gebauer W, Markl J, Nagel R (1995) Comparison of testing acute toxicity on embryo of zebrafish, Brachydanio rerio and RGT-2 cytotoxicity as possible alternatives to the acute fish test. Chemosphere 30:2087–2102
Larkin P, Folmar LC, Hemmer MJ, Poston AJ, Lee HS, Denslow ND (2002) Array technology as a tool to monitor exposure of fish to xenoestrogens. Mar Environ Res 54:395–399
Leaver MJ, Diab A, Boukouvala E, Williams TD, Chipman JK, Moffat CF, Robinson CD, George SG (2010) Hepatic gene expression in flounder chronically exposed to multiply polluted estuarine sediment: absence of classical exposure ‘biomarker’ signals and induction of inflammatory, innate immune and apoptotic pathways. Aquat Toxicol 96:234–245
LeBlanc GA, Suprenant DC (1985) A method of assessing the toxicity of contaminated freshwater sediments. In: Cardwell RD, Purdy R, Bahner RC (eds) Aquatic toxicology and hazard assessment seventh symposium STP 854. American Society for Testing and Materials, Philadelphia, pp 269–283
Lettieri T (2006) Recent applications of DNA microarray technology to toxicology and ecotoxicology. Environ Health Perspect 114:4–9
Lie KK, Lanzen A, Breilid H, Olsvik PA (2009) Gene expression profiling in Atlantic cod (Gadius morhua L.) from two contaminated sites using a custom-made cDNA microarray. Environ Toxicol Chem 28:1711–1721
Liss W, Ahlf W (1997) Evidence from whole-sediment, pore water, and elutriate testing in toxicity assessment of contaminated sediments. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 36:140–147
Louiz I, Kinani S, Gouze ME, Ben-Attia M, Menif D, Bouchonnet S, Porcher JM, Ben-Hassine OK, Ait-Aissa S (2008) Monitoring of dioxin-like, estrogenic and anti-androgenic activities in sediments of the Bizerta lagoon (Tunisia) by means of in vitro cell-based bioassays: contribution of low concentrations of polynuclear aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs). Sci Total Environ 402:318–329
Luckenbach T, Kilian M, Triebskorn R, Oberemm O (2001) Fish early life stage tests as a tool to assess embryotoxic potentials in small streams. J Aquat Ecosyst Stress Recovery 8:355–370
Luckenbach T, Kilian M, Triebskorn R, Oberemm A (2003) Assessment of the developmental success of brown trout (Salmo trutta f. fario L.) embryos in two differently polluted streams in Germany. Hydrobiologia 490:53–62
Mac MJ, Noguchi GE, Hesselberg RJ, Edsall CD, Shoesmith JA, Bowker JD (1990) A bioaccumulation bioassay for freshwater sediments. Environ Toxicol Chem 9:1405–1414
Magwood S, George S (1996) In vitro alternatives to whole animal testing. Comparative cytotoxicity studies of divalent metals in established cell lines derived from tropical and temperate water fish species in a neutral red assay. Mar Environ Res 42:37–40
McCain BB, Hudgins HO, Gronlund WD, Hawkes JW, Brown DW, Myers MS, Vandermuelen JH (1978) Bioavailability of crude oil from experimentally oiled sediments to English sole (Parophrys vetulus) and pathological consequences. J Fish Res Board Can 35:657–664
Menzel R, Swain SC, Hoess S, Claus E, Menzel S, Steinberg CEW, Reifferscheid G, Stürzenbaum SR (2009) Gene expression profiling to characterize sediment toxicity—a pilot study using Caenorhabditis elegans whole genome microarrays. BMC Genomics 10:160–174
Metcalfe CD, Balch GC, Cairns VW, Fitzsimons JD (1990) Carcinogenic and genotoxic activity of extracts from contaminated sediments in Western Lake Ontario. Sci Total Environ 94:125–141
Michallet-Ferrier P, Ait-Aissa S, Balaguer P, Dominik J, Douglas Haffner G, Pardos M (2004) Assessment of estrogen (ER) and aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) mediated activities in organic sediment extracts of the Detroit river, using in vitro bioassays based on human MELN and teleost PLHC-1 cell lines. J Great Lakes Res 30:82–92
Miller KM, Maclean N (2008) Teleost microarrays: development in a broad phylogenetic range reflecting diverse applications. J Fish Biol 72:2039–2050
Mondon JA, Duda S, Nowak BF (2001) Histological growth and 7-ethoxyresorufin-o-deethylase (EROD) activity responses of greenback flounder Rhombosolea tapirina to contaminated marine sediment and diet. Aquat Toxicol 54:231–247
Nagel R (2002) DarT: the embryo test with the zebrafish Danio rerio—a general model in ecotoxicology and toxicology. ALTEX: Alternativen zu Tierexperimenten 19:38–48
Nagler JJ, Cyr DG (1997) Exposure of male American plaice (Hippoglossoides platessoides) to contaminated marine sediments decreases the hatching success of their progeny. Environ Toxicol Chem 16:1733–1738
Nendza M (2002) Inventory of marine biotest methods for the evaluation of dredged material and sediments. Chemosphere 48:865–883
Netzband A, Brils J, Brauch HJ et al (2007) Sediment management: an essential element of river basin management plans. J Soils Sediments 7:117–132
Ni Shuilleabhain S, Davoren M, Mothersill C, Sheehan D, Hartl MGJ, Kilemade M, O’Brien NM, O’Halloran J, Van Pelt FNAM, Lyng FM (2005) Identification of a multixenobiotic resistance mechanism in primary cultured epidermal cells from Oncorhynchus mykiss and the effects of environmental complex mixtures on its activity. Aquat Toxicol 73:115–127
Oberemm A (2000) The use of a refined zebrafish embryo bioassay for the assessment of aquatic toxicity. Lab Anim 29:32–40
OECD (Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development) (1992) Guidelines for testing of chemicals 210: Fish, Early Life Stage Toxicity Test. Paris, France
OECD (Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (1998) OECD guidelines for the testing of chemicals. Section 2: effects on biotic systems Test No. 212: fish, short-term toxicity test on embryo and sac-fry stages. Paris, France
OECD (Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development) (2001) Guidelines for Testing of Chemicals, Proposal for a new Guideline 218, Sediment-Water Chironomid Toxicity Test Using Spiked Sediment. Paris, France
OECD (Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development) (2006) Guideline for testing of chemicals; Draft Proposal for a new guideline, Fish Embryo Toxicity (FET) Test
Ozoh PTE (1979) Malformations and inhibitory tendencies induced to Brachydanio rerio (Hamilton-Buchanan) eggs and larvae due to exposures in low concentrations of lead and copper ions. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 21:668–675
Park JW, Tompsett AR, Zhang X, Newsted JL, Jones PD, Au DWT, Kong R, Wu RSS, Giesy JP, Hecker M (2009) Advanced fluorescence in situ hybridization to localize and quantify gene expression in Japanese medaka (Oryzias latipes) exposed to endocrine-disrupting compounds. Environ Toxicol Chem 28:1951–1962
Perkins EJ, Lotufo GR (2003) Playing in the mud-using gene expression to assess contaminant effects on sediment dwelling invertebrates. Ecotoxicology 12:453–456
Powers DA (1989) Fish as model systems. Science 246:352–358
Power EA, Munkitittrick KR, Chapman PM (1992) An ecological impact assessment framework for decision-making related to sediment quality. Standard Technical Pub. 1124. American Society for Testing and Materials, Philadelphia
Quiros L, Pina B, Sole M, Blasco J, Lopez MA, Riva MC, Barcelo D, Raldua D (2007) Environmental monitoring by gene expression biomarkers in Barbus graellsii: laboratory and field studies. Chemosphere 67:1144–1154
Roberts MH, Hargis WJ Jr, Strobel CJ, De Lisle PF (1989) Acute toxicity of PAH contaminated sediments to the estuarine fish, Leiostomus xanthurus. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 42:142–149
Roberts AP, Oris JT, Burton GA Jr, Clements WH (2005) Gene expression in caged fish as a first-tier indicator of contaminant exposure in streams. Environ Toxicol Chem 24:3092–3098
Rocha PS, Luvizotto GL, Kosmehl T, Böttcher M, Storch V, Braunbeck T, Hollert H (2009) Sediment genotoxicity in the Tiete River (Sao Paulo, Brazil): In vitro comet assay versus in situ micronucleus assay studies. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 72:1842–1848
Rodgers PW, Kieser MS, Peterson GW (1985) Summary of the existing status of the upper great lakes connecting channels data. Limno-Tech, Ann Arbor
Rosenthal H, Alderdice DF (1976) Sublethal effects of environmental stressors, natural and pollutional, on marine fish eggs and larvae. J Fish Res Board Can 33:2047–2065
Savage WK, Quimby FW, DeCaprio AP (2002) Lethal and sublethal effects of polychlorinated biphenyls on Rana sylvatica tadpoles. Environ Toxicol Chem 21:168–174
Schirmer K (2006) Proposal to improve vertebrate cell cultures to establish them as substitutes for the regulatory testing of chemicals and effluents using fish. Toxicology 224:163–183
Schlenk D, Sapozhnikova Y, Irwin M, Xie L, Hwang W, Reddy S, Brownawell BJ, Armstrong J, Kelly M, Montagne DE (2005) In vivo bioassay-guided fractionation of marine sediment extracts from the Southern California Bight, USA, for estrogenic activity. Environ Toxicol Chem 24:2820–2826
Scholz S, Fischer S, Gündel U, Küster E, Luckenbach T, Voelker D (2008) The zebrafish embryo model in environmental risk assessment—applications beyond acute toxicity testing. Environ Sci Pollut Res 15:394–404
Schubauer-Berigan MK, Ankley GT (1991) The contribution of ammonia, metals and nonpolar organic compounds to the toxicity of sediment interstitial water from an Illinois River tributary. Environ Toxicol Chem 10:925–939
Schulte C, Nagel R (1994) Testing acute toxicity in the embryo of zebrafish, Brachydanio rerio, as an alternative to the acute fish test: preliminary results. ATLA 22:12–19
Segner H (1998) Isolation and primary culture of teleost hepatocytes. Comp Biochem Physiol 120:71–81
Segner H (2004) Cytotoxicity assay with fish cells as an alternative to the acute lethality assay with fish. ATLA 32:375–382
Seiler TB, Schulze T, Hollert H (2008) The risk of altering soil and sediment samples upon extract preparation for analytical and bio-analytical investigations—a review. Anal Bioanal Chem 390:1975–1985
Seitz N, Böttcher M, Keiter S, Kosmehl T, Manz W, Hollert H, Braunbeck T (2007) A novel statistical approach for the evaluation of comet assay data. Mutat Res 652:38–45
SETAC-Europe (1991) Guidance document on testing procedures for pesticides in freshwater static microcosms. Workshop 3-4. July 1991. Monks Wood Exp. St., UL
Skidmore JF (1965) Resistance to zinc sulphate of the zebrafish (Brachydanio rerio Hamilton–Buchanan) at different phases of its life history. Ann Appl Biol 56:47–53
Sleiderink HM, Beyer J, Scholtens E, Godsoyr A, Nieywenhuize J, Van Liere JM, Boon JP (1995) Influence of temperature and polyaromatic contaminants on CYP1A levels in North Sea dab (Limanda limanda). Aquat Toxicol 32:189–209
Snell TW, Brogdon SE, Morgan MB (2003) Gene expression profiling in ecotoxicology. Ecotoxicology 12:475–483
Solomon KR, Sibley P (2002) New concepts in ecological risk assessment: where do we go from here? Mar Pollut Bull 44:279–285
Sonstegard RA (1977) Environmental carcinogenesis studies in fishes of the Great Lakes of North America. Ann NY Acad Sci 298:261–269
Sprague JB (1969) Measurement of pollutant toxicity to fish. I. Bioassay methods for acute toxicity. Wat Res 3:793–821
Steinberg CEW, Stürzenbaum SR, Menzel R (2008) Genes and environment—striking the fine balance between sophisticated biomonitoring and true functional environmental genomics. Sci Total Environ 400:142–161
Strecker R, Seiler TB, Hollert H, Braunbeck T (2008) Oxygen requirements of zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryos in embryotoxicity tests with environmental samples. Proceedings Annual Meeting SETAC-GLB Frankfurt 23–26 Sept 2008
Strmac M, Braunbeck T (2000) Isolated hepatocytes of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) as a tool to discriminate between differently contaminated small river systems. Toxicol in Vitro 14:361–377
Strmac M, Oberemm A, Braunbeck T (2002) Assessment of sediment toxicity to early life stages of fish: effects of sediments from differently polluted small rivers on zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryos and larvae. J Fish Biol 61:24–38
Sundberg H, Ishaq R, Åkerman G, Tjärnlund U, Zebühr Y, Linderoth M, Broman D, Balk L (2005) A bio-effect directed fractionation study for toxicological and chemical characterization of organic compounds in bottom sediment. Toxicol Sci 84:63–72
Tanneberger K, Kramer NI, Scholz S, Bols NC, Lee LEJ, Hafner C, Hermens JLM, Schirmer K (2008) CEIISens-Eco8: development of a strategy to replace acute fish toxicity tests. Annual EPAA Conference. Research into alternative approaches (3Rs) in regulatory testing: are we on the right track? 03.11.2008. Brussels, Belgium
Teles M, Santos MA, Pacheco M (2004) Responses of European eel (Anguilla anguilla L.) in two polluted environments: in situ experiments. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 58:373–378
Tollefsen KE, Bratsberg E, Boyum O, Finne EF, Gregersen IK, Hegseth M, Sandberg C, Hylland K (2006) Use of fish in vitro hepatocyte assays to detect multi-endpoint toxicity in Slovenian river sediments. Mar Environ Res 62:S356–S359
Traven L, Zaja R, Loncar J, Smital T, Micovic V (2008) CYP1A induction potential and the concentration of priority pollutants in marine sediment samples—in vitro evaluation using the PLHC-1 fish hepatoma cell line. Toxicol in Vitro 22:1648–1656
Travis CC, Bishop WE, Clarke DP (2003) The genomic revolution: what does it mean for human and ecological risk assessment? Ecotoxicology 12:489–495
USEPA U.S Environmental Protection Agency (1977) Ecological evaluation of proposed discharge of dredged material into ocean waters. Environmental Effects Laboratory, US Army Engineer Waterways Experiment Station, Vicksburg
USEPA U.S Environmental Protection Agency (1981) Development of bioassay procedures for defining pollution of harbour sediments EPA 600/S3-81-025. Duluth, MN
USEPA U.S Environmental Protection Agency (1994) Methods for measuring the toxicity and bioaccumulation of sediment-associated contaminants with freshwater invertebrates. EPA 600/R-94/024. Duluth, MN
USEPA U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (2001) Draft report on the incidence and severity of sediment contamination in surface waters of the United States, national sediment quality survey. Washington DC: USEPA. EPA-823-F-01-031
Van Beelen P (2003) A review on the application of microbial toxicity tests for deriving sediment quality guidelines. Chemosphere 53:795–808
Van der Oost R, Beyer J, Vermeulen NPE (2003) Fish bioaccumulation and biomarkers in environmental risk assessment: a review. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 13:57–149
Vigano L, Arillo A, DeFlora S, Lazorchak J (1995) Evaluation of microsomal and cytosolic biomarkers in a 7-day larval trout sediment toxicity test. Aquat Toxicol 31:189–202
Vigano L, Arillo A, Falugi C, Melodia F (1998) Histochemical and biochemical markers in trout larvae exposed to river sediments. Chemosphere 37:2797–2807
Vigano L, Arillo A, Falugi C, Melodia F, Polesello S (2001) Biomarkers of exposure and effect in flounder (Platichthys flesus) exposed to sediments of the Adriatic Sea. Mar Pollut Bull 42:887–894
Völker D, Vess C, Tillmann M, Nagel R, Otto GW, Geisler R, Schirmer K, Scholz S (2007) Differential gene expression as a toxicant-sensitive endpoint in zebrafish embryos and larvae. Aquat Toxicol 81:355–364
von Westernhagen H, Dethlefsen V (1997) The use of malformations in pelagic fish embryos for pollution assessment. Hydrobiologia 352:241–250
Wedekind C, von Siebenthal B, Gingold R (2007) The weaker points of fish acute toxicity tests and how tests on embryos can solve some issues. Environ Pollut 148:385–389
Weil M, Scholz S, Zimmer M et al (2009) Gene expression analysis in zebrafish embryos: a potential approach to predict effect concentrations in the fish early life stage test. Environ Toxicol Chem 28:1970–1978
Westerfield M (2000) The zebrafish book: a guide for the laboratory use of zebrafish (Brachydanio rerio). 3 rd edition.USA-Eugene: University of Oregon Press, Institute of Neuroscience
Williams TD, Gensberg K, Minchin SD, Chipman JK (2003) A DNA expression array to detect toxic stress response in European flounder (Platichthys flesus). Aquat Toxicol 65:141–157
Wölz J, Engwall M, Maletz S, Olsman Takner H, van Bavel B, Kammann U, Klempt M, Weber R, Braunbeck T, Hollert H (2008) Changes in toxicity and Ah receptor agonst activity of suspended particulate matter during flood events at the rivers Neckar and Rhine—a mass balance, approach using in vitro methods and chemical analysis. Environ Sci Pollut Res 15:536–553
Wölz J, Borck D, Witt G, Hollert H (2009) Ecotoxicological characterization of sediment cores from the western Baltic Sea (Mecklenburg Bight) using GC-MS and in vitro biotests. J Soils Sediments 9:400–410
Wolz J, Hudjetz S, Roger S, Brinkmann M, Schmidt B, Schaffer A, Kammann U, Lennartz G, Hecker M, Schuttrumpf H, Hollert H (2009) In search for the ecological and toxicological relevance of sediment re-mobilisation and transport during flood events. J Soils Sediments 9:1–5
Yang LX, Ho NY, Alshut R, Legradi J, Weiss C, Reischl M, Mikut R, Liebel U, Muller F, Strahle U (2009) Zebrafish embryos as models for embryotoxic and teratological effects of chemicals. Repro Toxicol 28:245–253
Zapata-Perez O, Sima-Alvarez R, Norena-Barroso E, Guemes J, Gold-Bauchot G, Ortega A, Albores-Medina A (2000) Toxicity of sediments from Bahia de Chetumal, Mexico, as assessed by hepatic EROD induction and histology in nile tilapia Oreochromis niloticus. Mar Environ Res 50:385–391
Zhou B, Liu C, Wang J, Lam PKS, Wu SS (2006) Primary cultured cells as sensitive in vitro model for assessment of toxicants-comparison to hepatocytes and gill epithelia. Aquat Toxicol 80:109–118
Acknowledgments
This study has been generously supported by a Georg Forster Research Fellowship (Alexander von Humboldt Foundation) granted to the first author. We are also indebted to the two anonymous reviewers and to the subject editor Dr Ellen Petticrew for the valuable remarks and comments that have greatly improved the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Responsible editor: Ellen Petticrew
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hallare, A.V., Seiler, TB. & Hollert, H. The versatile, changing, and advancing roles of fish in sediment toxicity assessment—a review. J Soils Sediments 11, 141–173 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-010-0302-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-010-0302-7