Abstract
Purpose
Adsorption onto mineral and bacterial surfaces can profoundly affect the mobility and fate of dissolved ions in soils; however, currently, there is a poor understanding of antimony (Sb) adsorption onto mixture of these two sorbents. This study aims at investigating the adsorption of Sb(III) to an antimony-tolerant soil bacterium Bacillus cereus and cell-goethite binary composite under anaerobic condition.
Materials and methods
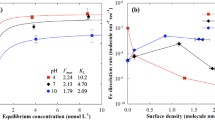
Adsorption isotherms and adsorption edges (pH 3–10) were conducted to explore the adsorption capacity of Sb(III) to goethite, bacteria, and the cell-goethite composite. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) was applied to determine the surface functional groups that are responsible for Sb adsorption.
Results and discussion
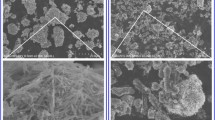
Scanning electron microscope shows that nano-particulate goethite is strongly adsorbed onto the cell surfaces to give a mineral film. The cell-goethite composite displays an additive Sb adsorption behavior, i.e., composite adsorptivity is the sum of the individual end-member metal adsorptivities (i.e., the additivity rule). Sb(III) adsorption to goethite, Bacillus cereus cells, and the cell-goethite composite is independent of pH. Using high-resolution XPS spectra, we identify the ferric hydroxyl functional groups of goethite and the carboxyl and amino/amide groups of bacteria responsible for Sb binding to the binary solid products. Moreover, the molecular binding mechanisms are very similar between the composite and the isolated end-member bacteria and mineral phases.
Conclusions
Sb(III) adsorption to the bacteria-goethite conforms to a component-additive rule. Goethite component plays a more important role in Sb binding to the bacteria-mineral composite. New findings of this research suggest that it should be careful to use the universal adsorption rule for cations as previously suggested, to simulate anion adsorption to organo-iron oxide composite.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahimou F, Boonaert CJ, Adriaensen Y, Jacques P, Thonart P, Paquot M, Rouxhet PG (2007) XPS analysis of chemical functions at the surface of Bacillus subtilis. J Colloid Interface Sci 309:49–55
Burnett PGG, Daughney CJ, Peak D (2006) Cd adsorption onto Anoxybacillus flavithermus: surface complexation modeling and spectroscopic investigations. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 70:5253–5269
Cao CY, Qu J, Yan WS, Zhu JF, Wu ZY, Song WG (2012) Low-cost synthesis of flowerlike α-Fe2O3 nanostructures for heavy metal ion removal: adsorption property and mechanism. Langmuir 28:4573–4579
Crawford SE, Lofts S, Liber K (2017) The role of sediment properties and solution pH in the adsorption of uranium(VI) to freshwater sediments. Environ Pollut 220:873–881
Dai C, Lin M, Hu Y (2017) Heterogeneous Ni- and cd-bearing ferrihydrite precipitation and recrystallization on quartz under acidic pH condition. ACS Earth Space Chem 1:621–628
Du H, Lin Y, Chen W, Cai P, Rong X, Shi Z, Huang Q (2017) Copper adsorption on composites of goethite, cells of Pseudomonas putida and humic acid. Eur J Soil Sci 68:514–523
Du H, Huang Q, Lei M, Tie B (2018a) Sorption of Pb(II) by nanosized ferrihydrite organo-mineral composites formed by adsorption versus coprecipitation. ACS Earth Space Chem 2:556–564
Du H, Huang Q, Yang R, Tie B, Lei M (2018b) Cd sequestration by bacteria–aluminum hydroxide composites. Chemosphere 198:75–82
Du H, Peacock CL, Chen W, Huang Q (2018c) Binding of cd by ferrihydrite organo-mineral composites: implications for cd mobility and fate in natural and contaminated environments. Chemosphere 207:404–412
Essington ME, Stewart MA (2016) Adsorption of antimonate by gibbsite: reversibility and the competitive effects of phosphate and sulfate. Soil Sci Soc Am J 80:1197–1207
Essington ME, Vergeer KA (2015) Adsorption of antimonate, phosphate, and sulfate by manganese dioxide: competitive effects and surface complexation modeling. Soil Sci Soc Am J 79:803–814
Franzblau RE, Daughney CJ, Moreau M, Weisener CG (2014) Selenate adsorption to composites of Escherichia coli and iron oxide during the addition, oxidation, and hydrolysis of Fe(II). Chem Geol 383:180–193
Franzblau RE, Daughney CJ, Swedlund PJ, Weisener CG, Moreau M, Johannessen B, Harmer SL (2016) Cu(II) removal by anoxybacillus flavithermus–iron oxide composites during the addition of Fe(II) aq. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 172:139–158
Gadd GM (2010) Metals, minerals and microbes: geomicrobiology and bioremediation. Microbiology 156:609–643
Glasauer S, Langley S, Beveridge TJ (2001) Sorption of Fe (hydr)oxides to the surface of Shewanella putrefaciens: cell-bound fine-grained minerals are not always formed de novo. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:5544–5550
Guo X, Wu Z, He M, Meng X, Jin X, Qiu N, Zhang J (2014) Adsorption of antimony onto iron oxyhydroxides: adsorption behavior and surface structure. J Hazard Mater 276:339–345
He M, Wang X, Wu F, Fu Z (2012) Antimony pollution in China. Sci Total Environ 421-422:41–50
Herath I, Vithanage M, Bundschuh J (2017) Antimony as a global dilemma: geochemistry, mobility, fate and transport. Environ Pollut 223:545–559
Huang W, Cheng W, Nie X, Dong F, Ding C, Liu M, Li Z, Hayat T, Alharbi NS (2017) Microscopic and spectroscopic insights into uranium phosphate mineral precipitated by Bacillus Mucilaginosus. ACS Earth Space Chem 1:483–492
Ji Y, Sarret G, Schulin R, Tandy S (2017) Fate and chemical speciation of antimony (Sb) during uptake, translocation and storage by rye grass using XANES spectroscopy. Environ Pollut 231:1322–1329
Li X, Yang H, Zhang C, Zeng G, Liu Y, Xu W, Wu Y, Lan S (2017) Spatial distribution and transport characteristics of heavy metals around an antimony mine area in Central China. Chemosphere 170:17–24
Li J, Hou H, Hosomi M (2018) Sorption-desorption of Sb(III) in different soils: kinetics and effects of the selective removal of hydroxides, organic matter, and humic substances. Chemosphere 204:371–377
Liu R, Liu F, Hu C, He Z, Liu H, Qu J (2015) Simultaneous removal of cd(II) and Sb(V) by Fe-Mn binary oxide: positive effects of cd(II) on Sb(V) adsorption. J Hazard Mater 300:847–854
Moon EM, Peacock CL (2012) Adsorption of cu(II) to ferrihydrite and ferrihydrite–bacteria composites: importance of the carboxyl group for cu mobility in natural environments. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 92:203–219
Moon EM, Peacock CL (2013) Modelling cu(II) adsorption to ferrihydrite and ferrihydrite–bacteria composites: deviation from additive adsorption in the composite sorption system. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 104:148–164
Nakamaru YM, Martin Peinado FJ (2017) Effect of soil organic matter on antimony bioavailability after the remediation process. Environ Pollut 228:425–432
Ojeda JJ, Romerogonzalez ME, Bachmann RT, Edyvean RG, Banwart SA (2008) Characterization of the cell surface and cell wall chemistry of drinking water bacteria by combining XPS, FTIR spectroscopy, modeling, and potentiometric titrations. Langmuir 24:4032–4040
Pastuszka JS, Talik E, Hacura A, Słoka J, Wlazło A (2005) Chemical characterization of airborne bacteria using X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIRS). Aerobiologia 21:181–192
Peng H, Gao P, Chu G, Pan B, Peng J, Xing B (2017) Enhanced adsorption of cu(II) and cd(II) by phosphoric acid-modified biochars. Environ Pollut 229:846–853
Pierart A, Dumat C, Maes AQ, Sejalon-Delmas N (2018) Influence of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on antimony phyto-uptake and compartmentation in vegetables cultivated in urban gardens. Chemosphere 191:272–279
Qi P, Pichler T (2016) Sequential and simultaneous adsorption of Sb(III) and Sb(V) on ferrihydrite: implications for oxidation and competition. Chemosphere 145:55–60
Qu C, Du H, Ma M, Chen W, Cai P, Huang Q (2018a) Pb sorption on montmorillonite-bacteria composites: a combination study by XAFS, ITC and SCM. Chemosphere 200:427–436
Qu C, Ma M, Chen W, Cai P, Yu X-Y, Feng X, Huang Q (2018b) Modeling of cd adsorption to goethite-bacteria composites. Chemosphere 193:943–950
Rakshit S, Sarkar D, Punamiya P, Datta R (2011) Antimony sorption at gibbsite–water interface. Chemosphere 84:480–483
Rakshit S, Sarkar D, Datta R (2015) Surface complexation of antimony on kaolinite. Chemosphere 119:349–354
Schwertmann HCU, Cornell RM (2000) Iron oxides in the laboratory: preparation and characterization. Clay Miner 27:393–393
Sun F, Yan Y, Liao H, Bai Y, Xing B, Wu F (2014) Biosorption of antimony(V) by freshwater Cyanobacteria microcystis from Lake Taihu, China: effects of pH and competitive ions. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21:5836–5848
Templeton AS, Spormann AM, Brown GE (2003) Speciation of Pb(II) sorbed by Burkholderia cepacia/goethite composites. Environ Sci Technol 37:2166–2172
Thanabalasingam P, Pickering WF (1990) Specific sorption of antimony (III) by the hydrous oxides of Mn, Fe, and Al. Water Air Soil Pollut 49:175–185
Uluozlu OD, Sarı A, Tuzen M (2010) Biosorption of antimony from aqueous solution by lichen (Physcia tribacia) biomass. Chem Eng J 163:382–388
Villalobos M, Leckie JO (2001) Surface complexation modeling and FTIR study of carbonate adsorption to goethite. J Colloid Interface Sci 235:15–32
Wu H, Chen W, Rong X, Cai P, Dai K, Huang Q (2014) Adhesion of Pseudomonas putida onto kaolinite at different growth phases. Chem Geol 390:1–8
Xi J, He M (2013) Removal of Sb(III) and Sb(V) from aqueous media by goethite. Water. Qual Res J Can 48:223–231
Xu W, Wang H, Liu R, Zhao X, Qu J (2011) The mechanism of antimony(III) removal and its reactions on the surfaces of Fe-Mn binary oxide. J Colloid Interface Sci 363:320–326
Zhang D, Pan X, Li Z, Mu G (2011) Biosorption of antimony (Sb) by the cyanobacterium synechocystis sp. Pol J Environ Stud 20:1353–1358
Zhou S, Sato T, Otake T (2018) Dissolved silica effects on adsorption and co-precipitation of Sb(III) and Sb(V) with ferrihydrite. Minerals 8:101
Funding
This study was financially supported by the National Science Foundation of China (41671475), Environmental Protection Department of Hunan Province (Xiangcai jianzhi 2016, 59), the Education Department of Hunan Foundation (16C0225), Hunan Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (2018JJ3239), National Key R&D Program of China (2017YFD0801505), and Science Foundation for Young Scholars of Hunan Agricultural University (No: 17QN37).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Yuan Ge
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 363 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lei, M., Tao, J., Yang, R. et al. Binding of Sb(III) by Sb-tolerant Bacillus cereus cell and cell-goethite composite: implications for Sb mobility and fate in soils and sediments. J Soils Sediments 19, 2850–2858 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-019-02272-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-019-02272-z