Abstract
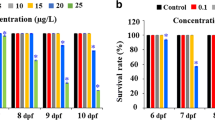
Graphene possesses unique physical and chemical properties, which have inspired a wide range of potential biomedical applications. However, little is known about the adverse effects of graphene on the human body and ecological environment. The purpose of our work is to make assessment on the toxicity of graphene oxide (GO) against human cell line (human bone marrow neuroblastoma cell line and human epithelial carcinoma cell line) and zebrafish (Danio rerio) by comparing the toxic effects of GO with its sister, multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWNTs). The results show that GO has a moderate toxicity to organisms since it can induce minor (about 20%) cell growth inhibition and slight hatching delay of zebrafish embryos at a dosage of 50 mg/L, but did not result in significant increase of apoptosis in embryo, while MWNTs exhibit acute toxicity leading to a strong inhibition of cell proliferation and serious morphological defects in developing embryos even at relatively low concentration of 25 mg/L. The distinctive toxicity of GO and MWNTs should be ascribed to the different models of interaction between nanomaterials and organisms, which arises from the different geometric structures of nanomaterials. Collectively, our work suggests that GO does actual toxicity to organisms posing potential environmental risks and the result is also shedding light on the geometrical structure-dependent toxicity of graphitic nanomaterials.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zerda ADL, Zavaleta C, Keren S, Vaithilingam S, Bodapati S, Liu Z, Levi J, Smith BR, Ma T-J, Oralkan O, Cheng Z, Chen X, Dai H, Khuri-Yakub BT, Gambhir SS. Carbon nanotubes as photoacoustic molecular imaging agents in living mice. Nat Biotech, 2008, 3: 557–562
Chen Z, Tabakman SM, Goodwin AP, Kattah MG, Daranciang D, Wang X, Zhang G, Li X, Liu Z, Utz PJ, Jiang K, Fan S, Dai H. Protein microarrays with carbon nanotubes as multicolor Raman labels. Nat Biotech, 2008, 26: 1285–1292
Zhang L, Zhen SJ, Sang Y, Li JY, Wang Y, Zhan L, Peng L, Wang J, Li YF, Huang CZ. Controllable preparation of metal nanoparticle/carbon nanotube hybrids as efficient dark field light scattering agents for cell imaging. Chem Commun, 2010, 46: 4303–4305
Liu Z, Fan AC, Rakhra K, Sherlock S, Goodwin A, Chen XY, Yang QW, Felsher DW, Dai HJ. Supramolecular stacking of doxorubicin on carbon nanotubes for in vivo cancer therapy. Angew Chem Int Ed, 2009, 48: 7668–7672
Zhen SJ, Chen LQ, Xiao SJ, Li YF, Hu PP, Zhan L, Peng L, Song EQ, Huang CZ. Carbon nanotubes as a low background signal platform for a molecular aptamer beacon on the basis of long-range resonance energy transfer. Anal Chem, 2010, 82: 8432–8437
Zhao YL, Xing GM, Chai ZF. Nanotoxicology: Are carbon nanotubes safe? Nat Nano, 2008, 3: 191–192
Schipper ML, Nakayama-Ratchford N, Davis CR, Kam NWS, Chu P, Liu Z, Sun X, Dai H, Gambhir SS. A pilot toxicology study of single-walled carbon nanotubes in a small sample of mice. Nat Nano, 2008, 3: 216–221
Jia G, Wang HF, Yan L, Wang X, Pei RJ, Yan T, Zhao YL, Guo XB. Cytotoxicity of carbon nanomaterials: Single-wall nanotube, multi-wall nanotube, and fullerene. Environ Sci Technol, 2005, 39: 1378–1383
Geim AK. Graphene: Status and prospects. Science, 2009, 324: 1530–1534
Li XL, Wang XR, Zhang L, Lee SW, Dai HJ. Chemically derived, ultrasmooth graphene nanoribbon semiconductors. Science, 2008, 319: 1229–1232
Jiang Z, Henriksen EA, Tung LC, Wang YJ, Schwartz ME, Han MY, Kim P, Stormer HL. Infrared spectroscopy of Landau levels of graphene. Phys Rev Lett, 2007, 98
Yang K, Zhang SA, Zhang GX, Sun XM, Lee ST, Liu ZA. Graphene in mice: Ultrahigh in vivo tumor uptake and efficient photothermal therapy. Nano Lett, 2010, 10: 3318–3323
Castro Neto AH, Guinea F, Peres NMR, Novoselov KS, Geim AK. The electronic properties of graphene. Rev Modern Phys, 2009, 81: 109–162
Li N, Zhang X, Song Q, Su R, Zhang Q, Kong T, Liu L, Jin G, Tang M, Cheng G. The promotion of neurite sprouting and outgrowth of mouse hippocampal cells in culture by graphene substrates. Biomaterials, 2011, 32: 9374–9382
Liu Z, Robinson JT, Sun X, Dai H. PEGylated nanographene oxide for delivery of water-insoluble cancer drugs. J Am Chem Soc, 2008, 130: 10876–10877
Yang K, Wan J, Zhang S, Zhang Y, Lee S-T, Liu Z. In vivo pharmacokinetics, long-term biodistribution, and toxicology of PEGylated graphene in mice. Acs Nano, 2010, 5: 516–522
Chang Y, Yang ST, Liu JH, Dong E, Wang Y, Cao A, Liu Y, Wang H. In vitro toxicity evaluation of graphene oxide on A549 cells. Toxicol Lett, 2011, 200: 201–210
Wang K, Ruan J, Song H, Zhang J, Wo Y, Guo S, Cui D. Biocompatibility of graphene oxide. Nanoscale Res Lett, 2011, 6: 1–8
Zhang YB, Ali SF, Dervishi E, Xu Y, Li ZR, Casciano D, Biris AS. Cytotoxicity effects of graphene and single-wall carbon nanotubes in neural phaeochromocytoma-derived PC12 cells. Acs Nano, 2010, 4: 3181–3186
Hu W, Peng C, Lv M, Li X, Zhang Y, Chen N, Fan C, Huang Q. Protein corona-mediated mitigation of cytotoxicity of graphene oxide. Acs Nano, 2011, 5: 3693–3700
Liao KH, Lin YS, Macosko CW, Haynes CL. Cytotoxicity of graphene oxide and graphene in human erythrocytes and skin fibroblasts. Acs Appl Mater Interface, 2011, 3: 2607–2615
Akhavan O, Ghaderi E. Toxicity of graphene and graphene oxide nanowalls against bacteria. Acs Nano, 2010, 4: 5731–5737
Hu W, Peng C, Luo W, Lv M, Li X, Li D, Huang Q, Fan C. Graphene-based antibacterial paper. Acs Nano, 2010, 4: 4317–4323
Liu S, Zeng TH, Hofmann M, Burcombe E, Wei J, Jiang R, Kong J, Chen Y. Antibacterial activity of graphite, graphite oxide, graphene oxide, and reduced graphene oxide: membrane and oxidative stress. Acs Nano, 2011, 5: 6971–6980
Sanchez VC, Jachak A, Hurt RH, Kane AB. Biological interactions of graphene-family nanomaterials: an interdisciplinary review. Chem. Res Toxicol, 2012, 25: 15–34
Zhang L, Huang CZ, Li YF, Xiao SJ, Xie JP. Label-free detection of sequence-specific DNA with multiwalled carbon nanotubes and their light scattering signals. J Phys Chem B, 2008, 112: 7120–7122
Hu P, Huang CZ, Li YF, Ling J, Liu YL, Fei LR, Xie JP. Magnetic particle-based sandwich sensor with DNA-modified carbon nanotubes as recognition elements for detection of DNA hybridization. Anal Chem, 2008, 80: 1819–1823
Park S, Ruoff RS. Chemical methods for the production of graphenes. Nat Nano, 2009, 4: 217–224
Chen LQ, Xiao SJ, Peng L, Wu T, Ling J, Li YF, Huang CZ. Aptamer-based silver nanoparticles used for intracellular protein imaging and single nanoparticle spectral analysis. J Phys Chem B, 2010, 114: 3655–3659
Kimmel CB, Ballard WW, Kimmel SR, Ullmann B, Schilling TF. Stages of embryonic development of the zebrafish. Dev Dynam, 1995, 203: 253–310
Usenko CY, Harper SL, Tanguay RL. In vivo evaluation of carbon fullerene toxicity using embryonic zebrafish. Carbon, 2007, 45: 1891–1898
Welsher K, Liu Z, Daranciang D, Dai H. Selective probing and imaging of cells with single walled carbon nanotubes as near-Infrared fluorescent molecules. Nano Lett, 2008, 8: 586–590
Brunner TJ, Wick P, Manser P, Spohn P, Grass RN, Limbach LK, Bruinink A, Stark WJ. In vitro cytotoxicity of oxide nanoparticles: Comparison to asbestos, silica, and the effect of particle solubility. Environ Sci Technol, 2006, 40: 4374–4381
Fako VE, Furgeson DY. Zebrafish as a correlative and predictive model for assessing biomaterial nanotoxicity. Adv Drug Del Rev, 2009, 61: 478–486
Cheng JP, Flahaut E, Cheng SH. Effect of carbon nanotubes on developing zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryos. Environ Toxicol Chem, 2007, 26: 708–716
Hallare AV, Köhler HR, Triebskorn R. Developmental toxicity and stress protein responses in zebrafish embryos after exposure to diclofenac and its solvent, DMSO. Chemosphere, 2004, 56: 659–666
Chen X, Tam UC, Lee GS, Rabuka D, Zettl A, Bertozzi CR. Interfacing carbon nanotubes with living cells. J Am Chem Soc, 2006, 128: 6292–6293
Liu XY, Vinson D, Abt D, Hurt RH, Rand DM. Differential toxicity of carbon nanomaterials in drosophila: Larval dietary uptake Is benign, but adult exposure causes locomotor impairment and mortality. Environ Sci Technol, 2009, 43: 6357–6363
Pyati UJ, Look AT, Hammerschmidt M. Zebrafish as a powerful vertebrate model system for in vivo studies of cell death. Semin Cancer Biol, 2007, 17: 154–165
Liu B, Li X, Li B, Xu B, Zhao Y. Carbon nanotube based artificial water channel protein: Membrane perturbation and water transportation. Nano Lett, 2009, 9: 1386–1394
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, L., Hu, P., Zhang, L. et al. Toxicity of graphene oxide and multi-walled carbon nanotubes against human cells and zebrafish. Sci. China Chem. 55, 2209–2216 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11426-012-4620-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11426-012-4620-z