Abstract
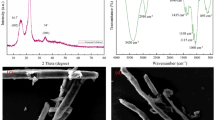
Nanofiber membranes from the composite of cellulose acetate/polyvinylpyrrolidone were prepared using electrospinning technique. After treated with water and alcoholic KOH to remove partially polyvinylpyrrolidone and deacetylate the cellulose acetate, the membranes were further functionalized with thiol groups using thioglycolic acid. Related materials were characterized using infrared and thermogravimetric analysis. And the results showed that the membranes were success of functionalisation. Then the nanofiber membranes were used in the sorption-desorption process. The effects of pH, contacting time and adsorption capacity of nanofiber membranes were studied against Cu(II), Cd(II) and Pb(II) ions. And the maximum adsorption capacities of Pb (II), Cu (II), and Cd (II) ions were estimated at 30.96, 19.63, 34.70 mg g−1. Our results suggested that the adsorption behaviour of metal ions could be described using Langmuir model. Their adsorption kinetics was in agreement with the model of pseudo-second order, suggesting chemical adsorption as the rate-limiting step of the adsorption mechanism. The durability of the thiol-functionalized cellulose nanofiber membranes was also evaluated by repetitive adsorption-desorption.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yang H, Xu R, Xue X, Li F, Li G. Hybrid surfactant-templated mesoporous silica formed in ethanol and its application for heavy metal removal. J Hazard Mater, 2008, 152:690–698
Chen YL, Ko MS, Lai YC, Chang JE. Hydration and leaching characteristics of cement pastes made from electroplating sludge. Waste Manag, 2011, 31:1357–1363
Nabi SA, Shahadat M, Bushra R, Shalla AH, Azam A. Synthesis and characterization of nano-composite ion-exchanger; its adsorption behavior. Colloids Surf, B, 2011, 87:122–128
Zhao X, Song L, Fu J, Tang P, Liu F. Adsorption characteristics of Ni(II) onto MA-DTPA/PVDF chelating membrane. J Hazard Mater, 2011, 189:732–740
Moreno-Piraján JC, Garcia-Cuello VS, Giraldo L. The removal and kinetic study of Mn, Fe, Ni and Cu ions from wastewater onto activated carbon from coconut shells. Adsorption, 2010, 17:505–514
Turan NG. Metal uptake from aqueous leachate of poultry litter by natural zeolite. Environ Prog Sustain, 2011, 30:152–159
Katsou E, Malamis S, Tzanoudaki M, Haralambous KJ, Loizidou M. Regeneration of natural zeolite polluted by lead and zinc in wastewater treatment systems. J Hazard Mater, 2011, 189:773–786
Lee YC, Chang SP. The biosorption of heavy metals from aqueous solution by Spirogyra and Cladophora filamentous macroalgae. Bioresour Technol, 2011, 102:5297–5304
Allouche FN, Mameri N, Guibal E. Pb(II) biosorption on Posidonia oceanica biomass. Chem Eng J, 2011, 168:1174–1184
Trakulsujaritchok T, Noiphom N, Tangtreamjitmun N, Saeeng R. Adsorptive features of poly(glycidyl methacrylate-co-hydroxyethyl methacrylate): effect of porogen formulation on heavy metal ion adsorption. J Mater Sci, 2011, 46:5350–5362
Wang B, Wang Y, Yin T, Yu Q. Applications of Electrospinning Technique in Drug Delivery, Chem Eng Commun, 2010, 197: 1315–1338
Wu Y, Jia W, An Q, Liu Y, Chen J, Li G. Multiaction antibacterial nanofibrous membranes fabricated by electrospinning: an excellent system for antibacterial applications. Nanotechnology, 2009, 20: 245101
Kulkarni A, Bambole VA, Mahanwar PA. Electrospinning of Polymers, Their Modeling and Applications. Polym Plast Technol Eng, 2010; 49: 427–441
Agarwal S, Wendorff JH, Greiner A. Progress in the field of electrospinning for tissue engineering applications. Adv Mater, 2009, 21:3343–3351
Shalumon KT, Binulal NS, Selvamurugan N, Nair SV, Menon D, Furuike T, Tamura H, Jayakumar R. Electrospinning of carboxymethyl chitin/poly(vinyl alcohol) nanofibrous scaffolds for tissue engineering applications. Carbohydr Polym, 2009, 77:863–869
Huang C, Chen S, Reneker DH, Lai C, Hou H. High-strength mats from electrospun poly(p-phenylene biphenyltetracarboximide) nanofibers. Adv Mater, 2006, 18:668–671
Ki C, Gang E, Um I, Park Y. Nanofibrous membrane of wool keratose/silk fibroin blend for heavy metal ion adsorption. J Membr Sci, 2007, 302:20–26
Tian Y, Wu M, Liu R, Li Y, Wang D, Tan J, Wu R, Huang Y. Electrospun membrane of cellulose acetate for heavy metal ion adsorption in water treatment. Carbohydr Polym, 2011, 83:743–748
Stephen M, Catherine N, Brenda M, Andrew K, Leslie P, Corrine G. Oxolane-2,5-dione modified electrospun cellulose nanofibers for heavy metals adsorption. J Hazard Mater, 2011, 192:922–927
Neghlani PK, Rafizadeh M, Taromi FA. Preparation of aminated-polyacrylonitrile nanofiber membranes for the adsorption of metal ions: comparison with microfibres. J Hazard Mater, 2011, 186:182–189
Kampalanonwat P, Supaphol P. Preparation and adsorption behavior of aminated electrospun polyacrylonitrile nanofiber mats for heavy metal ion removal. Appl Mater Interface, 2010, 2:3619–3627
Wu S, Li F, Wang H, Fu L, Zhang B, Li G. Effects of poly (vinyl alcohol) (PVA) content on preparation of novel thiol-functionalized mesoporous PVA/SiO2 composite nanofiber membranes and their application for adsorption of heavy metal ions from aqueous solution, Polymer, 2010, 51: 6203–6211
Ma Z, Ji H, Teng Y, Dong G, Zhou J, Tan D, Qiu J. Engineering and optimization of nano- and mesoporous silica fibres using sol-gel and electrospinning techniques for sorption of heavy metal ions. J Colloid Interface Sci, 2011, 358:547–553
Teng M, Wang H, Li F, Zhang B. Thioether-functionalized mesoporous fibre membranes: sol-gel combined electrospun fabrication and their applications for Hg2+ removal. J Colloid Interface Sci, 2011, 355:23–28
Wu Y, Zhang B, Li F, Zhu W, Xu D, Hannam P, Li G. Electrospun fibrous mats as a skeleton for fabricating hierarchically structured materials as sorbents for Cu2+. J Mater Chem, 2012, 22:5089–5097
Lin Y, Cai W, He H, Wang X, Wang G. Three dimensional hierarchically structured PAN@c-AlOOH fiber films based on a fiber templated hydrothermal route and their recycleable strong Cr(VI)-removal performance. RSC A dv, 2012, 2:1769–1773
Wang M, Meng G, Huang Q, Qian T. Electrospun 1,4-DHAQ-Doped cellulose nanofiber films for reusable fluorescence detection of trace Cu2+ and further for Cr3+. Environ Sci Technol, 2012, 46:367–373
Sun M, Ding B, Yu J. Sensitive metal ion sensors based on fibrous polystyrene membranes modified by polyethyleneimine. RSC Adv, 2012, 2:1373–1378
Liu H, Hsieh YL. Ultrafine fibrous cellulose membranes from electrospinning of cellulose acetate. J Polym Sci, Part B:Polym Phys, 2002, 40:2119–2129
Zhang L, Hsieh YL. Ultrafine Cellulose Acetate Fibres with Nanoscale Structural Features, J. Nanosci Nanotechno, 2008, 8:4461–4469
Wang QC, Zhang L, Zhao ZG. A method of preparing mercapto cotton. CN Patent, 2003, 200310115874.3
Ma Z, Ramakrishna S. Electrospun regenerated cellulose nanofiber affinity membrane functionalized with protein A/G for IgG purification. J Membr Sci, 2008, 319:23–28
Sharma R, Ahuja M. Thiolated pectin: Synthesis, characterization and evaluation as a mucoadhesive polymer. Carbohydr Polym, 2011, 85:658–663
Soeriyadi AH, Li GZ, Slavin S, Jones MW, Amos CM, Becer CR, Whittaker MR, Haddleton DM, Boyer C, Davis TP. Synthesis and modification of thermoresponsive poly(oligo(ethylene glycol) methacrylate) via catalytic chain transfer polymerization and thiol-ene Michael addition. Polym Chem, 2011, 2:815
John A. Dean, Lang’s Handbook of Chemistry, fifteenth edition, McGraw-Hill, Inc. New York, 1998
Paulino AT, Belfiore LA, Kubota LT, Muniz EC, Almeida VC, Tambourgi EB. Effect of magnetite on the adsorption behavior of Pb(II), Cd(II), and Cu(II) in chitosan-based hydrogels. Desalination, 2011, 275:187–196
Marina Šćiban BR, Žarko K, Mile K. Adsorption of heavy metals from electroplating wastewater by wood sawdust. Bioresour Technol, 2007, 98:402–409
Al-Johani H, Abdel Salam M. Kinetics and thermodynamic study of aniline adsorption by multi-walled carbon nanotubes from aqueous solution. J Colloid Interface Sci, 2011, 360:760–767
Ho YS. Review of second-order models for adsorption systems. J Hazard Mater, 2006, 136:681–689
Jihoon Cha MC, Jang M, Cho SH, Moon DH, Khim J. Kinetic and mechanism studies of the adsorption of lead onto waste cow bone powder (WCBP) surfaces. Environ Geochem Health, 2011, 33:81–89
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiang, T., Zhang, Z., Liu, H. et al. Characterization of cellulose-based electrospun nanofiber membrane and its adsorptive behaviours using Cu(II), Cd(II), Pb(II) as models. Sci. China Chem. 56, 567–575 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11426-012-4783-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11426-012-4783-7