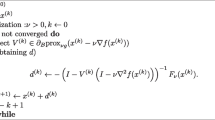Abstract
In this paper we propose an L 1/2 regularizer which has a nonconvex penalty. The L 1/2 regularizer is shown to have many promising properties such as unbiasedness, sparsity and oracle properties. A reweighed iterative algorithm is proposed so that the solution of the L 1/2 regularizer can be solved through transforming it into the solution of a series of L 1 regularizers. The solution of the L 1/2 regularizer is more sparse than that of the L 1 regularizer, while solving the L 1/2 regularizer is much simpler than solving the L 0 regularizer. The experiments show that the L 1/2 regularizer is very useful and efficient, and can be taken as a representative of the L p (0 > p > 1)regularizer.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akaike H. Information theory and an extension of the maximum likelihood principle. In: Petrov B N, Caki F, eds. Second International Symposium on Information Theory. Budapest: Akademiai Kiado, 1973. 267–281
Schwarz G. Estimating the dimension of a model. Ann Statist, 1978, 6: 461–464
Mallows C L. Some comments on Cp. Technometrics, 1973, 15: 661–675
Tibshirani R. Regression shrinkage and selection via the Lasso. J Royal Statist Soc B, 1996, 58: 267–288
Donoho D L, Huo X. Uncertainty principles and ideal atomic decomposition. IEEE Trans Inf Theory, 2001, 47: 2845–2862
Donoho D L, Elad E. Maximal sparsity representation via l 1 minimization. Proc Natl Acal Sci, 2003, 100: 2197–2202
Chen S, Donoho D L, Saunders M. Atomic decomposition by basis pursuit. SIAM Rev, 2001, 43: 129–159
Fan J, Heng P. Nonconcave penalty likelihood with a diverging number of parameters. Ann Statist, 2004, 32: 928–961
Zou H. The adaptive Lasso and its oracle properties. J Amer Statist Assoc, 2006, 101: 1418–1429
Zou H, Hastie T. Regularization and variable selection via the elastic net. J Royal Statist Soc B, 2005, 67: 301–320
Zhao P, Yu B. Stagewise Lasso. J Mach Learn Res, 2007, 8: 2701–2726
Candes E, Tao T. The Dantzig selector: Statistical estimation when p is much larger than n. Ann Statist, 2007, 35: 2313–2351
Knight K, Fu W J. Asymptotics for lasso-type estimators. Ann Statist, 2000, 28: 1356–1378
Friedman J, Hastie T, Tibshirani R. Additive logistic regression: a statistical view of boosting. Ann Statist, 2002, 28: 337–407
Efron B, Haistie T, Johnstone I, et al. Least angle regression. Ann Statist, 2004, 32: 407–499
Rosset S, Zhu J. Piecewise linear regularization solution paths. Ann Statist, 2007, 35: 1012–1030
Kim J, Koh K, Lustig M, et al. A method for large-scale l1-regularized least squares. IEEE J Se Top Signal Process, 2007, 1: 606–617
Horst R, Thoai N V. Dc programming: preview. J Optim Th, 1999, 103: 1–41
Yuille A, Rangarajan A. The concave convex procedure (CCCP). NIPS, 14. Cambridge, MA: MIT Press, 2002
Candes E, Wakin M, Boyd S. Enhancing sparsity by reweighted L1 minimization. J Fourier A, 2008, 14: 877–905
Blake C, Merz C. Repository of Machine Learning Databases [DB/OL]. Irvine, CA: University of California, Department of Information and Computer Science, 1998
Candes E, Romberg J, Tao T. Robust uncertainty principles: Exact signal reconstruction from highly incomplete frequency information. IEEE Trans Inf Theory, 2006, 52: 489–509
Donoho D L. Compressed sensing. IEEE Trans Inf Theory, 2006, 52: 1289–1306
Candes E, Tao T. Near optimal signal recovery from random projections: universal encoding strategies. IEEE Trans Inf Theory, 2006, 52: 5406–5425
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, Z., Zhang, H., Wang, Y. et al. L1/2 regularization. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 53, 1159–1169 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11432-010-0090-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11432-010-0090-0