Abstract
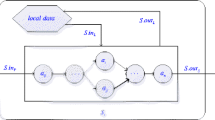
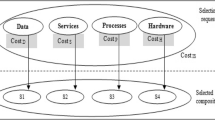
Trust plays a pivotal role in decision support for service-oriented computing networks. Recent advances in service evaluation and selection have provided some preliminary findings on the construction of composite services. However, the great expense of interdomain validations, the dynamic execution time and the subjective requirement for global execution time remain serious obstacles to the trust-based service composition. To solve these issues, this paper proposes a novel service-composition approach, modeling the trust-based service composition as the multi-domain scheduling and assignment problem using the minimum service resources within a certain time constraint. In our approach, each service is designed as an exclusive resource during its execution. By analyzing the required interdomain communications, the number of available services and the aggregated trust value in each domain, the optimal domain can be obtained at each step of service selection. Meanwhile, loop parallelization and predecessor reselection are adopted when the task cannot be completed on schedule. Finally, to raise higher trust value of the composite result, the redundant service resources of the initial composition are further optimized. The experimental results illustrate that the proposed trust-based service-composition approach outperforms traditional ones in both effectiveness and scalability under various time constraints.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Papazoglou M P. Web services and business transactions. World Wide Web, 2003, 6: 49–91
Hull R, Benedikt M, Christophides V, et al. E-services: a look behind the curtain. In: Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGMOD-SIGACT-SIGART Symposium on Principles of Database Systems, New York, 2003. 1–14
Medjahed B, Bouguettaya A, Elmagarmid A K. Composing Web services on the semantic Web. VLDB J, 2003, 12: 333–351
Vu L H, Hauswirth M, Aberer K. QoS-based service selection and ranking with trust and reputation management. In: Meersman R, Tari Z, eds. Proceedings of OTM’05. Agia Napa, Protaras, Cyprus: Springer, 2005. 466–483
Wang Y, Lin K J. Reputation-oriented trustworthy computing in e-commerce environments. IEEE Internet Comput, 2008, 12: 55–59
Jøsang A, Ismail R, Boyd C. A survey of trust and reputation systems for online service provision. Decis Support Syst, 2007, 43: 618–644
Xiao J, Boutaba R. QoS-aware service composition and adaptation in autonomic communication. IEEE J Sel Area Comm, 2005, 23: 2344–2360
She W, Yen I L, Thuraisingham B, et al. Rule-based run-time information flow control in service cloud. In: Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Web Services, Washington, 2011. 524–531
She W, Yen I L, Thuraisingham B, et al. Policy-driven service composition with information flow control. In: Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Web Services, Miami, 2010. 50–57
Xi N, Ma J F, Sun C, et al. Decentralized information flow verification framework for the service chain composition in mobile computing environments. In: Proceedings of IEEE 20th International Conference on Web Services, Santa Clara, 2013. 563–570
Hang C W, Kalia A K, Singh M P. Behind the curtain: service selection via trust in composite services. In: Proceedings of IEEE 19th International Conference on Web Services, Honolulu, 2012. 9–16
Zhang T, Ma J F, Sun C, et al. Service composition in multi-domain environment under time constraint. In: Proceedings of IEEE 20th International Conference on Web Services, Santa Clara, 2013. 227–234
Ardagna D, Pernici B. Global and local QoS constraints guarantee in Web service selection. In: Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Web Services, 2005
Ardagna D, Pernici B. Adaptive service composition in flexible processes. IEEE Trans Software Eng, 2007, 33: 369–384
Zeng L Z, Benatallah B, Ngu A H H, et al. Qos-aware middleware for web services composition. IEEE Trans Software Eng, 2004, 30: 311–327
Xiong P C, Fan Y S, Zhou M C. Qos-aware web service configuration. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cy A, 2008, 38: 888–895
Alrifai M, Risse T. Combining global optimization with local selection for efficient qos-aware service composition. In: Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on World Wide Web, New York, 2009. 881–890
Li J, Zhao Y W, Liu M, et al. An adaptive heuristic approach for distributed QoS-based service composition. In: Proceedings of 2010 IEEE Symposium on Computers and Communications, Riccione, 2010. 687–694
Li W J, Li X, Liang X J, et al. QoS-driven service composition with multiple flow structures. In: Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Services Computing, Washington, 2011. 362–369
Yu T, Zhang Y, Lin K J. Efficient algorithms for web services selection with end-to-end qos constraints. ACM Trans Web, 2007, 1: 1–26
Xu Z Q, Martin P, Powley W, et al. Reputation-enhanced qos-based web services discovery. In: Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Web Services, Salt Lake City, 2007. 249–256
Malik Z, Bouguettaya A. Rateweb: reputation assessment for trust establishment among web services. VLDB J, 2009, 18: 885–911
Li L, Wang Y, Lim E P. Trust-oriented composite service selection with qos constraints. J Univers Comput Sci, 2010, 16: 1720–1744
Menasce D. Composing web services: a QoS view. IEEE Internet Comput, 2004, 8: 88–90
Jiang J M, Zhang S, Gong P, et al. Modeling and analyzing mixed communications in service-oriented trustworthy software. Sci China Inf Sci, 2012, 55: 2738–2756
Liu X Z, Huang G, Mei H. A community-centric approach to automated service composition. Sci China Inf Sci, 2010, 53: 50–63
Shao Z L, Zhuge Q F, Xue C, et al, Efficient assignment and scheduling for heterogeneous DSP systems. IEEE Trans Parall Distr, 2005, 16: 516–525
Liu X Y, Song A L, Shao Z L, et al. Cluster based architecture synthesis minimizing the resources under time constraint. In: Proceedings of 2010 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, Dallas, 2010. 1558–1561
Li L, Wang Y. Trust evaluation in composite services selection and discovery. In: Proceedings of 2009 IEEE International Conference on Services Computing, Bangalore, 2009. 482–485
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, T., Ma, J., Li, Q. et al. Trust-based service composition in multi-domain environments under time constraint. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 57, 1–16 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11432-014-5104-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11432-014-5104-x