Abstract
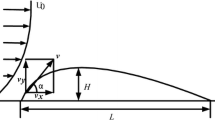
A high-speed digital camera is used to record the saltation of three sand samples (diameter range: 300–500, 200–300 and 100–125 μm). This is followed by an overlapping particle tracking algorithm to reconstruct the saltating trajectory and the differential scheme to abstract the kinetic parameters of saltating grains. The velocity results confirm the propagating feature of saltation in maintaining near-face aeolian sand transport. Moreover, the acceleration of saltating sand grains was obtained directly from the reconstructed trajectory, and the results reveal that the climbing stage of the saltating trajectory represents an critical process of energy transfer while the sand grains travel through air.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bagnold R A. The Physics of Blown Sand and Desert Dunes. London: Methuen, 1941
White B R, Schulz J C. Magnus effect on saltation. J Fluid Mech, 1977, 81: 497–512
Anderson R S, Haff P K. Simulation of aeolian saltation. Science, 1988, 241: 820–823
Anderson R S, Sorensen M, Willetts B B. A review of recent progress in our understanding of aeolian sediment transport. Acta Mech Suppl, 1991, 1: 1–20
McEwan I K, Willetts B B. Numerical model of the saltation cloud. Acta Mech Suppl 1991, l: 53–66
Sorensen M. An analytic model of wind-blown sand transport. Acta Mech Suppl, 1991, 1: 67–82
Spies P J, McEwan I K. Equilibration of saltation. Earth Surf Processes Landforms, 2000, 25: 437–453
Andreotti B, Claudin P, Douady S. Selection of dune shapes and velocities. Part 1: Dynamics of sand, wind and barchans. Eur Phys J B, 2002, 28: 321–339
Wang Y, Wang D W, Wang L, et al. Measurement of sand creep on a flat sand bed using a high-speed digital camera. Sedimentology, 2009, 56: 1705–1712
Zhang W, Kang J H, Lee S J. Tracking of saltating sand trajectories over a flat surface embedded in an atmospheric boundary layer. Geomorphology, 2007, 86: 320–321
Zhang W, Wang Y, Lee S J. Two-phase measurements of wind and saltating sand in an atmospheric boundary layer. Geomorphology, 2007, 88: 109–119
Willetts B B, Rice M A. Collisions in aeolian saltation. Acta Mech, 1986, 63: 255–265
McEwan I K, Willetts B B, Rice M A. The grain/bed collision in sand transport by wind. Sedimentology, 1992, 39: 971–981
Rice M A, Willetts B B, McEwan I K. Observation of collisions of saltating grains with a granular bed from high-speed cine-film. Sedimentology, 1996, 43: 21–31
Mitha S, Tran M Q, Werner B T, et al. The grain-bed impact process in aeolian saltation. Acta Mech, 1986, 63: 267–278
Nalpanis P, Hunt J C R, Barrett C F. Saltating particles over flat beds. J Fluid Mech, 1993, 251: 661–685
Uemura T, Yamamoto F, Ohmi K. A high-speed algorithm of image analysis for real time measurement of a two-dimensional velocity distribution. Flow Visualization ASME FED, 1989, 85: 129–134
Nishino K, Kasagi N, Hirata M. Three-dimensional particle tracking velocimetry based on automated digital image processing. J Fluid Eng, 1989, 111: 384–391
Okamoto K, Hassan Y A, Schmidl W D. New tracking algorithm for particle image velocimetry. Exp Fluids, 1995, 19: 342–347
Baek S J, Lee S J. A new two-frame particle tracking algorithm using match probability. Exp Fluids, 1996, 22: 23–32
Song X Q, Yamamoto F, Iguchi M, et al. A new tracking algorithm of PIV and removal of spurious vectors using Delaunay Tessellation. Exp Fluids, 1999, 26: 371–380
Ishikawa M, Murai Y, Wada A, et al. A novel algorithm for particle tracking velocimetry using the velocity gradient tensor. Exp Fluids, 2000, 29: 519–531
Ohmi K, Li H Y. Particle-tracking velocimetry with new algorithms. Meas Sci Technol, 2000, 11: 603–616
Wang D W, Wang Y, Yang B, et al. Statistical analysis of sand grain/bed collision process recorded by high-speed digital camera. Sedimentology, 2008, 55: 461–470
Barry B A. Errors in Practical Measurement in Science, Engineering, and Technology. New York: Wiley, 1978
Nicholas T, Xu H T, Eberhard B. A quantitative study of three-dimensional Lagrangian particle tracking algorithms. Exp Fluids, 2006, 40: 301–313
Saffman P G. The lift on a small sphere in a slow shear flow. J Fluid Mech, 1965, 6: 385–400
Rubinow A, Keller J. The transverse force on a spinning sphere moving in a viscous fluid. J Fluid Mech, 1991, 111: 447–459
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Wang, Y. & Jia, P. Measuring the kinetic parameters of saltating sand grains using a high-speed digital camera. Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 57, 1137–1143 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11433-013-5284-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11433-013-5284-1