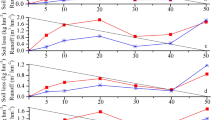
Abstract
The impact of highway construction upon surrounding ecosystems in the Longitudinal Range-Gorge Region of Southwestern China was detected based on field survey and experimental analysis. We conducted a study on Dali (from Dali City to Lijiang City) provincial road, Dabao (from Dali City to Baoshan City) highway and Baolong (from Baoshan City to Longling County) highway in the Longitudinal Range-Gorge Region to detect the effect of highway construction on surrounding soil quality using the method of space-for-time substitution, and predicted remediation of surrounding soil quality. The results showed that: (1) The effect of highway construction on both natural and cultivated soil quality is significant, and the effect is more significant in the period of highway construction than the period of highway in use. (2) The effects of highway construction is more apparent on downslope than upslope, and effect range was 200 m on downslope, while 150 m on upslope. (3) Soil remediation is mainly related to effect extent of highway construction, highway service time, vegetation restoration, soil organic matter and soil total nitrogen, among which, highway construction is the most important factor. (4) When vegetation coverage can be restored to 30% of the original condition, soil quality can be remedied to 44% of the original condition after 10 years, indicating that soil fertility remediation is rather difficult once it is destroyed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
He D M, Wu S H, Peng H, et al. A study of ecosystem changes in longitudinal range-gorge region and transboundary eco-security in southwest China. Adv Earth Sci, 2005, 20(3): 338–344
Zhu J J, Cui B S, Yang Z F, et al. Spatial distribution and variability of heavy metals contents in the topsoil along roadside in the Longitudinal Range-Gorge Region in Yunnan Province. Acta Ecolog Sin, 2006, 26(1): 146–153
Yu H. Land Rights, Reform and the Evolution of China’s Soil Resource. Beijing: Institute of Agricultural Economics, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 2002. 35–43
Zhai H J, Cui B S, Zhao X S, et al. Spatial variability and distribution of soil nutrient contents along different environmental gradients of Yilong lake shore. Acta Ecol Sin, 2006, 26(1): 61–69
Liu J, Cui B S, Yang Z F, et al. Effects caused by highway construction on plant biomass of roadsides in longitudinal range-gorge region. Acta Ecol Sin, 2006, 26(1): 83–90
Zhao J Q. Highway Traffic and Environmental Protection (in Chinese). Beijing: China Communications Press, 2002. 34–39
Yu H L, Gu W, Jiang W, et al. Research on soil quality degradation changes in expressway road area. J Soil Water Conserv, 2006, 20(4): 195–198
Auerbach N A, Walker M D, Walker D A. Effects of roadside disturbance on substrate and vegetation properties in Arctic Tundra. Ecol Appl, 1997, 7(1): 218–235
Forman R T T, Sperling D, Bissonette J A, et al. Road Ecology: Science and Solution. Washington D C. Inland Press, 2005. 3–397
Mahalinga-Lyer U, Williams D J. Properties and performance of lateriric soil in road pavement. Eng Geol, 1997, (46): 71–80
Shi D M. Study on eroded environment and its soil and water loss characteristics during expressway construction. J Soil Water Conserv, 2006, 20(2): 5–9
Pang X Y, Bao W K. Characteristic and population difference comparison of soil nutrients under cupressus Chengiana forests. J Mount Sci, 2005, 23(5): 596–605
Li J H. Effect and countermearures of soil erosion in highway construction. Chongqing Environ Sci, 2003, 25(2): 42–44
Bureau of Land administrative offices in Baoshan Prefecture of Yunnan Province. Land Resource in Baoshan Prefecture (in Chinese). Dehong: Dehong Nationalities Publishing House, 1996. 37–70
Sheng X B, Sun J Z, Liu Y X. Effect of land use and land cover on soil nutrients. Rural Eco-environ, 2002, 18(4): 10–14
Ouyang X J, Huang Z L, Zhou G Y, et al. Accumulative effects of forest community succession on soil chemical properties in dinghushan of tropical China. J Soil Water Conserv, 2003, 17(4): 51–54
Luo T S, Zhou G Y, Li Y D, et al. Distribution patterns of soil nutrients in vegetation types of Lianhuashan-Baipenzhu nature reserve. Guangdong Forest Sci Tech, 2005, 21(2): 9–13
Lou Y S, Li Z P, Zhang T L. Change in available P content in paddy soils as affected by phosphate fertilization and soil moisture regime. Soil, 2005, 37(6): 640–644
Wang H H, Yan T T, Wu S C, et al. Spatio-temporal difference of soil environmental quality in different basic farmland in Yunnan. Environ Sci Survey, 2006, 25(2): 53–55
Zheng H F, Guan D S, Liang A Z, et al. Characteristics of plant communities and soil properties of road green belts. Acta Sci Nat Univ Sunyatseni, 2006, 45(2): 114–118
Liu S L, Fu B J, Lv Y H, et al. Assessment of soil quality in relation to land use and landscape position on slope. Acta Ecolog Sin, 2003, 23(3): 414–420
Gregorich E G, Anderson D W. Effects of cultivation and erosion on soils of four toposequences in the Canadian prairies. Geoderma, 1985, 36(3–4): 343–354
Zhang Q F, Song Y C, You W H. Relationship between plant community secondary succession and soil fertility in Tiantong, Zhejiang province. Acta Ecolog Sin, 1999, 19(2): 174–178
Shen W S, Zhang H, Zhou C X, et al. Approaches to prediction of impact of Qinghai-Tibet Railway construction on alpine ecosystems alongside and its recovery. Chin Sci Bull, 2004, 49(8): 834–841
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the National Basic Research Program of China (Grant No. 2003CB415104)
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, S., Cui, B., Gao, L. et al. Effects of highway construction on soil quality in the Longitudinal Range-Gorge Region in Yunnan Province. Chin. Sci. Bull. 52 (Suppl 2), 192–202 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-007-7021-5
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-007-7021-5