Abstract
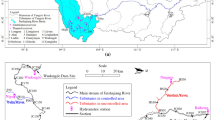
The water stored and sediment trapped by the reservoirs result in physical, chemical and ecological effects on downstream watercourse environment. Quantitative research on the reservoir sedimentation is the key to assess its environment impacts. The sediment load data obtained over 39 years at the gauging stations located in the upstream and downstream of the Manwan Reservoir were used to estimate the trapping efficiency (TE) of the Manwan Dam. The TE value was then compared with the estimates using the modified Brune and Siyam models. The results indicate that: (1) The TE of the Manwan Dam estimated by the gauging data was 60.48%, and both the TE values calculated by the modified Brune and Siyam models were 60.03%. The approximate TE values indicated that the modified Brune and Siyam models could be used to forecast the TEs of other reservoirs with similar storage capacities as the Manwan Reservoir in the mainstream of the Lancang River; (2) The TE values of Gongguoqiao, Dachaoshan and Jinghong Dams were about 30.23%, 66.05% and 63.50% estimated by the modified Brune model, and 38.81%, 63.97% and 62.30% by the modified Siyam model. The results and the methodologies adopted in the paper could also be used to estimate the TE in other river basins in southwestern China.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Milliman J D, Meade R H. World-wide delivery of river sediment to the oceans. J Geol, 1983, 91: 1–21
Milliman J D, Syvitski J P M. Geomorphic/tectonic control of sediment discharge to the ocean: The importance of small mountainous rivers. J Geol, 1992, 100: 525–544
You L Y. A study on temporal changes of river sedimentation in Lancang River Basin. Sci Geogr Sin (in Chinese), 1999, 54(supp.): 93–100
Gupta A, Hock L, Huang X J, et al. Evaluation of part of the Mekong River using satellite imagery. Geomorphology, 2002, 44(3–4): 221–239
Wolanski E, Nguyen N H, Le T D, et al. Fine sediment dynamic in the Mekong River estuary, Vietnam. Est Coast Shelf Sci, 1996, 43(5): 565–582
Blake D. Proposed Mekong dam scheme in China threatens millions in downstream countries. World Rivers Rev, 2001, 16(3): 4–5
Lu X X, Siew R Y. Water discharge and sediment flux changes over the past decades in the Lower Mekong River: Possible impacts of the Chinese dams. Hydr Earth Syst Sci, 2006, 10: 181–195
Fu K D, He D M, Li S J. Response of downstream sediment to water resource development in mainstream of the Lancang River. Chin Sci Bull, 2006, 51(Supp.): 119–126
Kummu M, Varis O. Sediment-related impacts due to upstream reservoir trapping, the Lower Mekong River. Geomorphology, 2007, 85(3–4): 275–293
He D M. Analysis of hydrological characteristics in Lancang-Mekong River. Yunnan Geogr Environ Res (in Chinese), 1995, 7(1): 58–74
Han Q W. Reservoir Deposit (in Chinese). Beijing: Science Press, 2003. 263–272, 533–641
Brune G M. Trap efficiency of reservoirs. Trans Am Geophys Union, 1953, 34(3): 407–418
Vörösmarty C J, Michel M, Balázs F, et al. Anthropogenic sediment retention: Major global impact from registered river impoundments. Glob Planet Change, 2003, 39(1–2): 169–190
He Y L, Zhang Y P. The climate characteristics and change trends on basins of Lancangjiang Valley in Yunnan Province. J Mount Sci (in Chinese), 2004, 22(5): 539–548
Qin W K, Fu R S, Wang C H. Silting of Dongting Lake before and after completion of the Three Gorges Project. J Tsinghua Univ (Sci & Tech) (in Chinese), 1998, 38(1): 84–87
Zhang Y X. Applied Calculation Methods of Reservoir Regulation (in Chinese). Beijing: China Water Power Press, 1990. 1–18
Yunnan Provincial Committee of Development and Planning, Yunnan Provincial Department of Land & Resources. Synthesis Investigation of Land and Resource in Yunnan Province Based on Remote Scene Technology (in Chinese). Kunming: Yunnan Science and Technology Press, 2004. 109–285
Li Z H, Song G B, Lü H Y, et al. Analysis of land use change and its driving force in Longitudinal Range-Gorge Region (LRGR). Chin Sci Bull, 2007, 52(supp. II): 10–20
Zhou C H, Wu S H, Dai E F, et al. Vapor corridor phenomenon and response of vegetation NPP in Longitudinal Range-Gorge Region. Chin Sci Bull, 2006, 51(Supp.): 97–107
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the National Basic Research Program of China (Grant No. 2003CB415105) and Natural Science Foundation of Yunnan Province (Grant No. 2007D003M)
About this article
Cite this article
Fu, K., He, D. Analysis and prediction of sediment trapping efficiencies of the reservoirs in the mainstream of the Lancang River. Chin. Sci. Bull. 52 (Suppl 2), 134–140 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-007-7026-0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-007-7026-0