Abstract
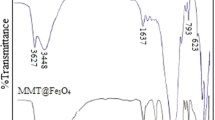
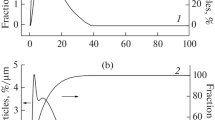
Zerovalent iron nanoparticles have been successfully synthesized using sodium borohydride solution reduction of ferric trichloride hexahydrate in the presence of montmorillonite as an effective protective reagent and support as well. A combination of characterizations reveals that with high monodispersity these obtained iron nanoparticles are well dispersed on clay surface, virginal from boron related impurity, and oxidation resistant well with iron core-iron oxide shell structure. The shell thickness of 3 nm remains almost invariable under ambient conditions. The size control of these iron nanoparticles has been achieved by tailoring the amount of the ferric iron, which mainly depends on the protective action of montmorillonite.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
López-López M T, Gómez-Ramírez A, Durán J D G, et al. Preparation and characterization of iron-based magnetorheological fluids stabilized by addition of oganoclay prticles. Langmuir, 2008, 24: 7076–7084
Stuckey D J, Carr C A, Martin-Rendon E, et al. Iron particles for noninvasive monitoring of bone marrow stromal cell engraftment into, and isolation of viable engrafted donor cells from, the heart. Stem Cells, 2006, 24: 1968–1975
Hayashi K, Ohsugi M, Kamigaki M, et al. Functional effects of carbon-coated iron metal particles for magnetic recording media. Electrochem Solid-State Lett, 2002, 5: J9–J12
Guczia L, Steflerb G, Gesztia O, et al. CO hydrogenation over cobalt and iron catalysts supported over multiwall carbon nanotubes: Effect of preparation. J Catal, 2006, 244: 24–32
Wang C B, Zhang W X. Synthesizing nanoscale iron particles for rapid and complete dechlorination of TCE and PCBs. Environ Sci Technol, 1997, 31: 2154–2156
Ponder S M, Darab J G, Mallouk T E, et al. Remediation of Cr(VI) and Pb(II) aqueous solutions using supported, nanoscale zero-valent iron. Environ Sci Technol, 2000, 34: 2564–2569
Wilkin R, McNeil M S. Laboratory evaluation of zero-valent iron to treat water impacted by acid mine drainage. Chemosphere, 2003, 53: 715–725
Sun Y P, Li X Q, Cao J, et al. Characterization of zero-valent iron nanoparticles. Adv Colloid Interface Sci, 2006, 120: 47–56
Rodrigues A R, Soares J M, Machado F L A, et al. Synthesis of α-Fe particles using a modified metal-membrane incorporation technique. J Magn Magn Mater, 2007, 310: 2497–2499
Zhang L, Manthiram A. Ambient temperature synthesis of fine metal particles in montmorillonite clay and their magnetic properties. Nanostruct Mater, 1996, 7: 437–451
Balakrishnan S, Bonder M J, Hadjipanayis G C. Particle size effect on phase and magnetic properties of polymer-coated magnetic nanoparticles. J Magn Magn Mater, 2009, 321: 117–122
Kuhn L T, Bojesen A, Timmermann L, et al. Structural and magnetic properties of core-shell iron-iron oxide nanoparticles. J Phys Condes Matter, 2002, 14: 13551–13567
Carpenter E E, Calvin S, Stroud R M, et al. Passivated iron as core-shell nanoparticles. Chem Mater, 2003, 15: 3245–3246
Shafranovsky E A, Petrov Yu I. Aerosol Fe nanoparticles with the passivating oxide shell. J Nanopart Res, 2004, 6: 71–90
Wang C M, Baer D R, Thomas L E, et al. Void formation during early stages of passivation: Initial oxidation of iron nanoparticles at room temperature. J Appl Phys, 2005, 98: 094308–094307
Mahajan D, Desai A, Rafailovich M, et al. Synthesis and characterization of nanosized metals embedded in polystyrene matrix. Composites Part B, 2006, 37: 74–80
Pal T, Sau T K, Jana N R. Reversible formation and dissolution of silver nanoparticles in aqueous surfactant media. Langmuir, 1997, 13: 1481–1485
Niu Y, Crooks R M. Dendrimer-encapsulated metal nanoparticles and their applications to catalysis. C R Chimie, 2003, 6: 1049–1059
Najman R, Cho J K, Coffey A F, et al. Entangled palladium nanoparticles in resin plugs. Chem Commun, 2007, 47: 5031–5033
Calla J T, Davis R J. Investigation of alumina-supported Au catalyst for CO oxidation by isotopic transient analysis and X-ray absorption spectroscopy. J Phys Chem B, 2005, 109: 2307–2314
Carrettin S, McMorn P, Johnston P, et al. Selective oxidation of glycerol to glyceric acid using a gold catalyst in aqueous sodium hydroxide. Chem Commun, 2002, 7: 696–697
Moreno M S, Weyland M, Midgley P A, et al. Highly anisotropic distribution of iron nanoparticles within MCM-41 mesoporous silica. Micron, 2006, 37: 52–56
Manikandan D, Divakar D, Sivakumar T. Utilization of clay minerals for developing Pt nanoparticles and their catalytic activity in the selective hydrogenation of cinnamaldehyde. Catal Commun, 2007, 8: 1781–1786
Yuan P, Fan M D, Yang D, et al. Montmorillonite-supported magnetite nanoparticles for the removal of hexavalent chromium [Cr(VI)] from aqueous solutions. J Hazard Mater, 2009, 166: 821–829
Papp S, Szel J, Oszko A, et al. Synthesis of polymer-stabilized nanosized rhodium particles in the interlayer space of layered silicates. Chem Mater, 2004, 16: 1674–1685
Király Z, Dékány I, Mastalir Á, et al. In situ generation of palladium nanoparticles in smectite clays. J Catal, 1996, 161: 401–408
Pinnavaia T J. Intercalated clay catalysts. Science, 1983, 220: 365–371
Paek S M, Jang J U, Hwang S J, et al. Exfoliation-restacking route to Au nanoparticle-clay nanohybrids. J Phys Chem Solids, 2006, 67: 1020–1023
Sun Y, Xia Y. Shape-controlled synthesis of gold and silver nanoparticles. Science, 2002, 298: 2176–2179
Bergaya F, Theng B K J, Lagaly G. Handbook of Olay Science. Amsterdam/London: Elsevier, 2006
Chen B, Evans J R G. Preferential intercalation in polymer-clay nanocomposites. J Phys Chem B, 2004, 108: 14986–14990
Mackenzie R C. A micromethod for determination of CEC of clay. J Colloid Sci, 1951, 6, 219–222
Huang K C, Ehrman S H. Synthesis of iron nanoparticles via chemical reduction with palladium ion seeds. Langmuir, 2007, 23: 1419–1426
Huang K C, Chou K S. Microstructure changes to iron nanoparticles during discharge/charge cycles. Electrochem Commun, 2007, 9: 1907–1912
Aihara N, Torigoe K, Esumi K. Preparation and characterization of gold and silver nanoparticles in layered Laponite suspensions. Langmuir, 1998, 14: 4945–4949
Fung K K, Qin B X, Zhang X X. Passivation of α-Fe nanoparticle by epitaxial γ-Fe2O3 shell. Mater Sci Eng A, 2000, 286: 135–138
Király Z, Veisz B, Mastalir Á, et al. Preparation of ultrafine palladium particles on cationic and anionic clays, mediated by oppositely charged surfactants: Catalytic probes in hydrogenations. Langmuir, 2001, 17: 5381–5387
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Fan, M., Yuan, P., Chen, T. et al. Synthesis, characterization and size control of zerovalent iron nanoparticles anchored on montmorillonite. Chin. Sci. Bull. 55, 1092–1099 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-010-0062-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-010-0062-1