Abstract
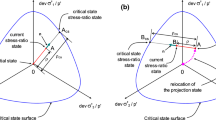
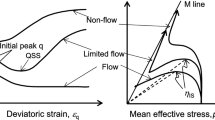
The paper describes the formulation and capabilities of a new constitutive model that accounts for the effects of fabric anisotropy on the response of granular materials under monotonic loading. It is developed within the framework of bounding surface plasticity in conjunction with the concept of (stress) reversal surfaces, i.e., the use of the last stress reversal point as projection center for defining the image stress on the bounding surface. A key constitutive ingredient is the fabric anisotropy variable A, relating the fabric tensor to the plastic strain rate direction, that acquires the value A = 1 as the third requirement for critical state according to the anisotropic critical state theory. This A is used in the definition of dilatancy, the plastic modulus and the evolution equation of the fabric tensor, thus simulating experimental results that show more dilative and stiff response when the loading is applied along the direction of the fabric. Model performance is verified against a large database of monotonic shearing tests on samples of Toyoura sand prepared with three different methods, as well as similar tests on samples whose (initially horizontal) deposition plane was rotated by up to 90 degrees. All simulations are performed with a single set of constants, thus validating the efficiency of the model to account for density, stress level and, most importantly, fabric anisotropy effects on the monotonic shearing response. The paper shows that considering dependence of strength and dilatancy on Lode angle θ and state parameter ψ does not suffice for simulating fabric anisotropy effects on sand response. It ends with a discussion of how fabric effects on sand response are more pronounced under undrained, versus drained conditions.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ando E, Viggiani G, Hall SA, Desrues J (2013) Experimental micro-mechanics of granular media studied by x-ray tomography: recent results and challenges. Géotech Lett 3:142–146
Andrianopoulos KI, Papadimitriou AG, Bouckovalas GD (2010) Bounding surface plasticity model for the seismic liquefaction analysis of geostructures. Soil Dyn Earthq Eng 30(10):895–911. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soildyn.2010.04.001
Andrianopoulos KI, Papadimitriou AG, Bouckovalas GD (2010) Explicit integration of bounding surface model for the analysis of earthquake soil liquefaction. Int J Numer Anal Methods Geomech 34(15):1586–1614. https://doi.org/10.1002/nag.875
Arthur JRF, Chua KS, Dunstan T (1977) Induced anisotropy in a sand. Géotechnique 27(1):13–30
Arthur JRF, Menzies BK (1972) Inherent anisotropy in a sand. Géotechnique 22(1):115–128
Azami A, Pietruszczak S, Guo P (2009) Bearing capacity of shallow foundations in transversely isotropic granular media. Int J Numer Anal Methods Geomech 34(8):771–793
Been K, Jefferies MG (1985) A state parameter for sands. Géotechnique 35(2):99–112
Dafalias YF (1986) Bounding surface plasticity. I: mathematical foundation and hypoplasticity. J Eng Mech, ASCE 112(9):966–987. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9399(1986)112:9(966)
Dafalias YF (2016) Must critical state theory be revisited to include fabric effects? Acta Geotech 11(3):479–491. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11440-016-0441-0
Dafalias YF, Popov EP (1975) A model of nonlinearly hardening materials for complex loading. Acta Mech 21:173–192. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01181053
Dafalias YF, Manzari MT (2004) Simple plasticity sand model accounting for fabric change effects. J Eng Mech, ASCE 130(6):622–634. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9399(2004)130:6(622)
Dafalias YF, Papadimitriou AG, Li XS (2004) Sand plasticity model accounting for inherent fabric anisotropy. J Eng Mech, ASCE 130(11):1319–1333. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9399(2004)130:11(1319)
Dafalias YF, Taiebat M (2016) SANISAND-Z: zero elastic range sand plasticity model. Géotechnique 66(12):999–1013. https://doi.org/10.1680/jgeot.15.P.271
Dowell M, Jarratt P (1972) The ‘Pegasus’ method for computing the root of an equation. BIT Numer Math 12(4):503–508. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01932959
Fu P, Dafalias YF (2011) Fabric evolution within shear bands of granular materials and its relation to critical state theory. Int J Numer Anal Methods Geomech 35(18):1918–1948. https://doi.org/10.1002/nag.988
Fu P, Dafalias YF (2015) Relationship between void-and contact normal-based fabric tensors for 2D idealized granular materials. Int J Solids Struct 63:68–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijsolstr.2015.02.041
Fukushima S, Tatsuoka F (1984) Strength and deformation characteristics of saturated sand at extremely low pressures. Soils Found 24(4):30–48
Gao Z, Zhao J (2015) Constitutive modeling of anisotropic sand behavior in monotonic and cyclic loading. J Eng Mech, ASCE 141(8):04015017
Gao Z, Zhao J (2017) A non-coaxial critical state model for sand accounting for anisotropy and fabric evolution. Int J Solids Struct 106–107:202–212
Gao Z, Zhao J, Li XS, Dafalias YF (2014) A critical state sand plasticity model accounting for fabric evolution. Int J Numer Anal Methods Geomech 38:370–390
Guo N, Zhao J (2013) The signature of shear-induced anisotropy in granular media. Comput Geotech 47:1–15
Kimura T, Kusakabe O, Saitoh K (1985) Geotechnical model tests of bearing capacity problems in a centrifuge. Géotechnique 35(1):33–45
Li XS (2002) A sand model with state-dependent dilatancy. Géotechnique 52(3):173–186
Li X, Li XS (2009) Micro-macro quantification of the internal structure of granular materials. J Eng Mech, ASCE 135(7):641–656
Li XS, Dafalias YF (2002) Constitutive modeling of inherently anisotropic sand behavior. J Geotech Geoenviron Eng, ASCE 128(10):868–880. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)1090-0241(2002)128:10(868)
Li XS, Dafalias YF (2012) Anisotropic critical state theory: role of fabric. J Eng Mech, ASCE 138(3):263–275. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)EM.1943-7889.0000324
Li XS, Dafalias YF (2015) Dissipation consistent fabric tensor definition from DEM to continuum for granular media. J Mech Phys Solids 78:141–153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmps.2015.02.003
Li XS, Wang Y (1998) Linear representation of steady-state line for sand. J Geotech Geoenviron Eng, ASCE 124(12):1215–1217
Loukidis D, Salgado R (2009) Modeling sand response using two-surface plasticity. Comput Geotech 36(1):166–186
Manzari MT, Dafalias YF (1997) A critical state two-surface plasticity model for sands. Géotechnique 47(2):255–272. https://doi.org/10.1680/geot.1997.47.2.255
Miura S, Toki S (1982) A sample preparation method and its effect on static and cyclic deformation-strength properties of sand. Soils Found 22(1):61–77
Mroz Z, Norris VA, Zienkiewicz OC (1979) Application of an anisotropic hardening model in the analysis of elasto-plastic deformation of soils. Géotechnique 29(1):1–34
Mroz Z, Zienkiewicz OC (1984) Uniform formulation of constitutive equations for clays and sands. In: Desai CS, Gallagher RH (eds) Mechanics of engineering materials. Wiley, pp 415–449
Nakata Y, Hyodo M, Murata H, Yasufuku N (1998) Flow deformation of sands subjected to principal stress rotation. Soils Found 38(2):115–128
Nemat-Nasser S, Tobita Y (1982) Influence of fabric on liquefaction and densification potential of cohesionless sand. Mech Mater 1:43–62
Nicot F, Darve F (2011) The H-microdirectional model: Accounting for a mesoscopic scale. Mech Mater 43(12):918–929
Oda M, Koishikawa I (1979) Effect of strength anisotropy on bearing capacity of shallow footing in a dense sand. Soils Found 19(3):15–28
Oda M, Koishikawa I, Higuchi T (1978) Experimental study of anisotropic shear strength of sand by plane strain test. Soils Found 18(1):25–38
Oda M, Nemat-Nasser S, Konishi J (1985) Stress-induced anisotropy in granular materials. Soils Found 25(3):85–97
Papadimitriou AG, Bouckovalas GD (2002) Plasticity model for sand under small and large cyclic strains: a multiaxial formulation. Soil Dyn Earthq Eng 22(3):191–204. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0267-7261(02)00009-X
Papadimitriou AG, Bouckovalas GD, Dafalias YF (2001) Plasticity model for sand under small and large cyclic strains. J Geotech Geoenviron Eng, ASCE 127(11):973–983. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)1090-0241(2001)127:11(973)
Papadimitriou AG, Dafalias YF, Yoshimine M (2005) Plasticity modeling of the effect of sample preparation method on sand response. Soils Found 40(2):109–124. https://doi.org/10.3208/sandf.45.2_109
Pradhan TBS, Tatsuoka F, Horii N (1988) Strength and deformation characteristics of sand in torsional simple shear. Soils Found 28(3):131–148
Qin J, Zeng X, Ming H (2016) Centrifuge modeling and the influence of fabric anisotropy on seismic response of foundations. J Geotech Geoenviron Eng, ASCE 142(3):4015082
Richart FE, Hall JR, Woods RD (1970) Vibrations of soils and foundations. International series in theoretical and applied mechanics. Prentice Hall, Englewood Cliffs
Roscoe KH, Schofield AN, Wroth CP (1958) On the yielding of soils. Géotechnique 8(1):22–53
Schofield AN, Wroth CP (1968) Critical state soil mechanics. McGraw-Hill, London
Taborda DMG, Zdravkovic L, Kontoe S, Potts DM (2014) Computational study on the modification of a bounding surface plasticity model for sands. Comput Geotech 59:145–160
Taiebat M, Dafalias YF (2008) SANISAND: simple anisotropic sand plasticity model. Int J Numer Anal Methods Geomech 32:915–948. https://doi.org/10.1002/nag.651
Tatsuoka F, Ishihara K (1974) Yielding of sand in triaxial compression”. Soils Found 14(2):63–76
Tatsuoka F, Sakamoto M, Kaeamura T, Fukushima S (1986) Strength and deformation characteristics of sand in plane strain compression at extremely low pressures. Soils Found 26(1):65–84
Theocharis AI, Vairaktaris E, Dafalias YF, Papadimitriou AG (2017) Proof of incompleteness of Critical State Theory in granular mechanics and its remedy. J Eng Mech, ASCE 143(2):04016117. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)EM.1943-7889.0001166
Theocharis AI, Vairaktaris E, Dafalias YF (2017) Scan line void fabric anisotropy tensors of granular media. Granular Matter 19:68. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10035-017-0752-3
Thornton C, Zhang L (2010) On the evolution of stress and microstructure during general 3D deviatoric straining of granular media. Géotechnique 60(5):333–341
Wan RG, Guo PJ (2004) Stress dilatancy and fabric dependencies on sand behavior. J Eng Mech, ASCE 130(6):635–645
Wang R, Fu P, Zhang J-M, Dafalias YF (2017) Evolution of various fabric tensors for granular media toward the critical state. J Eng Mech, ASCE 143(1):04017117. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)EM.1943-7889.0001342
Wang ZL, Dafalias YF, Shen CK (1990) Bounding surface hypoplasticity model for sand. J Eng Mech, ASCE 116(5):983–1001. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9399(1990)116:5(983)
Woo SI, Salgado R (2015) Bounding surface modeling of sand with consideration of fabric and its evolution during monotonic shearing. Int J Solids Struct 63:277–288
Verdugo R, Ishihara K (1996) The steady state of sandy soils. Soils Found 36(2):81–91
Yang ZX, Wu Y (2017) Critical state for anisotropic granular materials: a discrete element perspective. Int J Geomech, ASCE 17(2):04016054
Yimsiri S, Soga K (2010) DEM analysis of soil fabric effects on behaviour of sand. Géotechnique 60:483–495
Yoshimine M, Ishihara K, Vargas W (1998) Effects of principal stress direction and intermediate principal stress on undrained shear behavior of sand. Soils Found 38(3):179–188
Zhao J, Gao Z (2016) Unified anisotropic elastoplastic model for sand. J Eng Mech, ASCE 142(1):04015056
Zhao J, Guo N (2013) Unique critical state characteristics in granular media considering fabric anisotropy. Géotechnique 63(8):695–704
Acknowledgements
The research leading to these results has received funding from the European Research Council (ERC) under the European Union’s Seventh Framework Program (FP7/2007-2013)/ERC IDEAS Grant Agreement n# 290963 (SOMEF) and partial support by the National Science Foundation (NSF) project CMMI-1162096. The authors are grateful to the two reviewers for their insightful comments that improved the quality of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Papadimitriou, A.G., Chaloulos, Y.K. & Dafalias, Y.F. A fabric-based sand plasticity model with reversal surfaces within anisotropic critical state theory. Acta Geotech. 14, 253–277 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11440-018-0751-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11440-018-0751-5