Abstract
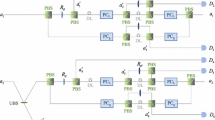
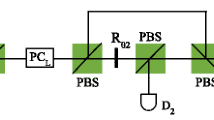
Hyperentanglement has attracted considerable attention recently because of its high-capacity for long-distance quantum communication. In this study, we present a hyperentanglement concentration protocol (hyper-ECP) for nonlocal three-photon systems in the polarization, spatial-mode, and time-bin partially hyperentangled Greenberger–Horne–Zeilinger (GHZ) states using the Schmidt projection method. In our hyper-ECP, the three distant parties must perform the parity-check measurements on the polarization, spatial-mode, and time-bin degrees of freedom, respectively, using linear optical elements and Pockels cells, and only two identical nonlocal photon systems are required. This hyper-ECP can be directly extended to the N-photon hyperentangled GHZ states, and the success probability of this general hyper-ECP for a nonlocal N-photon system is the optimal one, regardless of the photon number N.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
C. H. Bennett, G. Brassard, C. Crépeau, R. Jozsa, A. Peres, and W. K. Wootters, Teleporting an unknown quantum state via dual classical and Einstein–Podolsky–Rosen channels, Phys. Rev. Lett. 70(13), 1895 (1993)
X. F. Cai, X. T. Yu, L. H. Shi, and Z. C. Zhang, Partially entangled states bridge in quantum teleportation, Front. Phys. 9(5), 646 (2014)
P. Y. Xiong, X. T. Yu, H. T. Zhan, and Z. C. Zhang, Multiple teleportation via partially entangled GHZ state, Front. Phys. 11(4), 110303 (2016)
C. H. Bennett and S. J. Wiesner, Communication via one-and two-particle operators on Einstein–Podolsky–Rosen states, Phys. Rev. Lett. 69(20), 2881 (1992)
X. S. Liu, G. L. Long, D. M. Tong, and F. Li, General scheme for superdense coding between multiparties, Phys. Rev. A 65(2), 022304 (2002)
A. K. Ekert, Quantum cryptography based on Bell’s theorem, Phys. Rev. Lett. 67(6), 661 (1991)
C. H. Bennett, G. Brassard, and N. D. Mermin, Quantum cryptography without Bell’s theorem, Phys. Rev. Lett. 68(5), 557 (1992)
X. H. Li, F. G. Deng, and H. Y. Zhou, Efficient quantum key distribution over a collective noise channel, Phys. Rev. A 78(2), 022321 (2008)
F. Steinlechner, S. Ecker, M. Fink, B. Liu, J. Bavaresco, M. Huber, T. Scheidl, and R. Ursin, Distribution of high-dimensional entanglement via an intra-city freespace link, Nat. Commun. 8, 15971 (2017)
M. Hillery, V. Bužek, and A. Berthiaume, Quantum secret sharing, Phys. Rev. A 59(3), 1829 (1999)
G. L. Long and X. S. Liu, Theoretically efficient highcapacity quantum-key-distribution scheme, Phys. Rev. A 65(3), 032302 (2002)
F. G. Deng, G. L. Long, and X. S. Liu, Two-step quantum direct communication protocol using the Einstein–Podolsky–Rosen pair block, Phys. Rev. A 68(4), 042317 (2003)
F. G. Deng and G. L. Long, Secure direct communication with a quantum one-time pad, Phys. Rev. A 69(5), 052319 (2004)
J. Y. Hu, B. Yu, M. Y. Jing, L. T. Xiao, S. T. Jia, G. Q. Qin, and G. L. Long, Experimental quantum secure direct communication with single photons, Light Sci. Appl. 5(9), e16144 (2016)
W. Zhang, D. S. Ding, Y. B. Sheng, L. Zhou, B. S. Shi, and G. C. Guo, Quantum secure direct communication with quantum memory, Phys. Rev. Lett. 118(22), 220501 (2017)
X. H. Li, Quantum secure direct communication, Acta Physica Sinica 64, 160307 (2015)
F. Zhu, W. Zhang, Y. B. Sheng, and Y. D. Huang, Experimental long-distance quantum secure direct communication, Sci. Bull. 62(22), 1519 (2017)
L. Zhou and Y. B. Sheng, Recyclable amplification protocol for the single-photon entangled state, Laser Phys. Lett. 12(4), 045203 (2015)
L. Zhou and Y. B. Sheng, Complete logic Bell-state analysis assisted with photonic Faraday rotation, Phys. Rev. A 92(4), 042314 (2015)
Y. B. Sheng and L. Zhou, Two-step complete polarization logic Bell-state analysis, Sci. Rep. 5(1), 13453 (2015)
P. G. Kwiat, Hyper-entangled states, J. Mod. Opt. 44(11–12), 2173 (1997)
T. Yang, Q. Zhang, J. Zhang, J. Yin, Z. Zhao, M. Zukowski, Z. B. Chen, and J. W. Pan, All-versusnothing violation of local realism by two-photon, fourdimensional entanglement, Phys. Rev. Lett. 95(24), 240406 (2005)
J. T. Barreiro, N. K. Langford, N. A. Peters, and P. G. Kwiat, Generation of hyperentangled photon pairs, Phys. Rev. Lett. 95(26), 260501 (2005)
M. Barbieri, C. Cinelli, P. Mataloni, and F. De Martini, Polarization-momentum hyperentangled states: realization and characterization, Phys. Rev. A 72(5), 052110 (2005)
R. Ceccarelli, G. Vallone, F. De Martini, P. Mataloni, and A. Cabello, Experimental entanglement and nonlocality of a two-photon six-qubit cluster state, Phys. Rev. Lett. 103(16), 160401 (2009)
G. Vallone, R. Ceccarelli, F. De Martini, and P. Mataloni, Hyperentanglement of two photons in three degrees of freedom, Phys. Rev. A 79(3), 030301 (2009)
D. Bhatti, J. von Zanthier, and G. S. Agarwal, Entanglement of polarization and orbital angular momentum, Phys. Rev. A 91(6), 062303 (2015)
F. G. Deng, B. C. Ren, and X. H. Li, Quantum hyperentanglement and its applications in quantum information processing, Sci. Bull. 62(1), 46 (2017)
B. C. Ren and F. G. Deng, Hyper-parallel photonic quantum computation with coupled quantum dots, Sci. Rep. 4(1), 4623 (2015)
B. C. Ren, G. Y. Wang, and F. G. Deng, Universal hyperparallel hybrid photonic quantum gates with dipoleinduced transparency in the weak-coupling regime, Phys. Rev. A 91(3), 032328 (2015)
T. Li and G. L. Long, Hyperparallel optical quantum computation assisted by atomic ensembles embedded in double-sided optical cavities, Phys. Rev. A 94(2), 022343 (2016)
H. R. Wei, F. G. Deng, and G. L. Long, Hyper-parallel Toffoli gate on three-photon system with two degrees of freedom assisted by single-sided optical microcavities, Opt. Express 24(16), 18619 (2016)
B. C. Ren and F. G. Deng, Robust hyperparallel photonic quantum entangling gate with cavity QED, Opt. Express 25(10), 10863 (2017)
Y. B. Sheng, F. G. Deng, and G. L. Long, Complete hyperentangled-Bell-state analysis for quantum communication, Phys. Rev. A 82(3), 032318 (2010)
B. C. Ren, H. R. Wei, M. Hua, T. Li, and F. G. Deng, Complete hyperentangled-Bell-state analysis for photon systems assisted by quantum-dot spins in optical microcavities, Opt. Express 20(22), 24664 (2012)
T. C. Wei, J. T. Barreiro, and P. G. Kwiat, Hyperentangled Bell-state analysis, Phys. Rev. A 75(6), 060305 (2007)
T. J. Wang, Y. Lu, and G. L. Long, Generation and complete analysis of the hyperentangled Bell state for photons assisted by quantum-dot spins in optical microcavities, Phys. Rev. A 86(4), 042337 (2012)
Q. Liu and M. Zhang, Generation and complete nondestructive analysis of hyperentanglement assisted by nitrogen-vacancy centers in resonators, Phys. Rev. A 91(6), 062321 (2015)
G. Y. Wang, Q. Ai, B. C. Ren, T. Li, and F. G. Deng, Error-detected generation and complete analysis of hyperentangled Bell states for photons assisted by quantum-dot spins in double-sided optical microcavities, Opt. Express 24(25), 28444 (2016)
T. J. Wang, S. Y. Song, and G. L. Long, Quantum repeater based on spatial entanglement of photons and quantum-dot spins in optical microcavities, Phys. Rev. A 85(6), 062311 (2012)
P. G. Kwiat and H. Weinfurter, Embedded Bell-state analysis, Phys. Rev. A 58(4), R2623 (1998)
S. P. Walborn, S. P’adua, and C. H. Monken, Hyperentanglement-assisted Bell-state analysis, Phys. Rev. A 68(4), 042313 (2003)
C. Schuck, G. Huber, C. Kurtsiefer, and H. Weinfurter, Complete deterministic linear optics Bell state analysis, Phys. Rev. Lett. 96(19), 190501 (2006)
M. Barbieri, G. Vallone, P. Mataloni, and F. De Martini, Complete and detrministic deicrimination of polarization Bell states assisted by momentum entanglement, Phys. Rev. A 75(4), 042317 (2007)
Y. B. Sheng and F. G. Deng, Deterministic entanglement purification and complete nonlocal Bell-state analysis with hyperentangledment, Phys. Rev. A 81(3), 032307 (2010)
Y. B. Sheng and F. G. Deng, One-step deterministic polarization-entanglement purification using spatial entanglement, Phys. Rev. A 82(4), 044305 (2010)
X. H. Li, Deterministic polarization-entanglement purification using spatial entanglement, Phys. Rev. A 82(4), 044304 (2010)
F. G. Deng, One-step error correction for multipartite polarization entanglement, Phys. Rev. A 83(6), 062316 (2011)
Y. B. Sheng and L. Zhou, Deterministic polarization entanglement purification using time-bin entanglement, Laser Phys. Lett. 11(8), 085203 (2014)
B. C. Ren, F. F. Du, and F. G. Deng, Twostep hyperentanglement purification with the quantumstatejoining method, Phys. Rev. A 90(5), 052309 (2014)
G. Y. Wang, Q. Liu, and F. G. Deng, Hyperentanglement purification for two-photon six-qubit quantum systems, Phys. Rev. A 94(3), 032319 (2016)
C. H. Bennett, H. J. Bernstein, S. Popescu, and B. Schumacher, Concentrating partial entanglement by local operations, Phys. Rev. A 53(4), 2046 (1996)
Z. Zhao, J. W. Pan, and M. S. Zhan, Practical scheme for entanglement concentration, Phys. Rev. A 64(1), 014301 (2001)
T. Yamamoto, M. Koashi, and N. Imoto, Concentration and purification scheme for two partially entangled photon pairs, Phys. Rev. A 64(1), 012304 (2001)
Y. B. Sheng, F. G. Deng, and H. Y. Zhou, Nonlocal entanglement concentration scheme for partially entangled multipartite systems with nonlinear optics, Phys. Rev. A 77(6), 062325 (2008)
C. Wang, Efficient entanglement concentration for partially entangled electrons using a quantum-dot and microcavity coupled system, Phys. Rev. A 86(1), 012323 (2012)
S. Bose, V. Vedral, and P. L. Knight, Purification via entanglement swapping and conserved entanglement, Phys. Rev. A 60(1), 194 (1999)
B. S. Shi, Y. K. Jiang, and G. C. Guo, Optimal entanglement purification via entanglement swapping, Phys. Rev. A 62(5), 054301 (2000)
Y. B. Sheng, L. Zhou, S. M. Zhao, and B. Y. Zheng, Efficient single-photon-assisted entanglement concentration for partially entangled photon pairs, Phys. Rev. A 85(1), 012307 (2012)
F. G. Deng, Optimal nonlocal multipartite entanglement concentration based on projection measurements, Phys. Rev. A 85(2), 022311 (2012)
Y. B. Sheng, L. Zhou, and S. M. Zhao, Efficient twostep entanglement concentration for arbitraryWstates, Phys. Rev. A 85(4), 042302 (2012)
C. Cao, C. Wang, L. Y. He, and R. Zhang, Atomic entanglement purification and concentration using coherent state input-output process in low-Q cavity QED regime, Opt. Express 21(4), 4093 (2013)
X. Yan, Y. F. Yu, and Z. M. Zhang, Entanglement concentration for a non-maximally entangled four-photon cluster state, Front. Phys. 9(5), 640 (2014)
C. Cao, H. Ding, Y. Li, T. J. Wang, S. C. Mi, R. Zhang, and C. Wang, Efficient multipartite entanglement concentration protocol for nitrogen-vacancy center and microresonator coupled systems, Quantum Inform. Process. 14(4), 1265 (2015)
C. Wang, W. W. Shen, S. C. Mi, Y. Zhang, and T. J. Wang, Concentration and distribution of entanglement based on valley qubits system in graphene, Sci. Bull. 60(23), 2016 (2015)
C. Cao, T. J. Wang, R. Zhang, and C. Wang, Cluster state entanglement generation and concentration on nitrogen-vacancy centers in decoherence-free subspace, Laser Phys. Lett. 12(3), 036001 (2015)
Y. B. Sheng, J. Pan, R. Guo, L. Zhou, and L. Wang, Efficient N-particle W state concentration with different parity check gates, Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 58(6), 060301 (2015)
C. Shukla, A. Banerjee, and A. Pathak, Protocols and quantum circuits for implementing entanglement concentration in cat state, GHZ-like state and nine families of 4-qubit entangled states, Quantum Inform. Process. 14(6), 2077 (2015)
J. Pan, L. Zhou, S. P. Gu, X. F. Wang, Y. B. Sheng, and Q. Wang, Efficient entanglement concentration for concatenated Greenberger–Horne–Zeilinger state with the cross-Kerr nonlinearity, Quantum Inform. Process. 15(4), 1669 (2016)
C. Cao, X. Chen, Y. W. Duan, L. Fan, R. Zhang, T. J. Wang, and C. Wang, Concentrating partially entangled W-class states on nonlocal atoms using low-Q optical cavity and linear optical elements, Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 59(10), 100315 (2016)
B. C. Ren, F. F. Du, and F. G. Deng, Hyperentanglement concentration for two-photon four-qubit systems with linear optics, Phys. Rev. A 88(1), 012302 (2013)
B. C. Ren and F. G. Deng, Hyperentanglement purication and concentration assisted by diamond NV centers inside photonic crystal cavities, Laser Phys. Lett. 10(11), 115201 (2013)
B. C. Ren and G. L. Long, General hyperentanglement concentration for photon systems assisted by quantum dot spins inside optical microcavities, Opt. Express 22(6), 6547 (2014)
X. H. Li and S. Ghose, Hyperconcentration for multipartite entanglement via linear optics, Laser Phys. Lett. 11(12), 125201 (2014)
X. H. Li and S. Ghose, Efficient hyperconcentration of nonlocal multipartite entanglement via the cross-Kerr nonlinearity, Opt. Express 23(3), 3550 (2015)
B. C. Ren and G. L. Long, Highly efficient hyperentanglement concentration with two steps assisted by quantum swap gates, Sci. Rep. 5(1), 16444 (2015)
X. H. Li and S. Ghose, Hyperentanglement concentration for time-bin and polarization hyperentangled photons, Phys. Rev. A 91(6), 062302 (2015)
C. Cao, T. J. Wang, S. C. Mi, R. Zhang, and C. Wang, Nonlocal hyperconcentration on entangled photons using photonic module system, Ann. Phys. 369, 128 (2016)
L. L. Fan, Y. Xia, and J. Song, Efficient entanglement concentration for arbitrary less-hyperentanglement multi-photon W states with linear optics, Quantum Inform. Process. 13(9), 1967 (2014)
H. J. Liu, Y. Xia, and J. Song, Efficient hyperentanglement concentration for N-particle Greenberger–Horne–Zeilinger state assisted by weak cross-Kerr nonlinearity, Quantum Inform. Process. 15(5), 2033 (2016)
F. Z. Wu, G. J. Yang, H. B. Wang, J. Xiong, F. Alzahrani, A. Hobiny, and F. G. Deng, High-capacity quantum secure direct communication with two-photon six-qubit hyperentangled states, Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 60(12), 120313 (2017)
Y. Soudagar, F. Bussières, G. Berlín, S. Lacroix, J. M. Fernandez, and N. Godbout, Cluster-state quantum computing in optical fibers, J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 24(2), 226 (2007)
D. Kalamidas, Single-photon quantum error rejection and correction with linear optics, Phys. Lett. A 343(5), 331 (2005)
B. C. Ren, H. Wang, F. Alzahrani, A. Hobiny, and F. G. Deng, Hyperentanglement concentration of nonlocal two photon six-qubit systems with linear optics, Ann. Phys. 385, 86 (2017)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grants Nos. 11604226, 11674033, and 11474026, and the Science and Technology Program Foundation of the Beijing Municipal Commission of Education of China under Grant No. KM201710028005.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, H., Ren, BC., Wang, A.H. et al. General hyperentanglement concentration for polarization-spatial-time-bin multi-photon systems with linear optics. Front. Phys. 13, 130315 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11467-018-0801-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11467-018-0801-3