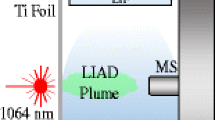
Abstract
The laser desorption/ionization (LDI) assisted by gold nanospheres, nanorods and nanostars has been investigated. Laser fluence thresholds for the appearance of cationized adducts of a polydispersed polyether standard (polyethylenglycol PEG600) have been determined at the near ultraviolet–visible–near infrared wavelengths delivered by a Nd:YAG laser (266, 355, 532, 1,064 nm). The results demonstrate the efficiency of surface plasmon excitation to assist laser desorption/ionizaton at laser wavelengths extending to the visible and near infrared, with advantages with respect to conventional LDI techniques using ultraviolet wavelengths. A close correlation is found between the optical absorbance of the nanoparticles and the LDI thresholds, although for the nanospheres plasmonic excitation in the visible appears to be more efficient than non-plasmonic excitation at shorter UV wavelengths. The recorded molecular weight distributions for the PEG600 standard show that the LDI process tends to be less efficient for the heavier components of the polymer mixture, presumably as a consequence of their stronger bonding to the nanoparticle substrate. The role of the coating agent of the nanoparticles in the observed LDI behavior is discussed.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tanaka K, Waki H, Ido Y, Akita S, Yoshida Y, Yoshida T (1988) Protein and polymer analyses up to m/z 100000 by laser ionization time–of–flight mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 2:151–153. doi:10.1002/rcm.1290020802
Sunner J, Dratz E, Chen YCh (1995) Graphite-]-assisted laser desorption/ionization time–of–flight mass spectrometry of peptides and proteins from liquid solutions. Anal Chem 67:4335–4342. doi:10.1021/ac00119a021
Owega S, Lai EPC, Bawagan ADO (1998) Surface plasmon resonance-laser desorption/ionization time–of–flight mass spectrometry. Anal Chem 70:2360–2365. doi:10.1021/ac971166u
Schürenberg M, Dreisewerd K, Hillenkamp F (1999) Laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry of peptides and proteins with particle suspension matrixes. Anal Chem 71:221–229. doi:10.1021/ac980634c
McLean JA, Stumpo KA, Russell DH (2005) Size–selected (2–10 nm) gold nanoparticles for matrix assisted laser desorption ionization of peptides. J Am Chem Soc 127:5304–5305. doi:10.1021/ja043907w
Vanderpuije BNY, Han G, Rotello VM, Vachet RW (2006) Mixed monolayer-protected gold nanoclusters as selective peptide extraction agents for MALDI-MS analysis. Anal Chem 78:5491–5496. doi:10.1021/ac0604181
Hua L, Chen JR, Ge L, Tan SN (2007) Silver nanoparticles as matrix for laser desorption/ionization of peptides. J Nanopart Res 9:1133–1138. doi:10.1007/s11051-007-9244-4
Su CL, Tseng WL (2007) Gold nanoparticles as assisted matrix for determining neutral small carbohydrates through laser desorption/ionization time–of–flight mass spectrometry. Anal Chem 79:1626–1633. doi:10.1021/ac061747w
Chen LC, Yonehama J, Ueda T, Hori H, Hirakoa K (2007) Visible-laser desorption/ionization on gold nanostructures. J Mass Spectrom 42:346–353. doi:10.1002/jms.1165
Chen LC, Ueda T, Sagisaka M, Hori, H, Hirakoa K (2007) Visible laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry using gold nanorods. J Phys Chem C 111:2409–2415. doi:10.1021/jp065540i
Spencer MT, Furutani H, Oldenburg SJ, Darlington TK, Prather KA (2008) Gold nanoparticles as a matrix for visible–wavelength single-particle matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry of small biomolecules. J Phys Chem C 112:4803–4090. doi:10.1021/jp076688k
Castellana ET, Russell DH (2007) Tailoring nanoparticle surface chemistry to enhance laser desorption ionization of peptides and proteins. Nano Lett 7:3023–3025. doi:10.1021/nl071469w
Kawasaki H, Yonezawa T, Watanabe T, Arakawa R (2007) Platinum nanoflowers for surface–assisted laser desorption/ ionization mass spectrometry of biomolecules. J Chem Phys C 11:16278–16283. doi:10.1021/jp075159d
Kawasaki H, Sugitani T, Watanabe T, Yonezawa T, Moriwaki H, Arakawa R (2008) Layer-by-layer self-assembled mutilayer films of gold nanoparticles for surface-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry. Anal Chem 80:7524–7533. doi:10.1021/ac800789t
Chen LC, Mori K, Hori H, Hirakoa K (2009) Au-assisted visible laser MALDI. Int J Mass Spectrom 279:41–46. doi:10.1016/j.ijms.2008.10.005
Yonezawa T, Kawasaki H, Tarui A, Watanabe T, Arakawa R, Shimada T, Mafune F (2009) Detailed investigation on the possibility of nanoparticles of various metal elements for surface-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry. Anal Sci 25:339–346. ISSN: 0910-6340
Duan J, Linman MJ, Chen ChY, Cheng QJ (2009) CHCA–modified Au nanoparticles for laser desorption ionization mass spectrometric analysis of peptides. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom 20:1530–1539. doi:10.1016/j.jasms.2009.04.009
Cioffi N, Colaianni L, Pilolli R, Calvano CD, Palmisano F, Zambonin PG (2009) Silver nanofractals: electrochemical synthesis, XPS characterization and application in LDI-MSAnal. Bioanal Chem 394:1375–1383. doi:10.1007/s00216-009-2820-y
Huang YF, Chang HT (2006) Nile red–adsorbed gold nanoparticle matrixes for determining aminothiols through surface–assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry. Anal Chem 78:1485–1493. doi:10.1021/ac0517646
Shrivas K, Wu HF (2008) Applications of silver nanoparticles capped with different functional groups as the matrix and affinity probes in surface–assisted laser desorption/ionization time–of–flight and atmospheric pressure matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization ion trap mass spectrometry for rapid analysis of sulfur drugs and biothiols in human urine. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 22:2863–2872. doi:10.1002/rcm.3681
Daniel MC, Astruc D (2004) Gold nanoparticles: assembly, supramolecular chemistry, quantum–size–related properties, and applications toward biology, catalysis, and nanotechnology. Chem Rev 104:293–346. doi:10.1021/cr030698+
Anker JN, Hall WP, Lyandres O, Shah NC, Zhao J, van Duyne RP (2008) Biosensing with plasmonic nanosensors. Nat Mater 7:442–453. doi:10.1038/nmat2162
Guo Z, Ganawi AAA, Liu Q, He L (2006) Nanomaterials in mass spectrometry ionization and prospects for biological application. Anal Bioanal Chem 308:584–592. doi:10.1007/s00216-005-0125-3
Batoy SMAB, Akhmetova E, Miladinovic S, Smeal J, Wilkins CL (2008) Developments in MALDI mass spectrometry: the quest for the perfect matrix. Appl Spectrosc Rev 43:485–550. doi:10.1080/05704920802108198
Link S, El–Sayed MA (2000) Shape and size dependence of radiative, non–radiative and photothermal properties of gold nanocrystals. Int Rev Phys Chem 19:409–453. doi:10.1080/01442350050034180
Link S, El–Sayed MA (2003) Optical properties and ultrafast dynamics of metallic nanocrystals. Annu Rev Phys Chem 54:331–366. doi:10.1146/annurev.physchem.54.011002.103759
Zhao J, Pinchuk AO, McMahon JM, Li S, Ausman LK, Atkinson AL, Shatz GC (2008) Methods for describing the electromagnetic properties of silver and gold nanoparticles. Acc Chem Res 41:1710–1720. doi:10.1021/ar800028j
Moores A, Goettmann F (2006) The plasmon band in noble metal nanoparticles: an introduction to theory and applications. New J Chem 30:1121–1132. doi:10.1039/b604038c
Pelton M, Aizpurua J, Bryant G (2008) Metal–nanoparticle plasmonics. Laser & Photon Rev 2:136–159. doi:10.1002/lpor.200810003
Hayat M (1989) Colloidal gold: principles, methods and applications. Academic, San Diego
Liu X, Atwater M, Wang J, Huo Q (2007) Extinction coefficient of gold nanoparticles with different sizes and different capping ligands. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 58:3–7. doi:10.1016/j.colsurfb.2006.08.005
Sau TK, Murphy CJ (2004) Seeded high yield synthesis of short Au nanorods in aqueous solution. Langmuir 20:6414–6420. doi:10.1021/la049463z
Zweifel DA, Wei A (2005) Sulfide–arrested growth of gold nanorods. Chem Mater 17:4259–4261. doi:10.1021/cm0506858
Hao F, Nehl CL, Hafner JH, Nordlander P (2007) Plasmon resonances of a gold nanostar. Nano Lett 7:729–732. doi:10.1021/nl062969c
Khouri CG, Vo–Dinh T (2008) Gold nanostars for surface–enhanced raman scattering: synthesis, characterization and optimization. J Phys Chem C 112:18849–18859. doi:10.1021/jp8054747
Hortal AR, Hurtado P, Martínez–Haya B, Arregui A, Bañares L (2008) Solvent-free MALDI investigation of the cationization of linear polyethers with alkali metals. J Phys Chem B 112:8530–8535. doi:10.1021/jp802089r
Montaudo G, Samperi F, Montaudo MS (2006) Characterization of synthetic polymers by MALDI–MS. Prog Polym Sci 31:277–357. doi:10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2005.12.001
Cheng WL, Dong SJ, Wang EK (2003) Iodine–induced gold–nanoparticle fusion/fragmentation/aggregation and iodine–linked nanostructured assemblies on a glass substrate. Angew Chem Int Ed 42:449–452. doi:10.1002/anie.200390136
Stumpo KA, Russell DH (2009) Anion effects on ionization efficiency using gold nanoparticles as matrices for LDI-MS. J Phys Chem C 113:1641–1647. doi:10.1021/jp804032z
Nehl CL, Liao H, Hafner JH (2006) Optical properties of star–shaped gold nanoparticles. Nano Lett 6:683–688. doi:10.1021/nl052409y
Armentrout PB (1999) Cation–ether complexes in the gas phase: thermodynamic insight into molecular recognition. Int J Mass Spectrom 193:227–240. doi:10.1016/S1387-3806(99)00165-7
Robinson EW, Garcia DE, Leib RD, Williams ER (2006) Enhanced mixture analysis of poly(ethylene glycol) using high–field asymmetric waveform ion mobility spectrometry combined with fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry. Anal Chem 78:2190–2198. doi:10.1021/ac051709x
Acknowledgements
Funding is acknowledged from the Government of Spain through project CTQ2009-10477, from the Andalusian Health Council through project PI-0070/2008, and from the Innovation and Science Council through projects P07-FQM-02600 and P07-FQM-02595.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gámez, F., Hurtado, P., Castillo, P.M. et al. UV-Vis-NIR Laser Desorption/Ionization of Synthetic Polymers Assisted by Gold Nanospheres, Nanorods and Nanostars. Plasmonics 5, 125–133 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-010-9125-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-010-9125-z