Abstract
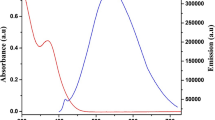
Water dispersible zinc sulfide quantum dots (ZnS QDs) with an average diameter of 2.9 nm were synthesized in an environment friendly method using chitosan as stabilizing agent. These nanocrystals displayed characteristic absorption and emission spectra having an absorbance edge at 300 nm and emission maxima (λ emission) at 427 nm. Citrate-capped silver nanoparticles (Ag NPs) of ca. 37-nm diameter were prepared by modified Turkevich process. The fluorescence of ZnS QDs was significantly quenched in presence of Ag NPs in a concentration-dependent manner with K sv value of 9 × 109 M−1. The quenching mechanism was analyzed using Stern–Volmer plot which indicated mixed nature of quenching. Static mechanism was evident from the formation of electrostatic complex between positively charged ZnS QDs and negatively charged Ag NPs as confirmed by absorbance study. Due to excellent overlap between ZnS QDs emission and surface plasmon resonance band of Ag NPs, the role of energy transfer process as an additional quenching mechanism was investigated by time-resolved fluorescence measurements. Time-correlated single-photon counting study demonstrated decrease in average lifetime of ZnS QDs fluorescence in presence of Ag NPs. The corresponding Förster distance for the present QD–NP pair was calculated to be 18.4 nm.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhong W (2009) Nanomaterials in fluorescence-based biosensing. Anal Bioanal Chem 394:47–59
Alivisatos AP (1996) Perspectives on the physical chemistry of semiconductor nanocrystals. J Phys Chem 100:13226–13239
Smith AM, Ruan G, Rhyner MN, Nie S (2006) Engineering luminescent quantum dots for in vivo molecular and cellular imaging. Anal Biomed Eng 34:3–14
Medintz IL, Uyeda HT, Goldman ER, Mattoussi H (2005) Quantum dot bioconjugates for imaging, labelling and sensing. Nat Mater 4:435–446
Han M, Gao X, Su JZ, Nie S (2001) Quantum-dot-tagged microbeads for multiplexed optical coding of biomolecules. Nat Biotechnol 19:631–635
Alviastos P (2004) The use of nanocrystals in biological detection. Nat Biotechnol 22:47–52
Jamieson T, Bakhshi R, Petrova D, Pocock R, Imani M, Seifalian AM (2007) Biological applications of quantum dots. Biomaterials 28:4717–4732
Li X, Qian J, Jiang L, He S (2009) Fluorescence quenching of quantum dots by gold nanorods and its application to DNA detection. Appl Phys Lett 94:063111–063113
Dyadyusha L, Yin H, Jaiswal S, Brown T, Baumberg JJ, Booy FP, Melvin T (2005) Quenching of CdSe quantum dot emission, a new approach for biosensing. Chem Commun 25:3201–3203
Willard DM, Orden AV (2003) Quantum dots: resonant energy-transfer sensor. Nat Mater 2:575–576
Medintz IL, Clapp AR, Mattoussi H, Goldman ER, Fisher B, Mauro JM (2003) Self-assembled nanoscale biosensors based on quantum dot FRET donors. Nat Mater 2:630–638
Ray K, Badugu R, Lakowicz JR (2006) Metal-enhanced fluorescence from CdTe nanocrystals: a single-molecule fluorescence study. J Am Chem Soc 128:8998–8999
Dulkeith E, Ringler M, Klar TA, Feldmann J, Javier AM, Parak WJ (2005) Gold nanoparticles quench fluorescence by phase induced radiative rate suppression. Nano Lett 5:585–589
Murgadoss A, Chattopadhyay A (2008) Tuning photoluminescence of ZnS nanoparticles by silver. Bull Mater Sci 31:533–539
Zhang J, Fu Y, Chowdhury MH, Lakowicz JR (2007) Metal-enhanced single-molecule fluorescence on silver particle monomer and dimer: coupling effect between metal particles. Nano Lett 7:2101–2107
Pompa PP, Martiradonna L, Torre AD, Sala FD, Manna L, Vittorio MD, Calabi F, Cingolani R, Rinaldi R (2006) Metal-enhanced fluorescence of colloidal nanocrystals with nanoscale control. Nat Nanotechnol 1:126–130
Aslan K, Gryczynski I, Malicka J, Matveeva E, Lakowicz JR, Geddes CD (2005) Metal-enhanced fluorescence: an emerging tool in biotechnology. Curr Opin Biotechnol 16:55–62
Aslan K, Lakowicz JR, Geddes CD (2005) Metal-enhanced fluorescence using anisotropic silver nanostructures:critical progress to date. Anal Bioanal Chem 382:926–933
Sabatini CA, Pereira RV, Gehlen MH (2007) Fluorescence modulation of acridine and coumarin dyes by silver nanoparticles. J Fluoresc 17:377–382
Nabika H, Deki S (2003) Enhancing and quenching functions of silver nanoparticles on the luminescent properties of europium complex in the solution phase. J Phys Chem B 107:9161–9164
Tay LL, Rowell N, Boukherroub R (2005) Colloidal silver nanoparticle induced photoluminescence quench on the surface functionalized planar si. Mater Res Soc 901:221
Umadevi M, Vanelle P, Terme T, Rajkumar BJM, Ramakrishnan V (2009) Fluorescence quenching of 1, 4-Dihydroxy-2, 3-Dimethyl-9, 10-anthraquinone by silver nanoparticles: size effect. J Fluoresc 19:3–10
Zhang J, Fu Y, Chowdhury MH, Lakowicz JR (2007) Enhanced Förster resonance energy transfer on single metal particle. 2. dependence on donor − acceptor separation distance, particle size, and distance from metal surface. J Phys Chem C 111:11784–11792
Yun CS, Javier A, Jennings T, Fisher M, Hira S, Peterson S, Hopkins B, Reich NO, Strouse GF (2005) Nanometal surface energy transfer in optical rulers, breaking the FRET barrier. J Am Chem Soc 127:3115–3119
Saini S, Bhowmick S, Shenoy VB, Bagchi B (2007) Rate of excitation energy transfer between fluorescent dyes and nanoparticles. J Photochem Photobiol A Chem 190:335–341
H. C. Warad, C. Thanachayanont, G. Tumcharern, J. Dutta, (2007) Proceedings of the 2nd IEEE International Conference on Nano/Micro Engineered and Molecular System; Bangkok Thailand.
Williams ATR, Winfield SA, Miller JN (1983) Relative fluorescence quantum yields using a computer-controlled luminescence spectrometer. Analyst 108:1067–1071
Lakowicz JR (1999) Principles of fluorescence spectroscopy, 3 rdth edn. Kluwer/Plenum, New York
Turkevich J, Stevenson PC, Hillier J (1951) A study of the nucleation and growth processes in the synthesis of colloidal gold, John Turkevich Discuss. Faraday Soc 11:55–75
Xiao Q, Xiao C (2008) Synthesis and photoluminescence of water-soluble Mn2 + -doped ZnS quantum dots. Appl Surf Sci 254:6432–6435
Lippens PE, Lannoo M (1989) Calculation of the band gap for small CdS and ZnS crystallites. Phys Rev B 39:10935–10942
Brus L (1986) Electronic wave functions in semiconductor clusters: experiment and theory. J Phys Chem 90:2555–2560
Mall M, Kumar L (2010) Optical studies of Cd2+ and Mn2+ Co-doped ZnS nanocrystals. J Lumin 130:660–665
Sapra S, Prakash A, Ghangrekar A, Periasamy N, Sarma DD (2005) Emission properties of manganese-doped ZnS nanocrystals. J Phys Chem B 109:1663–1668
Pillai ZS, Kamat PV (2004) What factors control the size and shape of silver nanoparticles in the citrate ion reduction method. J Phys Chem B 108:945–951
Puebla RAA, Aroca RF (2009) Synthesis of silver nanoparticles with controllable surface charge and their application to surface-enhanced Raman scattering. Anal Chem 81:2280–2285
Fan C, Wang S, Hong JW, Bazan GC, Plazco KW, Heeger AJ (2003) Beyond superquenching: hyper-efficient energy transfer from conjugated polymers to gold nanoparticles. PNAS 100:6297–6301
Longa D, Wua G, Chen S (2007) Preparation of oligochitosan stabilized silver nanoparticles by gamma irradiation. Radiat Phys Chem 76:1126–1131
Tan WB, Huang N, Zhang Y (2007) Ultrafine biocompatible chitosan nanoparticles encapsulating multi-coloured quantum dots for bioapplications. J Colloid Interface Sci 310:464–470
O'Connella MJ, Chana CK, Lia W, Hicksa RK, Doorna SK, Wang HL (2007) Polyelectrolyte platform for sensitive detection of biological analytes via reversible fluorescence quenching. Polymer 48:7582–7589
Ghosh SK, Pal A, Kundu S, Nath S, Pal T (2004) Fluorescence quenching of 1-methylaminopyrene near gold nanoparticles: size regime dependence of the small metallic particles. Chem Phys Lett 395:366–372
Griffin J, Singh AK, Senapati D, Rhodes P, Mitchell K, Robinson B, Yu E, Ray PC (2008) Size- and distance-dependent nanoparticle surface-energy transfer (NSET) method for selective sensing of hepatitis C virus RNA. Chem Eur J 15:342–351
Sarkar S, Bose R, Jana S, Jana NR, Pradhan N (2010) Doped semiconductor nanocrystals and organic dyes: an efficient and greener FRET system. J Phys Chem Lett 1:636–640
Huang F, Lerner E, Sato S, Amir D, Haas E, Fersht AR (2009) Time-resolved fluorescence resonance energy transfer study shows a compact denatured state of the B domain of protein A. Biochemistry 48:3468–3476
Williams G, Kamat PV (2009) Graphene − semiconductor nanocomposites: excited-state interactions between ZnO nanoparticles and graphene oxide. Langmuir 25:13869–13873
Acknowledgement
This research was supported by the Department of Biotechnology (Nos. BT/01/NE/PS/08, and BT/PR9988/NNT/28/76/2007), Department of Science and Technology (SR/S5/NM-01/2005 and 2/2/2005-S.F.), and Council of Scientific and Industrial research (CSIR). Pallab Sanpui is thankful to CSIR for fellowship. Assistance from Central instruments facility (CIF) IIT Guwahati is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jaiswal, A., Sanpui, P., Chattopadhyay, A. et al. Investigating Fluorescence Quenching of ZnS Quantum Dots by Silver Nanoparticles. Plasmonics 6, 125–132 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-010-9177-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-010-9177-0