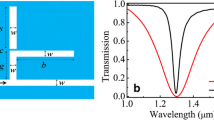
Abstract
A nanoscale surface plasmon all-optical diode is proposed based on a plasmonic slot waveguide having an asymmetric plasmonic grating in the center. The asymmetric configuration of the plasmonic grating and the unique dispersion relations of the plasmonic slot waveguide ensure the nonreciprocal transmission properties. High transmittance contrast ratio of 1,150 is achieved theoretically. The performance of the surface plasmon all-optical diode does not have any high power requirement. This may open a new way for the study of integrated photonic devices based on surface plasmons.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Scalora M, Dowling JP, Bowden CM, Bloemer MJ (1994) The photonic band edge optical diode. J Appl Phys 76:2023–2026
Tocci MD, Bloemer MJ, Scalora M, Dowling JP, Bowden CM (1995) Thin-film nonlinear optical diode. Appl Phys Lett 66:2324–2326
Lin XS, Yan JH, Wu LJ, Lan S (2008) High transmission contrast for single resonator based all-optical diodes with pump-assisting. Opt Express 16:20949–20954
Zhou H, Zhou KF, Hu W, Guo Q, Lan S, Lin XS, Gopal AV (2006) All-optical diodes based on photonic crystal molecules consisting of nonlinear defect pairs. J Appl Phys 99:123111
Mingaleev SF, Kivshar YS (2002) Nonlinear transmission and light localization in photonic-crystal waveguides. J Opt Soc Am B 19:2241–2249
Gevorgyan AH, Harutyunyan MZ (2007) Chiral photonic crystals with an anisotropic defect layer. Phys Rev E 76:031701
Feise MW, Shadrivov IV, Kivshar YS (2005) Bistable diode action in left-handed periodic structures. Phys Rev E 71:037602
Khanikaev AB, Steel MJ (2009) Low-symmetry magnetic photonic crystals for nonreciprocal and unidirectional devices. Opt Express 17:5265–5272
Gallo K, Assanto G, Parameswaran KR, Fejer MM (2001) All-optical diode in a periodically poled lithium niobate waveguide. Appl Phys Lett 79:314–316
Konorov SO, Biryukov DAS, Bugar I, Beloglazov MJ, Skibina NB, Chorvatjr D, Chorvat D, Scalora M, Zheltikov AM (2004) Experimental demonstration of a photonic-crystal-fiber optical diode. Appl Phys B: Lasers Opt 34:1417–1420
Biryukov DAS, Fedotov AB, Konorov SO, Mitrokhin VP, Scalora M, Zheltikov AM (2004) Photonic crystal fiber optical diode. Laser Phys 14:764–766
Philip R, Anija M, Yelleswarapu CS, Rao DVGLN (2007) Passive all-optical diode using asymmetric nonlinear absorption. Appl Phys Lett 91:141118
Lin XS, Wu WQ, Zhou H, Zhou KF (2006) Enhancement of unidirectional transmission through the coupling of nonlinear photonic crystal defects. Opt Express 14:2429–2439
Zhao NS, Zhou H, Guo Q, Hu W, Yang XB, Lan S (2006) Design of highly efficient optical diodes based on the dynamics of nonlinear photonic crystal molecules. J Opt Soc Am B 23:2434–2240
Hwang J, Song MH, Park B, Nishimura S, Toyooka T, Wu JW, Takanishi Y, Ishikawa K, Takezoe H (2005) Electro-tunable optical diode based on photonic bandgap liquid-crystal heterojunctions. Nature Mater 4:383–387
Song MH, Park B, Takanishi Y, Ishikawa K, Nishimura S, Toyooka T, Takezoe H (2006) Simple electro-tunable optical diode using photonic and anisotropic liquid crystal films. Thin Solid Films 509:49–52
Cakmakyapan S, Caglayan H, Serebryannikov AE, Ozbay E (2011) Experimental validation of strong directional selectivity in nonsymmetric metallic gratings with a subwavelength slit. Appl Phys Lett 98:051103
Hu XY, Xin C, Li ZQ, Gong QH (2010) Ultrahigh-contrast all-optical diodes based on tunable surface plasmon polaritons. New J Phys 12:1023029
Dionne JA, Sweatlock LA, Atwater HA, Polman A (2006) Plasmon slot waveguides: towards chip-scale propagation with subwavelength-scale localization. Phys Rev B 73:035407
Barnes WL, Preist TW, Kitson SC, Sambles JR (1996) Physical origin of photonic energy gaps in the propagation of surface plasmons on gratings. Phys Rev B 54:6227–6244
Balci S, Kocabas A, Kocabas C, Aydinli A (2010) Slowing surface plasmon polaritons on plasmonic coupled cavities by tuning grating grooves. Appl Phys Lett 97:131103
Zayats AV, Smolyaninov II, Maradudin AA (2005) Nano-optics of surface plasmon polaritons. Phys Report 408:131–314
Ding CY, Hu XY, Jiang P, Gong QH (2008) Tunable surface plasmon polariton microcavity. Phys Lett A 372:4536–4538
Johnson PB, Christy RW (1972) Optical constant of the noble metals. Phys Rev B 6:4370–4379
Kim MK, Lee SH, Choi M, Ahn BH, Park N, Lee YH, Min B (2010) Low-loss surface-plasmonic nanobeam cavities. Opt Express 18:11089–11096
Kurokwaw Y, Miyazaki HT (2007) Metal-insulator-metal plasmon nanocavities: analysis of optical properties. Phys Rev B 75:035411
McGurn AB, Christensen KT, Mueller FM, Maradudin AA (1993) Anderson localization in one-dimensional randomly disordered optical system that are periodic on average. Phys Rev B 47:13120–13125
Frigerio JM, Rivory J, Sheng P (1993) Photonic bandtail in 1D randomly-perturbed periodic system. Opt Commun 98:231–235
Martinez A, Blasco J, Sanchis P, Galan JV, Ruperez JG, Jordana E, Gautier P, Lebour Y, Hernandez S, Guider R, Daldosso N, Garrido B, Fedeli JM, Pavesi L, Marti J (2010) Ultrafast all-optical switching in a silicon-nanocrystal-based silicon slot waveguide at telecom wavelengths. Nano Lett 10:1506–1511
Chang YT, Wu YT, Lee JH, Chen HH, Hsueh CY, Huang HF, Jiang YW, Chang PE, Lee SC (2009) Emission properties of Ag/dielectric/Ag plasmonic thermal emitter with different lattice type, hole shape, and dielectric material. Appl Phys Lett 95:213102
Briggs RM, Grandidier J, Burgos SP, Feigenbaum E, Atwater HA (2010) Efficient coupling between dielectric-loaded plasmonic and silicon photonic waveguides. Nano Lett 10:4851–4857
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under grants 61077027, 10874010, 10821062, 90921008, and 10434020 and the National Basic Research Program of China under grant 2007CB307001.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, X., Zhang, Y., Xu, X. et al. Nanoscale Surface Plasmon All-Optical Diode Based on Plasmonic Slot Waveguides. Plasmonics 6, 619–624 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-011-9243-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-011-9243-2