Abstract
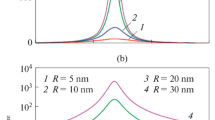
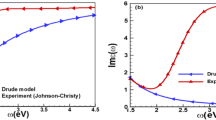
We present a quantum mechanical approach to calculate broadening of plasmonic resonances in metallic nanostructures due to collisions of electrons with the surface of the structure. The approach is applicable if the characteristic size of the structure is much larger than the de Broglie electron wavelength in the metal. The approach can be used in studies of plasmonic properties of both single nanoparticles and arrays of nanoparticles. Energy conservation is insured by a self-consistent solution of Maxwell's equations and our model for the photon absorption at the metal boundaries. Consequences of the model are illustrated for the case of spheroid nanoparticles, and results are in good agreement with earlier theories. In particular, we show that the boundary-collision broadening of the plasmonic resonance in spheroid nanoparticles can depend strongly on the polarization of the impinging light.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang F, Shen YR (2006) General properties of local plasmons in metal nanostructures. Phys Rev Lett 97:206806
Kreibig U, Vollmer M (1995) Optical properties of metal clusters. Springer, Berlin
Ruppin R, Yatom H (1976) Size and shape effects on the broadening of the plasma resonance absorption in metals. Phys Stat Sol (b) 74:647–654
Schatz GC, Kraus WA (1983) Plasmon resonance broadening in small metal particles. J Chem Phys 79:6130–6139
Cini M (1983) Classical and quantum aspects of size effects. J Opt Soc Am 71:386–392
Raza S, Stenger N, Kadkhodazadeh S, Fischer SV, Kostesha N, Jauho AP, Burrows A, Wubs M, Mortensen NA (2013) Blueshift of the surface plasmon resonance in silver nanoparticles studied with EELS. Nanophotonics 2:131–138
Aersq GC, Inglesfieldt JE (1983) Photoyield enhancement from small metal particles. J Phys F Met Phys 13:1743–1756
Tamm I, Schubin S (1931) Zur theorie des photoeffektes an metallen. Z Phys 68:97–113
Brodsky AM, Gurevich YY (1973) Theory of electron emission from metals. Nauka, Moscow
Brodsky AM, YuYa G (1968) Theory of external photoeffect from the surface of a metal. Sov Phys JETP 27:114–121
Maier SA (2007) Plasmonics: fundamentals and applications. Springer Science + Business Media LLC, USA
Knight MW, Sobhani H, Nordlander P, Halas NJ (2011) Photodetection with active optical antennas. Science 332:702–704
Novitsky A, Uskov AV, Gritti C, Protsenko IE, Kardynał BE, Lavrinenko AV (2012) Photon absorption and photocurrent in solar cells below semiconductor bandgap due to electron photoemission from plasmonic nanoantennas. Prog Photovolt Res Appl. doi:10.1002/pip.2278
Goykhman I, Desiatov B, Khurgin J, Shappir J, Levy U (2012) Waveguide based compact silicon Schottky photodetector with enhanced responsivity in the telecom spectral band. Opt Express 20:28594–28602
Landau LD, Lifshitz EM (1960) Electrodynamics of continuous media. Pergamon Press, Oxford
Protsenko IE, Uskov AV (2012) Photoemission from metal nanoparticles. Phys-Usp 55:508–518
Mitchell K (1934) The theory of the surface photoelectric effect in metals. Proc R Soc Lond Ser A 146:442–464
Zou S, Janel N, George Schatz C (2004) Silver nanoparticle array structures that produce remarkably narrow plasmon lineshapes. J Chem Phys 120:10871–10875
Raza S, Toscano G, Jauho AP, Wubs M, Mortensen NA (2011) Unusual resonances in nanoplasmonic structures due to nonlocal response. Phys Rev B 84:121412(R)
Ginzburg P, Zayats AV (2013) Localized surface plasmon resonances in spatially dispersive nano-objects: phenomenological treatise. ACS Nano. doi:10.1021/nn400842m
Yan W, Mortensen NA, Wubs M (2012) Hyperbolic metamaterials: nonlocal response regularizes broadband supersingularity. Phys Rev B 86:205429
Acknowledgments
This work was partly supported by Science Foundation Ireland (06/IN.1/I90) and by Russian Foundation for Basic Research (14-02-00125). The Center for Nanostructured Graphene (CNG) is sponsored by the Danish National Research Foundation, Project DNRF58.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Uskov, A.V., Protsenko, I.E., Mortensen, N.A. et al. Broadening of Plasmonic Resonance Due to Electron Collisions with Nanoparticle Boundary: а Quantum Mechanical Consideration. Plasmonics 9, 185–192 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-013-9611-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-013-9611-1