Abstract
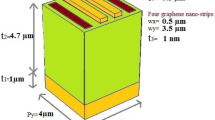
This report makes a comparison between the spectrum features of plasmonic metamaterial metal-insulator-conductor (MIC) sensor with a monolayer of graphene and another MIC sensor with a multilayer of graphite as the back reflector. In both structures, the silicon substrate as an insulator layer was sandwiched between subwavelength periodic nanogold cones as the first layer and graphene and graphite as the third layer, respectively. Nanolayer of chromium nanorods was also considered in the structure of MIC sensors as an interface layer between silicon and nanogold cone metasurface. The performance of the sensor was evaluated under different incident polarized light angles and different thickness of the metasurface when the metasurface infiltrated with seawater and air. The transmission spectrum of monolayer graphene-based MIC sensor, respecting to s-polarized waves, reveals prominent feature to detect the air rather than seawater in invisible regime. Meanwhile, the reflection spectrum of graphite-based MIC sensor provides ∼0 % reflection under resonance condition regarding s- and p-polarized waves for detecting air in visible spectrum.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atwater HA (2007) The promise of plasmonics. Sci Am 296(4):56–62
Vasile GC, Popescu AA, Stafe M, Koziukhin SA, Savastru D, Donţu S, Neguţu C (2013) Plasmonic waveguides features correlated with surface plasmon resonance performed with a low refractive index prism. Changes 4(10):5
Berini P, De Leon I (2012) Surface plasmon-polariton amplifiers and lasers. Nat Photonics 6(1):16–24
Dang X, Qi J, Klug MT, Chen PY, Yun DS, Fang NX, Hammond PT, Belcher AM (2013) Tunable localized surface plasmon-enabled broadband light-harvesting enhancement for high-efficiency panchromatic dye-sensitized solar cells. Nano Lett 13(2):637–642
Huang YJ, Wen GJ, Li J, Zhu WR, Wang P, Sun YH (2013) Wide-angle and polarization-independent metamaterial absorber based on snowflake-shaped configuration. J Electromagn Waves Appl 27(5):552–559
Grady NK, Heyes JE, Chowdhury DR, Zeng Y, Reiten MT, Azad AK, Taylor AJ, Dalvit DAR, Chen H-T (2013) Terahertz metamaterials for linear polarization conversion and anomalous refraction. Science 340(6138):1304–1307
Willets KA, Van Duyne RP (2007) Localized surface plasmon resonance spectroscopy and sensing. Annu Rev Phys Chem 58:267–297
Murray WA, Barnes WL (2007) Plasmonic materials. Adv Mater 19(22):3771–3782
Maier SA, Atwater HA (2005) Plasmonics: localization and guiding of electromagnetic energy in metal/dielectric structures. J Appl Phys 98(1):011101
Polo J, Mackay T, Lakhtakia A (2013) Electromagnetic surface waves: a modern perspective. Elsevier, p 314
Hedayati MK, Faupel F, Elbahri M (2014) Review of plasmonic nanocomposite metamaterial absorber. Materials 7(2):1221–1248
Ok JG, Youn HS, Kwak MK, Lee K-T, Shin YJ, Guo LJ, Greenwald A, Liu Y (2012) Continuous and scalable fabrication of flexible metamaterial films via roll-to-roll nanoimprint process for broadband plasmonic infrared filters. Appl Phys Lett 101(22):223102
Preiner MJ, Shimizu KT, White JS, Melosh NA (2008) Efficient optical coupling into metal-insulator-metal plasmon modes with subwavelength diffraction gratings. Appl Phys Lett 92(11):113109
Puscasu I, Schaich WL (2008) Narrow-band, tunable infrared emission from arrays of microstrip patches. Appl Phys Lett 92(23):233102
Cheng C-W, Abbas MN, Chang Z-C, Shih MH, Wang C-M, Wu MC, Chang Y-C (2011) Angle-independent plasmonic infrared band-stop reflective filter based on the Ag/SiO2/Ag T-shaped array. Opt Lett 36(8):1440–1442
Le KQ, Bai J (2015) Enhanced absorption efficiency of ultrathin metamaterial solar absorbers by plasmonic Fano resonance. JOSA B 32(4):595–600
Zayats AV, Smolyaninov II, Maradudin AA (2005) Nano-optics of surface plasmon polaritons. Phys Rep 408(3):131–314
Pitarke JM, Silkin VM, Chulkov EV, Echenique PM (2006) Theory of surface plasmons and surface-plasmon polaritons. Rep Prog Phys 70(1):1
Zheng HY, Jin XR, Park JW, Lu YH, Rhee JY, Jang WH, Cheong H, Lee YP (2012) Tunable dual-band perfect absorbers based on extraordinary optical transmission and Fabry-Perot cavity resonance. Opt Express 20(21):24002–24009
Hedayati MK, Faupel F, Elbahri M (2014) Review of plasmonic nanocomposite metamaterial absorber. Materials 7:1221–1248
Li W, Valentine J (2014) Metamaterial perfect absorber based hot electron photodetection. Nano Lett 14:3510–3514
Vora A, Gwamuri J, Pala N, Kulkarni A, Pearce JM, Guney DO (2014) Exchanging ohmic losses in metamaterial absorbers with useful optical absorption for photovoltaics. Sci Rep 4:4901
Hao J, Wang J, Liu X, Padilla WJ, Zhou L, Qiu M (2010) High performance optical absorber based on a plasmonic metamaterial. Appl Phys Lett 96(25):251104
Le KQ (2014) Enhanced plasmonic Brewster transmission through metascreens by tapered slits. J Appl Phys 115(3):033110
Mattiucci N, Bloemer MJ, Aközbek N, D’Aguanno G (2013) Impedance matched thin metamaterials make metals absorbing. Sci Rep 3
Argyropoulos C, Le KQ, Mattiucci N, D’Aguanno G, Alu A (2013) Broadband absorbers and selective emitters based on plasmonic Brewster metasurfaces. Phys Rev B87(20):205112
Le KQ, Argyropoulos C, Alù A (2012) Plasmonic Brewster transmission in photonic gratings and crystals. Proc SPIE 8423:842313
Lee C, Wei X, Kysar JW, Hone J (2008) Measurement of the elastic properties and intrinsic strength of monolayer graphene. Science 321(5887):385–388
Koenig SP, Boddeti NG, Dunn ML, Bunch JS (2011) Ultrastrong adhesion of graphene membranes. Nat Nanotechnol 6(9):543–546
Acknowledgments
The author, Masih Ghasemi, is greatly thankful of Dr. Linus and Mr. Ding from CST division in Malaysia for their great consultancy and help in accomplishing this work. Furthermore, the author, IS Amiri, would like to acknowledge the grant number LRGS(2015)NGOD/UM/KPT, GA010-2014 (ulung), and RU007/2015 from the University of Malaya (UM).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ahmad, H., Ghasemi, M., Amiri, I.S. et al. Gold Cone Metasurface MIC Sensor with Monolayer of Graphene and Multilayer of Graphite. Plasmonics 12, 497–508 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-016-0290-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-016-0290-6