Abstract
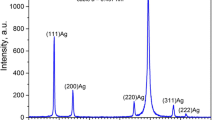
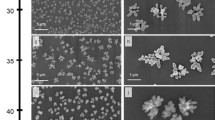
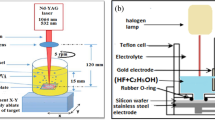
Different forms of modified and well-controlled plasmonic silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) were synthesized by silver ion reduction process of porous silicon (PS). Fine control of PS surface morphology was accomplished by employing two etching processes: light-induced etching (LIE) and photo electrochemical etching (PECE). The idea was to prepare excellent and reproducible surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) substrates with high enhancement performance. PS surface modification was employed to create efficient and nearly uniformly distributed AgNP hotspot regions with very high specific surface areas. Reproducibility deviation of no more than 5% and enhancement factor of 1.2 × 1014 were obtained by SERS measurements at very low, rhodamine 6G (R6G) dye, concentration 10−15 M. The PS morphology SERS substrate was well discussed and analyzed using field emission scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM), X-ray diffraction spectroscopy (XRD), and Raman measurements.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhang D, Xiao SJ, Zheng LL, Lia YF, Huang CZ (2014) Mater Chem B
Fleischmann M, Hendra PJ, McQuillan A (1974) Raman spectra of pyridine adsorbed at a silver electrode. Chem Phys Lett 26:163–166
Li Q-l, Li B-w, Wang Y-q (2013) Surface-enhanced Raman scattering microfluidic sensor. RSC Adv 3:13015–13026
Sánchez-Iglesias A, Aldeanueva-Potel P, Ni W, Pérez-Juste J, Pastoriza-Santos I, Alvarez-Puebla RA et al (2010) Chemical seeded growth of ag nanoparticle arrays and their application as reproducible SERS substrates. Nano Today 5:21–27
Santos A, Kumeria T (2015) Electrochemical etching methods for producing porous silicon. In Electrochemically engineered nanoporous materials, ed. Springer, pp. 1–36
Al-Khazraji KK, Rasheeda BG, Ibrahem MA, Mohammed AF (2012) Effect of laser-induced etching process on porous structures. Procedia Eng 38:1381–1390
Soni R, Bassam G, Abbi S (2003) Laser-controlled photoluminescence characteristics of silicon nanocrystallites produced by laser-induced etching. Appl Surf Sci 214:151–160
Yamanishi M, Suemune I (1983) Quantum mechanical size effect modulation light sources–a new field effect semiconductor laser or light emitting device. Jpn J Appl Phys 22:L22
Kolasinski KW, Mills D, Nahidi M (2006) Laser assisted and wet chemical etching of silicon nanostructures. J Vac Sci Technol Vacuums Surf Films 24:1474
Kowalik I, Guziewicz E, Kopalko K, Yatsunenko S, Wójcik-Głodowska A, Godlewski M et al (2009) Structural and optical properties of low-temperature ZnO films grown by atomic layer deposition with diethylzinc and water precursors. J Cryst Growth 311:1096–1101
Alwan AM, Hayder AJ, Jabbar AA (2015) Study on morphological and structural properties of silver plating on laser etched silicon. Surf Coat Technol 283:22–28
Stewart MP, Buriak JM (2000) Chemical and biological applications of porous silicon technology. Adv Mater 12:859–869
Menna P, Di Francia G, La Ferrara V (1995) Porous silicon in solar cells: a review and a description of its application as an AR coating. Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells 37:13–24
Sun X, Wang N, Li H (2013) Deep etched porous Si decorated with au nanoparticles for surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS). Appl Surf Sci 284:549–555
Chan S, Kwon S, Koo TW, Lee LP, Berlin AA (2003) Surface-enhanced Raman scattering of small molecules from silver-coated silicon Nanopores. Adv Mater 15:1595–1598
Panarin AY, Terekhov S, Kholostov K, Bondarenko V (2010) SERS-active substrates based on n-type porous silicon. Appl Surf Sci 256:6969–6976
Adawyia JH, Alwan MA, Allaa AJ (2016) Optimizing of porous silicon morphology for synthesis of silver nanoparticles. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 227:152–160
Huang Z, Fang H, Zhu J (2007) Fabrication of silicon nanowire arrays with controlled diameter, length, and density. Adv Mater 19:744–748
Tsuboi T, Sakka T, Ogata YH (1998) Metal deposition into a porous silicon layer by immersion plating: influence of halogen ions. J Appl Phys 83:4501–4506
Antunez EE et al (2014) Controlled morphology and optical properties of n-type porous silicon: effect of magnetic field and electrode-assisted LEF. Nanoscale Res Lett 9.1:512
Bisi O, Ossicini S, Pavesi L (2000) Porous silicon: a quantum sponge structure for silicon based optoelectronics. Surf Sci Rep 38:1–126
Sze SM (2008) Semiconductor devices: physics and technology: John Wiley & Sons
Ben-Chorin M, Möller F, Koch F (1994) Nonlinear electrical transport in porous silicon. Phys Rev B 49:2981
Peng C, Hirschman K, Fauchet P (1996) Carrier transport in porous silicon light-emitting devices. J Appl Phys 80:295–300
Zheng H (2011) Molecular dynamic simulation of thin film growth stress evolution
Novara C, Dalla Marta S, Virga A, Lamberti A, Angelini A, Chiadò A et al (2016) SERS-active ag nanoparticles on porous silicon and PDMS substrates: a comparative study of uniformity and Raman efficiency. J Phys Chem C 120:16946–16953
Zhang C, Jiang SZ, Yang C, Li CH, Huo YY, Liu XY et al (2016) Gold@ silver bimetal nanoparticles/pyramidal silicon 3D substrate with high reproducibility for high-performance SERS. Scientific reports, vol. 6
Le Ru E, Blackie E, Meyer M, Etchegoin PG (2007) Surface enhanced Raman scattering enhancement factors: a comprehensive study. J Phys Chem C 111:13794–13803
Bykkam S, Ahmadipour M, Narisngam S, Kalagadda VR, Chidurala SC (2015) Extensive studies on X-ray diffraction of green synthesized silver nanoparticles. Adv Nanopart 4:1
Harraz FA, Ismail AA, Bouzid H, Al-Sayari S, Al-Hajry A, Al-Assiri M (2015) Surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS)-active substrates from silver plated-porous silicon for detection of crystal violet. Appl Surf Sci 331:241–247
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jabbar, A.A., Alwan, A.M. & Haider, A.J. Modifying and Fine Controlling of Silver Nanoparticle Nucleation Sites and SERS Performance by Double Silicon Etching Process. Plasmonics 13, 1171–1182 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-017-0618-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-017-0618-x