Abstract
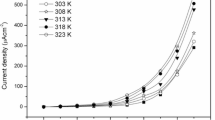
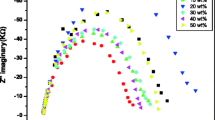
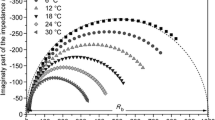
Impedance and dielectric properties of nanocomposite polymer electrolyte systems modified with nano size MMT and ferroelectric fillers have been investigated for varying lithium to oxygen ratios. The changes in the structural properties of the electrolyte samples were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD) and differential scanning calorimetric (DSC) technique. The ion transport number estimated by DC polarization technique is found to be between 0.86 and 0.95. The bulk conductivities of nanocomposite polymer electrolyte films were studied using impedance spectroscopic technique. The impedance plot shows high frequency semicircle, due to the bulk effect of sample and maximum ionic conductivity of 2.15 × 10−4 Scm−1 was observed for (PEO)4LiCBSM at 323 K with lithium to oxygen ratio 1: 4. The complex impedance data was used to evaluate ionic conductivity and dielectric relaxation process, to understand the ion transport mechanism in these systems.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gray FM (1991) Solid polymer electrolytes, fundamentals and technological applications. VCH, New York
Agrawal RC, Pandey GP (2008) Solid polymer electrolytes: materials designing and all-solid-state battery applications: an overview. J Phys D Appl Phys 41(22):223001
MacCallum, JR, Vincent CA (eds.) (1987, 1989) Polymer electrolyte review, vol I. & vol. II. Elsevier, London
Rao RP, Reddy MV, Adams S, Chowdari BVR (2012) Preparation and mobile ion transport studies of Ta and Nb doped Li 6Zr2O7 Li-fast ion conductors. Mater Sci Eng B Solid-State Mater Adv Technol 177:100–105
Agrawal RC, Gupta RK, Sinha CK, et al. (2004) Transport properties and battery discharge characteristics of the Ag + ion conducting composite electrolyte system (1 − x)[0.75AgI: 0.25AgCl]: xFe2O3. Ionics (Kiel) 10:113–117
Caproni E, Carvalho FMS, Muccillo R (2008) Development of zirconia-magnesia/zirconia-yttria composite solid electrolytes. Solid State Ionics 179:1652–1654
Chandra A, Bhatt A, Chandra A (2013) Ion conduction in superionic glassy electrolytes: an overview. J Mater Sci Technol 29:193–208
Chen M, Yin X, Reddy MV, Adams S (2015) All-solid-state MoS 2 /Li 6 PS 5 Br/In–Li batteries as a novel type of Li/S battery. J Mater Chem A 3:10698–10702
Bruce PG, Vincent CA (1993) Polymer electrolytes. J Chem Soc Faraday Trans 89:3187–3203
Fenton DE, Parker JM, Wright PV (1973) Complexes of alkali metal ions with poly(ethylene oxide). Polymer (Guildf) 14:589
Prad Pradhan DK, Choudhary RNP, Samantaray BK (2008) Studies of dielectric relaxation and AC conductivity behavior of plasticized polymer nanocomposite electrolytes. Int J Electrochem Sci 3:597–608
Manoratne CH, Rajapakse RMG, Dissanayake MAKL (2006) Ionic conductivity of poly ( ethylene oxide ) ( PEO )—montmorillonite ( MMT ) nanocomposites prepared by intercalation from aqueous medium. Int J Electrochem Sci 1:32–46
Shanmukaraj D, Murugan R (2005) Characterization of PEG : LiClO 4 + SrBi 4 Ti 4 O 15 nanocomposite polymer electrolytes for lithium secondary batteries. J Power Sources 149:90–95. doi:10.1016/j.jpowsour.2005.02.008
Sun H-Y (1999) Enhanced lithium-ion transport in PEO-based composite polymer electrolytes with ferroelectric BaTiO[sub 3]. J Electrochem Soc 146:1672
Strawhecker KE, Manias E (2003) Crystallization behavior of poly(ethylene oxide) in the presence of Na + montmorillonite fillers. Chem Mater 15:844–849
Kitajima S, Bertasi F, Vezzù K, et al. (2013) Dielectric relaxations and conduction mechanisms in polyether-clay composite polymer electrolytes under high carbon dioxide pressure. Phys Chem Chem Phys 15:16626–16633
Singh PK, Chandra A (2003) Role of the dielectric constant of ferroelectric ceramic in enhancing the ionic conductivity of a polymer electrolyte composite. J Phys D Appl Phys 36:L93–L96
Kremer F, Schonhals, A (eds.) (2003) Broad band dielectric spectroscopy. Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg, New York
Sunitha VR, Radhakrishnan S (2015) Field enhanced Li ion conduction in nanoferroelectric modified polymer electrolyte systems. Ionics 3:949–954
Choudhary S, Sengwa RJ (2013) Effects of preparation methods on structure, ionic conductivity and dielectric relaxation of solid polymeric electrolytes. Mater Chem Phys 142:172–181
Mohapatra SR, Thakur AK, Choudhary RNP (2009) Effect of nanoscopic confinement on improvement in ion conduction and stability properties of an intercalated polymer nanocomposite electrolyte for energy storage applications. J Power Sources 191:601–613
Mohd Noor SAB (2010) Solid polymeric electrolyte of poly(ethylene)oxide-50 % epoxidized natural rubber-lithium triflate (PEO-ENR50-LiCF3SO3). Nat Sci 02(3):190–196
Qian X, Gu N, Cheng Z, et al. (2001) Impedance study of (PEO) 10LiClO4-Al2O3 composite polymer electrolyte with blocking electrodes. Electrochim Acta 46:1829–1836
Zen J, Ilangovan G, Jou J (1999) Square-wave voltammetric determination and ac impedance study of dopamine on preanodized perfluorosulfonated ionomer-coated glassy. Anal Chem 71:2797–2805
Qian X, Gu N, Cheng Z, et al. (2002) Plasticizer effect on the ionic conductivity of PEO-based polymer electrolyte. Mater Chem Phys 74:98–103
Shukla N, Thakur AK, Shukla A, Marx DT (2014) Ion conduction mechanism in solid polymer electrolyte: an applicability of almond-west formalism. Int J Electrochem Sci 9(12):7644–7659
Bertasi F, Vezz K, Giffin GA, et al. (2014) Single-ion-conducting nanocomposite polymer electrolytes based on PEG400 and anionic nanoparticles: part 2. Electrical characterization. Int J Hydrog Energy 39:2884–2895
MacCallum JR. and Vincent CA (1989) (ed.), Polymer Electrolyte Review vol-II, Elsevier, London
Dutt P, Biswas S, De SK (2002) Dielectric relaxation in polyaniline–polyvinyl alcohol composites. Mater Res Bull 37:193–200
Ramesh S, Yahaya AH, Arof AK (2002) Dielectric behaviour of PVC-based polymer electrolytes. Solid State Ionics 152-153:291–294
Kyritsis A, Pissis P, Grammatikakis J (1995) Dielectric relaxation spectroscopy in poly(hydroxyethyl acrylates)/water hydrogels. J Polym Sci B Polym Phys 33:1737–1750
Pradhan DK, Choudhary RNP, Samantaray BK (2009) Studies of dielectric and electrical properties of plasticized polymer nanocomposite electrolytes. Mater Chem Phys 115(2–3):557–561
Naili H, Zouari N, Mhiri T, Daoud A (2000) Conductivity and dielectric studies in CS0.4 Rb0.6 H2PO4 mixed crystals. J Mol Struct 519:143–151
Chaurasia SK, Singh RK, Chandra S (2011) Dielectric relaxation and conductivity studies on (PEO:LiClO4) polymer electrolyte with added ionic liquid [BMIM][PF6]: evidence of ion-ion interaction. J Polym Sci Part B Polym Phys 49:291–300
A. K. Jonscher (1975) The interpretation of non-ideal dielectric admittance and impedance diagrams. Phys Status Solidi (A) 32:665–676
Paper O, Sengwa RJ, Choudhary S (2014) Dielectric relaxation spectroscopy and X-ray diffraction studies of poly ( ethylene oxide )–lithium perchlorate electrolytes. Indian J Phys. doi:10.1007/s12648-014-0440-7
Scrosati B, Croce F, Persi L (2000) Impedance spectroscopy study of PEO-based nanocomposite polymer electrolytes. J Electrochem Soc 147:1718
H. K. Patel, S. W. Martin (1992) “Fast ionic conduction in NazS + B2S3 glasses: Compositional contributions to non-exponentiality in conductivity relaxation in the extreme low-alkali-metal limit”, P. Review, “No Title,” 45(18):292–300
Karmakar A, Ghosh A (2012) Dielectric permittivity and electric modulus of polyethylene oxide (PEO)-LiClO4 composite electrolytes. Curr Appl Phys 12:539–543
Acknowledgments
This work was carried out under the Naval Research Board-DRDO (Government of India) project grant (project no: DNRD/05/4003/NRB/187).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sunitha, V.R., Radhakrishnan, S. Impedance and dielectric studies of nanocomposite polymer electrolyte systems using MMT and ferroelectric fillers. Ionics 22, 2437–2446 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-016-1784-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-016-1784-0