Abstract
In this paper, we report the effect of a small quantity of acetonitrile (ACN) addition to an ionic liquid-based electrolyte for lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries, which is comprised of lithium bis(trifluoromethylsulfonyl)imide (LiTFSI) salt dissolved in 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium bis(trifluoromethylsulfonyl)imide (BMIMTFSI). The addition of a small amount of ACN results in the increase of ionic conductivity, and at a proper molal fraction, it may significantly improve the charge-discharge capacity of its half-cell battery. A large amount of ACN addition, however, reduces the specific capacity because ACN molecules are more susceptible to irreversible redox reactions at the battery electrodes. The experimental results are also compared with the X-ray diffraction (XRD pattern) of the solutions, which may lead to a suggestion in the formation of coordination complexes between the Li+ cations with ACN molecules, which effectively hinders the formation of strong Li+-TFSI− ionic bonding and therefore increases the Li+ cation mobility. Different from other reports, the role of this small quantity of ACN is considered not only as a co-solvent, but also as an additive to this LiTFSI/BMIMTFSI electrolyte.

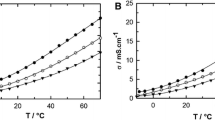
The ac conductivity spectra of LiTFSI in EC:DEC measured in a coin cell with an O-ring Teflon spacer and Celgard membrane separator (commonly used in Li-ion battery). Extra figure was captured as "Graphical abstract." Please check if it is presented and captured correctly.Please replace the figure for this Graphical Abstract with the figure from Fig. 7 (The charge-discharge characteristics of the half-cells with Li|electrolyte|LiFePO4 configuration using a 1-BT-0 (1 molal of LiTFSI, without ACN additive), b 1-BT-1 (1 molal of LiTFSI and 1 molal of ACN), and c 4-BT-1 (4 molal of LiTFSI and 1 molal of ACN) electrolytes.)The extra figure (representing the ac conductivity spectra of LiTFSI in EC:DEC measured in a coin cell with an O-ring Teflon spacer and Celgard membrane separator (commonly used in Li-ion battery) was sent for reviewing process as additional data/information to the reviewer. It's not intended to be included in this manuscript.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ryou MH, Lee JN, Lee DJ, Kim WK, Jeong YK, Choi JW, Park JK, Lee YM (2012) Effects of lithium salts on thermal stabilities of lithium alkyl carbonates in SEI layer. Electrochim Acta 83:259–263. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2012.08.012
Alias N, Mohamad AA (2015) Advances of aqueous rechargeable lithium-ion battery: a review. J Power Sources 274:237–251. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2014.10.009
Zhang R, Chen Y, Montazami R (2015) Ionic liquid-doped gel polymer electrolyte for flexible lithium-ion polymer batteries. Materials (Basel) 8:2735–2748. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma8052735
Haregewoin AM, Wotango AS, Hwang BJ (2016) Electrolyte additives for lithium ion battery electrodes: progress and perspectives. Energy Environ Sci 9:1955–1988. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6ee00123h
Yang H, Zhuang GV, Ross PN (2006) Thermal stability of LiPF6 salt and Li-ion battery electrolytes containing LiPF6. J Power Sources 161:573–579. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2006.03.058
Gnanaraj JS, Thompson RW, DiCarlo JF, Abraham KM (2007) The role of carbonate solvents on lithium intercalation into graphite. J Electrochem Soc 154:A185. https://doi.org/10.1149/1.2424419
Zhang Z, Chen X, Li F, Lai Y, Li J, Liu P, Wang X (2010) LiPF6 and lithium oxalyldifluoroborate blend salts electrolyte for LiFePO4/artificial graphite lithium-ion cells. J Power Sources 195:7397–7402. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2010.05.056
Dougassa YR, Tessier C, Ouatani LE, Anouti M, Jacquemin J (2013) Low pressure carbon dioxide solubility in lithium-ion batteries based electrolytes as a function of temperature. Measurement and prediction. J Chem Thermodyn 61:32–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jct.2012.12.025
Zhang L, Chai L, Zhang L, Shen M, Zhang X, Battaglia VS, Zheng H (2014) Synergistic effect between lithium bis (fluorosulfonyl) imide (LiFSI) and lithium bis-oxalato borate (LiBOB) salts in LiPF6 -based electrolyte for high-performance Li-ion batteries. Electrochim Acta 127:39–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2014.02.008
Kawamura T, Okada S, Yamaki J i (2006) Decomposition reaction of LiPF6-based electrolytes for lithium ion cells. J Power Sources 156:547–554. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2005.05.084
Chen Z, Lu WQ, Liu J, Amine K (2006) LiPF6/LiBOB blend salt electrolyte for high-power lithium-ion batteries. Electrochim Acta 51:3322–3326. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2005.09.027
Lux SF, Lucas IT, Pollak E, Passerini S, Winter M, Kostecki R (2012) The mechanism of HF formation in LiPF6 based organic carbonate electrolytes. Electrochem Commun 14:47–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.elecom.2011.10.026
Sloop SE, Pugh JK, Wang S, Kerr JB, Kinoshita K (2001) Chemical reactivity of PF5 and LiPF6 in ethylene carbonate/dimethyl carbonate solutions. Electrochem Solid-State Lett 4:A42. https://doi.org/10.1149/1.1353158
Yaakov D, Gofer Y, Aurbach D, Halalay IC (2010) On the study of electrolyte solutions for Li-ion batteries that can work over a wide temperature range. J Electrochem Soc 157:A1383. https://doi.org/10.1149/1.3507259
Dahbi M, Ghamouss F, Tran-Van F, Lemordant D, Anouti M (2011) Comparative study of EC/DMC LiTFSI and LiPF6 electrolytes for electrochemical storage. J Power Sources 196:9743–9750. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2011.07.071
Zhang X, Kostecki R, Richardson TJ, Pugh JK, Ross PN (2001) Electrochemical and infrared studies of the reduction of organic carbonates. J Electrochem Soc 148:A1341. https://doi.org/10.1149/1.1415547
Seo DM, Chalasani D, Parimalam BS, Kadam R, Nie M, Lucht BL (2014) Reduction reactions of carbonate solvents for lithium ion batteries. ECS Electrochem Lett 3:A91–A93. https://doi.org/10.1149/2.0021409eel
Papageorgiou N (1996) The performance and stability of ambient temperature molten salts for solar cell applications. J Electrochem Soc 143:3099. https://doi.org/10.1149/1.1837171
Wachter P, Zistler M, Schreiner C, Berginc M, Krasovec UO, Gerhard D, Wasserscheid P, Hinsch A, Gores HJ (2008) Characterisation of DSSC-electrolytes based on 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium dicyanamide: measurement of triiodide diffusion coefficient, viscosity, and photovoltaic performance. J Photochem Photobiol A Chem 197:25–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotochem.2007.12.001
Grätzel M (2003) Dye-sensitized solar cells. J Photochem Photobiol C: Photochem Rev 4:145–153. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1389-5567(03)00026-1
Hallett JP, Welton T (2011) Room-temperature ionic liquids: solvents for synthesis and catalysis. 2. Chem Rev 111:3508–3576. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr1003248
Earle MJ, Seddon KR (2000) Ionic liquids. Green solvents for the future. Pure Appl Chem 72:1391–1398. https://doi.org/10.1351/pac200072071391
Laali KK (2003) Ionic liquids in synthesis. Synthesis-Stuttgart 2003:1752–1752. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2003-40869
Gorlov M, Kloo L (2008) Ionic liquid electrolytes for dye-sensitized solar cells. J Chem Soc Dalton Trans:2655–2666. https://doi.org/10.1039/b716419j
Brandt A, Ramirez-Castro C, Anouti M, Balducci A (2013) An investigation about the use of mixtures of sulfonium-based ionic liquids and propylene carbonate as electrolytes for supercapacitors. J Mater Chem A 1:12669–12678. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3ta12737k
Timperman L, Skowron P, Boisset A, Galiano H, Lemordant D, Frackowiak E, Beguin F, Anouti M (2012) Triethylammonium bis (tetrafluoromethylsulfonyl) amide protic ionic liquid as an electrolyte for electrical double-layer capacitors. Phys Chem Chem Phys 14:8199–8207. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2cp40315c
Arsyad WOS, Bahar H, Prijamboedi B, Hidayat R (2018) Revealing the limiting factors that are responsible for the working performance of quasi-solid state DSSCs using an ionic liquid and organosiloxane-based polymer gel electrolyte. Ionics 24:901–914. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-017-2230-7
Zhong C, Deng Y, Hu W, Qiao J, Zhang L, Zhang J (2015) A review of electrolyte materials and compositions for electrochemical supercapacitors. Chem Soc Rev 44:7484–7539. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5cs00303b
Kazemiabnavi S, Zhang Z, Thornton K, Banerjee S (2016) Electrochemical stability window of imidazolium-based ionic liquids as electrolytes for lithium batteries. J Phys Chem B 120:5691–5702. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcb.6b03433
Lewandowski A, Swiderska-mocek A (2009) Ionic liquids as electrolytes for Li-ion batteries — an overview of electrochemical studies. J Power Sources 194:601–609. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2009.06.089
Lahiri A, Schubert TJS, Iliev B, Endres F (2015) LiTFSI in 1-butyl-1-methylpyrrolidinium bis (fluorosulfonyl)amide: a possible electrolyte for ionic liquid based lithium ion batteries. Phys Chem Chem Phys 17:11161–11164. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5cp01337b
Diaw M, Chagnes A, Carr B, Willmann P, Lemordant D (2005) Mixed ionic liquid as electrolyte for lithium batteries. J Power Sources 146:682–684. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2005.03.068
Vogl T, Menne S, Balducci A (2014) Mixtures of protic ionic liquids and propylene carbonate as advanced electrolytes for lithium-ion batteries. Phys Chem Chem Phys 16:25014–25023. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4cp03830d
Boyes W (2010) Instrumentation reference book 4th Ed. Elsevier
Shinkle AA, Pomaville TJ, Sleightholme AES, Thompson LT, Monroe CW (2014) Solvents and supporting electrolytes for vanadium acetylacetonate flow batteries. J Power Sources 248:1299–1305. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2013.10.034
Bandara TMWJ, Mellander B (2011) Evaluation of mobility, diffusion coefficient and density of charge carriers in ionic liquids and novel electrolytes based on a new model for dielectric response. In: Ionic liquids: theory, properties, new approaches. pp 384–407
Gouverneur M, Kopp J, Van Wullen L, Schonhoff M (2015) Direct determination of ionic transference numbers in ionic liquids by electrophoretic NMR. Phys Chem Chem Phys 17:30680–30686. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5cp05753a
Monti D, Jónsson E, Palacín MR, Johansson P (2014) Ionic liquid based electrolytes for sodium-ion batteries : Na þ solvation and ionic conductivity. J Power Sources 245:630–636. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2013.06.153
Pitawala J, Kim J, Jacobsson P, Koch V (2012) Phase behaviour, transport properties, and interactions in Li-salt doped ionic liquids. Faraday Discuss 154:71–80. https://doi.org/10.1039/c1fd00056j
Kartini E, Sakuma T, Basar K, Ihsan M (2008) Mixed cation effect on silver-lithium solid electrolyte (Agl)0.5(LiPO3)0.5. Solid State Ionics 179:706–711. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssi.2008.04.015
Nasri S, Ben Hafsia AL, Tabellout M, Megdiche M (2016) Complex impedance, dielectric properties and electrical conduction mechanism of La0.5Ba0.5FeO3-δperovskite oxides. RSC Adv 6:76659–76665. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6ra10589k
Kumari K, Ashutosh Prasad KP (2016) Dielectric, impedance modulus and conductivity studies on [Bi0.5(Na1-xKx)0.5]0.94Ba0.06TiO3, (0.16 ≤ x ≤0.20) Lead-Free Ceramics.pdf. Am J Mater Sci 6:1–18. https://doi.org/10.5923/j.materials.20160601.01
Ayu NIP, Kartini E, Prayogi LD, Faisal M (2016) Crystal structure analysis of Li3PO4 powder prepared by wet chemical reaction and solid-state reaction by using X-ray diffraction (XRD). Ionics 22:1051–1057. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-016-1643-z
Austen Angell C, Ansari Y, Zhao Z (2012) Ionic liquids: past, present and future. Faraday Discuss 154:9–27. https://doi.org/10.1039/c1fd00112d
Li W-J, Han B-X, Tao R-T, Zhang ZF, Zhang JL (2007) Measurement and correlation of the ionic conductivity of ionic liquid-molecular solvent solutions. Chin J Chem 25:1349–1356. https://doi.org/10.1002/cjoc.200790251
Comminges C, Barhdadi R, Laurent M, Troupel M (2006) Determination of viscosity, ionic conductivity, and diffusion coefficients in some binary systems: ionic liquids + molecular solvents. J Chem Eng Data 51:680–685. https://doi.org/10.1021/JE0504515
Han S-D, Borodin O, Seo DM, Zhou ZB, Henderson WA (2014) Electrolyte solvation and ionic association. J Electrochem Soc 161:A2042–A2053. https://doi.org/10.1149/2.0101414jes
Seo DM, Boyle PD, Sommer RD, Daubert JS, Borodin O, Henderson WA (2014) Solvate structures and spectroscopic characterization of LiTFSI electrolytes. J Phys Chem B 118:13601–13608. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp505006x
Yuan K, Bian H, Shen Y, Jiang B, Li J, Zhang Y, Chen H, Zheng J (2014) Coordination number of Li+ in nonaqueous electrolyte solutions determined by molecular rotational measurements. J Phys Chem B 118:3689–3695. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp500877u
Peng Q, Zhang ZY, Yang L, Wang XL (2015) Effects of acetonitrile on electrochemical performance of LiFePO4/Li. Russ J Electrochem 51:339–344. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1023193515040096
Trinh ND, Lepage D, Aymé-Perrot D, Badia A, Dolle M, Rochefort D (2018) An artificial lithium protective layer that enables the use of acetonitrile-based electrolytes in lithium metal batteries. Angew Chem Int Ed 57:5072–5075. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201801737
Nilsson V, Younesi R, Brandell D, Edstrom K, Johansson P (2018) Critical evaluation of the stability of highly concentrated LiTFSI - acetonitrile electrolytes vs. graphite, lithium metal and LiFePO4electrodes. J Power Sources 384:334–341. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2018.03.019
Yamada Y, Furukawa K, Sodeyama K, Kikuchi K, Yaegashi M, Tateyama Y, Yamada A (2014) Unusual stability of acetonitrile-based superconcentrated electrolytes for fast-charging lithium-ion batteries. J Am Chem Soc 136:5039–5046. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja412807w
Septiana AR, Honggowiranto W, Sudaryanto KE, Hidayat R (2018) Comparative study on the ionic conductivities and redox properties of LiPF6 and LiTFSI electrolytes and the characteristics of their rechargeable lithium ion batteries. IOP Conf Ser Mater Sci Eng 432:012061. https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899X/432/1/012061
Triolo A, Russina O, Bleif HJ, Di Cola E (2007) Nanoscale segregation in room temperature ionic liquids. J Phys Chem B 111:4641–4644. https://doi.org/10.1021/JP067705T
Greaves TL, Kennedy DF, Mudie ST, Drummond CJ (2010) Diversity observed in the nanostructure of protic ionic liquids. J Phys Chem B 114:10022–10031. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp103863z
Chen H, Chen X, Deng J, Zheng J (2018) Isotropic ordering of ions in ionic liquids on the sub-nanometer scale. Chem Sci 9:1464–1472. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7sc05184k
Funding
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support from the Ministry of Research and Technology of Indonesia through Program INSINAS Konsorsium Riset Energi Baru dan Terbarukan: Pengembangan Baterai Lithium sebagai Energy Storage Pembangkit Listrik Tenaga Surya under contract no. IRPK-2018-148.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rofika, R.N.S., Honggowiranto, W., Jodi, H. et al. The effect of acetonitrile as an additive on the ionic conductivity of imidazolium-based ionic liquid electrolyte and charge-discharge capacity of its Li-ion battery. Ionics 25, 3661–3671 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-019-02919-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-019-02919-4