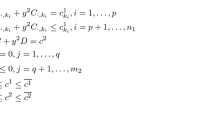Abstract
The interval linear programming (IvLP) is a method for decision making under uncertainty. A weak feasible solution to IvLP is called weakly optimal if it is optimal for some scenario of the IvLP. One of the basic and difficult tasks in IvLP is to check whether a given point is weak optimal. In this paper, we investigate linear programming problems with interval right-hand side. Some necessary and sufficient conditions for checking weak optimality of given feasible solutions are established, based on the KKT conditions of linear programming. The proposed methods are simple, easy to implement yet very effective, since they run in polynomial time.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chinneck, J.W., Ramadan, K.: Linear programming with interval coefficients. J. Oper. Res. Soc. 51(2), 209–220 (2000)
Fiedler, M., Nedoma, J., Ramik, J., Rohn, J., Zimmermann, K.: Linear optimization problems within exact data. Springer-Verlag, New York (2006)
Liu, S.-T., Wang, R.-T.: A numerical solution method to interval quadratic programming. Appl. Math. Comput. 189, 1274–1281 (2007)
Li, W., Tian, X.: Numerical solution method for general interval quadratic programming. Appl. Math. Comput. 202, 589–595 (2008)
Li, W., Tian, X.: Fault detection in discrete dynamic systems with uncertainty based on interval optimization. Math. Model. Anal. 16(4), 549–557 (2011)
Hladík, M.: Optimal value range in interval linear programming. Fuzzy Optim. Decis. Mak. 8(3), 283–294 (2009)
Hladík, M.: Interval linear programming: a survey. In: Adam Mann, Z (ed.) Linear Programming New Frontiers. Nova Science Publishers Inc, Nova (2011)
Hladík, M.: Optimal value bounds in nonlinear programming with interval data. TOP 19(1), 93–106 (2011)
Virgini, G., Cecile, M., Nabila, R.: Linear programming with interval right hand sides. Int. Trans. Oper. Res. 17(3), 397–408 (2010)
Ralph, E.: Steuer, algorithms for linear programming problems with interval objective function coefficients. Math. Oper. Res. 6, 333–348 (1981)
Ishibuchi, H., Tanaka, H.: Multiobjective programming in optimization of the interval objective function. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 48, 219–225 (1990)
Moore, R.E., Kearfott, R.B., Cloud, M.J.: Introduction to interval analysis. SIAM, Philadelphia (2009)
Alefeld, G., Herzberger, J.: Introduction to interval computations. Academic Press, NewYork (1983)
Neumaier, A.: Interval methods for systems of equations. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (1990)
Rohn, J., Kreslová, J.: Linear interval inequalities. Linear Multilinear Algebra 38, 79–82 (1994)
Rohn, J.: An algorithm for computing the hull of the solution set of interval linear equations. Linear Algebra Appl. 435, 193–201 (2011)
Rohn, J.: A general method for enclosing solutions of interval linear equations. Optim. Lett. 6, 709–717 (2012). doi:10.1007/s11590-011-0296-0
Shary, S.P.: A new technique in systems analysis under interval uncertainty and ambiguity. Reliab. Comput. 8(5), 321–418 (2002)
Shary, S.P.: Solving the interval linear tolerance problem. Math. Comput. Simul. 39, 53–85 (1995)
Prokopyev, O.A., Butenko, S., Trapp, A.: Checking solvability of systems of interval linear equations and inequalities via mixed integer programming. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 199, 117–121 (2009)
Alefeld, G., Kreinovich, V., Mayer, G.: On the solution sets of particular classes of linear interval systems. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 152, 1–15 (2003)
Li, W., Wang, H., Wang, Q.: Localized solutions to interval linear equations. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 238, 29–38 (2013)
Allahdadi, M., Mishmast Nehi, H.: The optimal solution set of the interval linear programming problems. Optim. Lett. doi:10.1007/s11590-012-0530-4
Hladík, M.: How to determine basis stability in interval linear programming. Optim. Lett. doi:10.1007/s11590-012-0589-y
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the editor and both the anonymous referees for their constructive comments and suggestions, which have improved the presentation of this paper. This project was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 61003194, 11171316) and PPKC2013YB011.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
We use abbreviation Ivlp, instead of ILP, for interval linear programming, to avoid confusion with the abbreviation for integer linear programming.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, W., Luo, J., Wang, Q. et al. Checking weak optimality of the solution to linear programming with interval right-hand side. Optim Lett 8, 1287–1299 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11590-013-0654-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11590-013-0654-1