Abstract
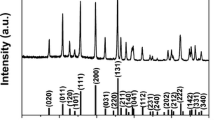
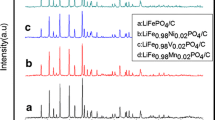
LiFe x Mn1−x PO4/C composites were synthesized by a solid-state reaction route using phenolic resin as both reducing agent and carbon source. The effect of Fe doping on the crystallinity and electrochemical performance of LiFe x Mn1−x PO4/C was investigated. The experimental results show that the Fe2+ substitution for Mn2+ will lead to crystal lattice shrinkage of LiFe x Mn1−x PO4/C particles due to the smaller ionic radii of Fe2+. In the investigated Fe doping range (x = 0 to 0.7), LiFe x Mn1−x PO4/C (x = 0.4) composites exhibited a maximum discharge capacity of 148.8 mAh/g at 0.1 C while LiFe x Mn1−x PO4/C (x = 0.7) composite showed the best cycle capability with a capacity retention ratio of 99.0% after 30 cycles at 0.2 C. On the contrary, the LiFe x Mn1−x PO4/C (x = 0.5) composite performed better trade-off on discharge capacity and capacity retention ratio, 127.2 mAh/g and 94.7% after the first 30 cycles at 0.2 C, respectively, which is more preferred for practical applications.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Padhi AK, Nanjundaswamy KS, Goodenough JB. Phospho-olivines as Positive-electrode Materials for Rechargeable Lithium Batteries[J]. J. Electrochem Soc., 1997, 144(4): 1188–1194
Delacourt C, Laffont L, Bouchet R, et al. Toward Understanding of Electrical Limitations (Electronic, Ionic) in LiMPO4 (M=Fe, Mn) Electrode Materials[J]. J. Electrochem. Soc., 2005, 152(5): A913–A921
Yonemura M, Yamada A, Takei Y, et al. Comparative Kinetic Study of Olivine LixMPO4 (M=Fe, Mn)[J]. J. Electrochem. Soc., 2004, 151(9): A1352–A1356
Molenda J, Ojczyk W, Swierczek K, et al. Diffusional Mechanism of Deintercalation in LiFe1-yMnyPO4 Cathode Material[J]. Solid State Ionics, 2006, 177(26-32): 2617–2 624
Burba CA, Frech R. Local Structure in the Li-ion Battery Cathode Material Lix(MnyFe1-y)PO4 for 0<x≤1 and y=0.0, 0.5 and 1.0[J]. J. Power Sources, 2007, 172(2): 870–876
Drezen T, Kwon NH, Bowen P, et al. Effect of Particle Size on LiMnPO4 Cathodes[J]. J. Power Sources, 2007, 174(2): 949–953
Kim J, Park KY, Park I, et al. The Effect of Particle Size on Phase Stability of the Delithiated LixMnPO4[J]. J. Electrochem Soc., 2012, 159(1): A55–A59
Bramnik NN, Ehrenberg H. Precursor-based Synthesis and Electrochemical Performance of LiMnPO4[J]. J. Alloys and Compounds, 2008, 464(1-2): 259–264
Kumar PR, Venkateswarlu M, Misra M, et al. Carbon Coated LiMnPO4 Nanorods for Lithium Batteries[J]. J. Electrochem. Soc., 2011, 158(3): A227–A230
Zhang B, Wang X, Li H, et al. Electrochemical Performances of LiFe1-xMnxPO4 with High Mn Content[J]. J. Power Sources, 2011, 196(16): 6992–6996
Hong J, Wang F, Wang X, et al. LiFexMn1-xPO4: A Cathode for Lithiumion Batteries[J]. J. Power sources, 2011, 196(7): 3659–3663
Mi CH, Zhang XG, Zhao XB, et al. Synthesis and Performance of LiMn0.6Fe0.4PO4/nano-carbon Webs Composite Cathode[J]. Materials Science and Engineering B, 2006, 129(1-3): 8–13
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Funded by the Applied Basic Research Special Program of Guangzhou City (No.7411793079907), the Guangdong Province Science & Technology Bureau (Nos.2012B091100351, 2012B050300004) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.21376035)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, X., Qin, X., Wang, X. et al. Synthesis and performance of LiFe x Mn1−x PO4/C as cathode material for lithium ion batteries. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol.-Mat. Sci. Edit. 30, 655–659 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11595-015-1206-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11595-015-1206-6