Abstract
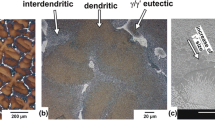
Centrifugal casting was applied to produce cylindrical castings using SiCp/Al composite slurry, which contained 20% SiC particles. The castings comprised a particle free zone and a particle rich zone. The amount of SiC particles had a dramatic transformation from the particle rich zone to the particle free zone, and the maximum content of SiC particles in the particle rich zone reached up to 40 vol%. The ultimate tensile strength (UTS) of the as-cast SiCp / Al composites in the particle rich zone was 143 MPa, and the fracture was caused by the desorption of SiC particles from matrix alloy. The coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE) of the SiCp / Al composites in the range of 20 and 100 °C was determined as 16.67×10-6 s-1, and the experimental CTE was lower than the predicted data based on the Kerner’s model. The results show that the decrease in CTE in the case of the composites at high temperature stage can be attributed to the solute concentration of Si in Al and the plastic deformation of the matrix alloy in the composites with void architecture.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lee HS, Yeo JS, Hong SH, et al. The Fabrication Process and Mechanical Properties of SiCp/Al-Si Metal Matrix Composites for Automobile Air-conditioner Compressor Pistons[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2001, 113 (1-3): 202–208
Ortega-Celaya F, Pech-Canul M I, López- Cuevas J, et al. Microstructure and Impact Behavior of Al/SiCp Composites Fabricated by Pressureless Infiltration with Different Types of SiCp[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2007, 183 (2-3): 368–373
Chen N, Zhang H, Gu M, et al. Effect of Thermal Cycling on the Expansion Behavior of Al/SiCp Composite[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2009, 209 (3): 1 471–1 476
Zhang Q, Wu G, Jiang L, et al. Thermal Expansion and Dimensional Stability of Al-Si Matrix Composite Reinforced with High Content SiC[J]. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 2003, 82 (3): 780–785
Park CS, Kim CH, Kim MH, et al. The Effect of Particle Size and Volume Fraction of the Reinforced Phases on the Linear Thermal Expansion in the Al–Si–SiCp System[J]. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 2004, 88 (1): 46–52
Beffort O, Long S, Cayron C, et al. Alloying Effects on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of High Volume Fraction SiC-particle Reinforced Al-MMCs Made by Squeeze Casting Infiltration[J]. Composites Science and Technology, 2007, 67 (3-4): 737–745
Aghajanian MK, Rocazella MA, Burke JT, et al. The Fabrication of Metal Matrix Composites by a Pressureless Infiltration Technique[J]. Journal of Materials Science, 1991, 26 (2): 447–454
Bahraini M, Minghetti T, Zoellig M, et al. Activated Pressureless Infiltration of Metal-matrix Composites with Graded Activator Content[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing, 2009, 40 (10): 1 566–1 572
Dash K, Ray BC, Chaira D. Synthesis and Characterization of Copperalumina Metal Matrix Composite by Conventional and Spark Plasma Sintering[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2012, 516: 78–84
Scudino S, Liu G, Prashanth KG, et al. Mechanical Properties of Albased Metal Matrix Composites Reinforced with Zr-based Glassy Particles Produced by Powder Metallurgy[J]. Acta Materialia, 2009, 57 (6): 2 029–2 039
Yue TM, Chadwick GA. Squeeze Casting of Light Alloys and Their Composites[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 1996, 58 (2-3): 302–307
Wang K, Cheng JF, Sun WJ, et al. An Approach for Increase of Reinforcement Content in Particle Rich Zone of Centrifugally Cast SiCp/Al Composites[J]. Journal of Composite Materials, 2011, 46 (9): 1 021–1 027
Hoffman M, Skirl S, Pompe W, et al. Thermal Residual Strains and Stresses in Al2O3/Al Composites with Interpenetrating Networks[J]. Acta Materialia, 1999, 47 (2): 565–577
Benal MM, Shivanand HK. Influence of Heat Treatment on the Coefficient of Thermal Expansion of Al (6061) Based Hybrid Composites[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2006, 435-436: 745–749
Seo YH, Kang CG. The Effect of Applied Pressure on Particledispersion Characteristics and Mechanical Properties in Melt-stirring Squeeze-cast SiCp/Al Composites[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 1995, 55 (3-4): 370–379
Wang K, Sun W, Li B, et al. Microstructures in Centrifugal Casting of SiCp/AlSi9Mg Composites with Different Mould Rotation Speeds[J]. Journal of Wuhan University of Technology -Mater. Sci. Ed., 2011, 26 (3): 504–509
Schöbel M, Altendorfer W, Degischer HP, et al. Internal Stresses and Voids in SiC Particle Reinforced Aluminum Composites for Heat Sink Applications[J]. Composites Science and Technology, 2011, 71 (5): 724–733
Schöbel M, Degischer HP, Vaucher S, et al. Reinforcement Architectures and Thermal Fatigue in Diamond Particle-reinforced Aluminum[J]. Acta Materialia, 2010, 58 (19): 6 421–6 430
Rodríguez-Castro R, Wetherhold RC, Kelestemur MH. Microstructure and Mechanical Behavior of Functionally Graded Al A359/SiCp Composite[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2002, 323 (1-2): 445–456
Mazahery A, Shabani MO. Mechanical Properties of Squeeze-Cast A356 Composites Reinforced With B4C Particulates[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance, 2012, 21 (2) 247–252
Leggoe JW, Hu XZ, Bush MB. Crack Tip Damage Development and Crack Growth Resistance in Particulate Reinforced Metal Matrix Composites[J]. Engineering Fracture Mechanics, 1996, 53 (6) 873–895
Elomari S, Skibo MD, Sundarrajan A, et al. Thermal Expansion Behavior of Particulate Metal-matrix Composites[J]. Composites Science and Technology, 1998, 58 (3-4): 369–376
Lemieux S, Elomari S, Nemes JA, et al. Thermal Expansion of Isotropic Duralcan Metal-matrix Composites[J]. Journal of Materials Science, 1998, 33 (17) 4 381–4 387
Geiger AL, Jackson M. Low-Expansion MMCs Boost Avionics[J]. Advanced Materials and Processes, 1993, 7 (136) 23–30
Hahn TA, Armstrong RW. Internal Stress and Solid Solubility Effects on the Thermal Expansivity of Al-Si Eutectic Elloys[J]. International Journal of Thermophysics, 1988, 9 (2) 179–193
Berry CR. Effect of Internal Strains on Linear Expansion, X-ray Lattice Constant, and Density of Crystals[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 1953, 24 (5) 658–659
Neite G, Mielke S. Thermal Expansion and Dimensional Stability of Alumina Fibre Reinforced Aluminium Alloys[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 1991, 148 (1) 85–92
Elomari S, Boukhili R, San Marchi C, et al. Thermal Expansion Responses of Pressure Infiltrated SiC/Al Metal-matrix Composites[J]. Journal of Materials Science, 1997, 32 (8) 2 131–2 140
Schöbel M, Requena G, Kaminski H, et al. Residual Stresses and Void Kinetics in AISiC MMCs during Thermal Cycling[J]. Materials Science Forum, 2008, 571-572: 413–418
Wang K, Xue HS, Zou MH, et al. Microstructural Characteristics and Properties in Centrifugal Casting of SiCp/Zl104 Composite[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2009, 19 (6) 1 410–1 415
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51174244), the Foundational and Cutting-edge Research Plan of Chongqing, China(No. csts2013jcyjA50014) and the Fundamental Research Funds for Central University, China (No. CDJZR12240056)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, K., Jiang, T., Huang, Z. et al. Mechanical and thermal expansion properties of SiCp/ZAlSi9Mg composites produced by centrifugal casting. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol.-Mat. Sci. Edit. 31, 197–203 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11595-016-1352-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11595-016-1352-5