Abstract
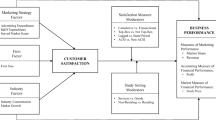
In this article, we propose a path-analytic approach to model the relationships among overall satisfaction, satisfaction with higher order performance domains and the lower order performance attributes for business-to-business services. The model is estimated using data from the business customers of a large provider of electronics products and services. Our results show that overall satisfaction in such contexts may be driven by satisfaction on multiple higher order performance domains and the relevant lower order performance attributes may not drive satisfaction. An adoption of our modeling approach can help service providers make resource allocation decisions across performance domains and identify the micro-level performance levers that they can pull to manage satisfaction levels of their business clients.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson E, Mittal V (2000) Strengthening the satisfaction-profit chain. J Serv Res 3(2):107
Anderson E, Fornell C, Lehmann D (1994) Customer satisfaction, market share, and profitability: findings from Sweden. J Mark 58:53–66
Backhaus K, Bauer M (2001) The impact of critical incidents on customer satisfaction in business-to-business relationships. J Bus To Bus Mark 8(1):25–54
Bitner MJ (1990) Evaluating service encounters: the effects of physical surroundings and employee responses. J Mark 54(2):69–82
Bolton R, Lemon K (1999) A dynamic model of customers’ usage of services: usage as an antecedent and consequence of satisfaction. J Mark Res 36:171–186
Bolton R, Lemon K, Verhoef P (2008) Expanding business-to-business customer relationships: modeling the customer’s upgrade decision. J Mark 72(1):46–64
Bowman D, Narayandas D (2004) Linking customer management effort to customer profitability in business markets. J Mark Res 41(4):433–447
Cronin J, Brady M, Hult G (2000) Assessing the effects of quality, value, and customer satisfaction on consumer behavioral intentions in service environments. J Retail 76(2):193–218
Fornell C (1992) A national customer satisfaction barometer: the Swedish experience. J Mark 56(1):6–21
Gale BT (1997) Managing customer value: creating quality and service that customers can see. Free Press, New York
Gardial S, Clemons D, Woodruff R, Schumann D, Burns M (1994) Comparing consumers’ recall of prepurchase and postpurchase product evaluation experiences. J Consum Res 20(4):548–560
Garson GD (2002) Structural equation modeling. http://www2.chass.ncsu.edu/garson/pa765/structur.htm
Goff BG, Boles JS, Bellenger DN, Stojack C (1997) The influence of salesperson selling behaviors on customer satisfaction with products. J Retail 73(2):171–183
Griffin A, Hauser J (1993) The voice of the customer. Mark Sci 12(1):1–27
Gustafsson A, Johnson M (2004) Determining attribute importance in a service satisfaction model. J Serv Res 7(2):124
Ha H, Janda S (2008) An empirical test of a proposed customer satisfaction model in e-services. J Serv Mark 22(5):399–408
Hofmann D (1997) An overview of the logic and rationale of hierarchical linear models. J Manag 23(6):723
Homburg C, Giering A, Menon A (2003) Relationship characteristics as moderators of the satisfaction-loyalty link: findings in a business-to-business context. J Bus To Bus Mark 10(3):35–62
Homburg C, Wieseke J, Bornemann T (2009) Implementing the marketing concept at the employee–customer interface: the role of customer need knowledge. J Mark 73(4):64–81
Kalwani M, Narayandas N (1995) Long-term manufacturer-supplier relationships: do they pay off for supplier firms? J Mark 59(1):1–16
Keiningham T, Perkins-Munn T, Evans H (2003) The impact of customer satisfaction on share-of-wallet in a business-to-business environment. J Serv Res 6(1):37
Kim H, Jeon S, Kim J (2008) Asp effects in the small-sized enterprise: the case of the Bizmeka service from Korea telecom. Serv Bus 2(4):287–301
Kim C, Oh E, Yang KH (2009) The appealing characteristics of download type mobile games. Serv Bus 4(3–4):253–269
Kumar P (2002) The impact of performance, cost, and competitive considerations on the relationship between satisfaction and repurchase intent in business markets. J Serv Res 5(1):55
Lam S, Shankar V, Erramilli M, Murthy B (2004) Customer value, satisfaction, loyalty, and switching costs: an illustration from a business-to-business service context. J Acad Mark Sci 32(3):293
Lee H, Lee Y, Yoo D (2000) The determinants of perceived service quality and its relationship with satisfaction. J Serv Mark 14(3):217–231
Mithas S, Krishnan M, Fornell C (2005) Why do customer relationship management applications affect customer satisfaction? J Mark 69(4):201–209
Mittal V, Kamakura W (2001) Satisfaction, repurchase intent, and repurchase behavior: investigating the moderating effect of customer characteristics. J Mark Res 38(1):131–142
Mittal V, Kumar P, Tsiros M (1999) Attribute-level performance, satisfaction, and behavioral intentions over time: a consumption-system approach. J Mark 63(2):88–101
Oliver RL (1980) A cognitive model of the antecedents and consequences of satisfaction decisions. J Mark Res 17:460–469
Oliver RL (1981) Measurement and evaluation of satisfaction processes in retail settings. J Retail 57(3):25–48
Oliver RL (1987) An investigation of the interrelationships between consumer (dis)satisfaction and complaining reports. In: Wallendorf M, Anderson P (eds) Advances in consumer research. Association for Consumer Research, Provo, UT
Oliver RL (1997) Satisfaction: a behavioral perspective on the consumer. McGraw Hill International Editions, New York, pp 2–7
Raposo ML, Alves HM, Duarte PA (2009) Dimensions of service quality and satisfaction in healthcare: a patient’s satisfaction index. Serv Bus 3(1):85–100
Reichheld F (2003) The one number you need to grow. Harvard Bus Rev 81(12):46–55
Richins M (1983) Negative word-of-mouth by dissatisfied consumers: a pilot study. J Mark 47(1):68–78
Richins M (1991) Social comparison and the idealized images of advertising. J Consum Res 18(1):71–83
Schneider B, White SS, Paul MC (1998) Linking service climate and customer perceptions of service quality: tests of a causal model. J Appl Psychol 83(2):150–163
Singh J (1991) Understanding the structure of consumers’ satisfaction evaluations of service delivery. J Acad Mark Sci 19(3):223–244
Singh J, Wilkes RE (1996) When consumers complain: a path analysis of the key antecedents of consumer complaint response estimates. J Acad Mark Sci 24(4):350–365
Spreng RA, Harrell GD, Mackoy RD (1995) Service recovery: impact on satisfaction and intentions. J Serv Mark 9(1):15–23
Stock R, Hoyer W (2005) An attitude-behavior model of salespeople’s customer orientation. J Acad Mark Sci 33(4):536–552
Szymanski D, Henard D (2001) Customer satisfaction: a meta-analysis of the empirical evidence. J Acad Mark Sci 29(1):16–35
Taylor S, Hunter G (2003) An exploratory investigation into the antecedents of satisfaction, brand attitude, and loyalty within the (b2b) e-crm industry. J Consum Satisf Dissat Complain Behav 16:19–35
van Doorn J (2008) Is there a halo effect in satisfaction formation in business-to-business services? J Serv Res 11(2):124
Westbrook R (1997) Observations on applied cs/d research. J Consum Satisf Dissat Complain Behav 10:1–6
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, P., Dass, M. & Topaloglu, O. Exploring satisfaction in business-to-business services: a path-analytic approach. Serv Bus 5, 13–27 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11628-010-0099-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11628-010-0099-x