Abstract
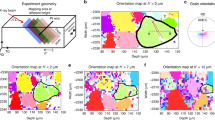
The role of strain transfer in the activation of deformation twinning at grain boundaries has been characterized in commercially pure titanium deformed in bending. Two different orientations of a textured polycrystal were deformed in bending and were analyzed using electron backscattered diffraction (EBSD) to determine the active slip and twinning systems in the surface tensile region. Prismatic slip and \( \left\{ {10\bar{1}2} \right\}\left\langle {\bar{1}011} \right\rangle \) twinning were the most widely observed deformation modes in both orientations. Nonprismatic slip systems were also activated, most likely to accommodate local strain heterogeneities. A slip-stimulated twin nucleation mechanism was identified for soft/hard grain pairs: dislocation slip in a soft-oriented grain can stimulate twin nucleation in the neighboring hard grain when the slip system is well aligned with the twinning system. This alignment was described by a slip-transfer parameter m′.[24] Twins activated by this mechanism always had the highest m′ value among the six available \( \left\{ {10\bar{1}2} \right\}\left\langle {\bar{1}011} \right\rangle \) twinning systems, while the Schmid factor, based on the global (uniaxial tensile) stress state, was a less significant indicator of twin activity. Through slip transfer, deformation twins sometimes formed despite having a very low global Schmid factor. The frequency of slip-stimulated twin nucleation depends strongly on the texture and loading direction in the material. For grain pairs having one grain with a large Schmid factor for twinning, nonparametric statistical analysis confirms that those with a larger m′ are more likely to display slip-stimulated twinning.











Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Camscan is a trademark of Obducat CamScan Ltd, Waterbeach, Cambridgeshire, UK.
Orientation Imaging Microscopy is a trademark of EDAX/TSL, Draper, UT.
References
M.H. Yoo: Metall. Trans. A, 1981, vol. 12A, pp. 409–18.
F. Bridier, P. Villechaise, and J. Mendez: Acta Mater., 2005, vol. 53, pp. 555–67.
S. Zaefferer: Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2003, vol. 344, pp. 20–30.
X. Tan, H. Guo, H. Gu, C. Laird, and N.D.H. Munroe: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 1998, vol. 29A, pp. 513–18.
U.F. Kocks: Metall. Trans., 1970, vol. 1, pp. 1121–43.
M.H. Yoo, J.R. Morris, K.M. Ho, and S.R. Agnew: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2002, vol. 33A, pp. 813–22.
A.A. Salem, S.R. Kalidindi, and R.D. Doherty: Acta Mater., 2003, vol. 51, pp. 4225–37.
F.P.E. Dunne, A. Walker, and D. Rugg: Proc. R. Soc. London, Ser. A, 2007, vol. 463, pp. 1467–89.
J.W. Christian and S. Mahajan: Prog. Mater. Sci., 1995, vol. 39, pp 1–157.
N. Thompson and D.J. Millard: Philos. Mag., 1952, vol. 43, pp. 422–40.
B.A. Bilby and A.G. Crocker: Proc. R. Soc. London, Ser. A, 1965, vol. 288, pp. 240–55.
Y.B. Chun, S.H. Yu, S.L. Semiatin, and S.K. Hwang: Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2005, vol. 398, pp. 209–19.
A. Serra and D.J. Bacon: Philos. Mag., 1996, vol. 73, pp. 333–43.
S.G. Song and G.T. Gray III: Acta Metall. Mater., 1995, vol. 43, pp. 2339–2350.
A. Serra, D.J. Bacon, and R.C. Pond: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2002, vol. 33A, pp. 809–12.
G.C. Kaschner, C.N. Tom′e, R.J. McCabe, A. Misra, S.C. Vogel, and D.W. Brown: Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2007, vol. 463, pp. 122–27.
A.A. Salem, S.R. Kalidindi, and S.L. Semiatin: Acta Mater., 2005, vol. 53, pp. 3495–3502.
S. Nemat-Nasser, W.G. Guo, and J.Y. Cheng: Acta Mater., 1999, vol. 47, pp. 3705–20.
Y. Chino, K. Kimura, M. Mabuchi: Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2008, vol. 486, pp. 481–88.
L. Kucherov and E.B. Tadmor: Acta Mater., 2007, vol. 55, pp. 2065–74.
L. Capolungo and I.J. Beyerlein: Phys. Rev. B, 2008, vol. 78, art. no. 024117.
T.A. Mason, J.F. Bingert, G.C. Kaschner, S.I. Wight, and R.J. Larsen: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2002, vol. 33A, pp. 949–54.
Y. Hu and V. Randle: Scripta Mater., 2007, vol. 57, pp. 1051–54.
J. Luster and M.A. Morris: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 1995, vol. 26A, pp. 1745–56.
W.A.T. Clark, R.H. Wagoner, Z.Y. Shen, T.C. Lee, I.M. Robertson, and H.K. Birnbaum: Scripta Metall. Mater., 1992, vol. 26, pp. 203–06.
B.A. Simkin, B.C. Ng, T.R. Bieler, M.A. Crimp, and D.E. Mason: Intermetallics, 2003, vol. 11, pp. 215–23.
D.L. Davidson, R.G. Tryon, M. Oja, R. Matthews, and K.S. Ravi Chandran: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2007, vol. 38A, pp. 2214–25.
R.G. Miller: Beyond ANOVA: Basics of Applied Statistics, Texts in Statistical Science, Chapman and Hall/CRC, Boca Raton, FL, 1998, pp. 41–64.
H.W. Lilliefors: J. Am. Statistical Assoc., 1967, vol. 62 (318), pp. 399–402.
J.E. Freund: Mathematical Statistics with Applications, 7th ed., Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ, 2004, pp. 529–86.
E.S. Keeping: Introduction to Statistical Inference, D. Von Nostrand Company, Princeton, NJ, 1962, p. 432.
D. Kumar, T.R. Bieler, D.E. Mason, M.A. Crimp, F. Roters, and D. Raabe: J. Eng. Mater. Technol., 2008, vol. 130, art. no. 021012.
A. Fallahi, D.E. Mason, D. Kumar, T.R. Bieler, and M.A. Crimp: Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2006, vol. 432, pp. 281–91.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by a Materials World Network grant from the National Science Foundation (North Arlington, VA, Grant No. DMR-0710570) and Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (Grant No. EI 681/2-1).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted May 9, 2009.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, L., Yang, Y., Eisenlohr, P. et al. Twin Nucleation by Slip Transfer across Grain Boundaries in Commercial Purity Titanium. Metall Mater Trans A 41, 421–430 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-009-0097-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-009-0097-6