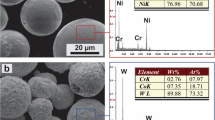
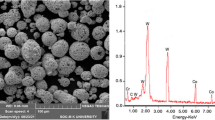
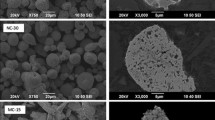
Abstract
Thermal spraying of fine feedstock powders allow the deposition of cermet coatings with significantly improved characteristics and is currently of great interest in science and industry. However, due to the high surface to volume ratio and the low specific weight, fine particles are not only difficult to spray but also show a poor flowability in the feeding process. In order to process fine powders reliably and to preserve the fine structure of the feedstock material in the final coating morphology, the use of novel thermal spray equipment as well as a thorough selection and optimization of the process parameters are fundamentally required. In this study, HVOF spray experiments have been conducted to manufacture fine structured, wear-resistant cermet coatings using fine 75Cr3C2-25(Ni20Cr) powders (−8 + 2 μm). Statistical design of experiments (DOE) has been utilized to identify the most relevant process parameters with their linear, quadratic and interaction effects using Plackett-Burman, Fractional-Factorial and Central Composite designs to model the deposition efficiency of the process and the majorly important coating properties: roughness, hardness and porosity. The concept of desirability functions and the desirability index have been applied to combine these response variables in order to find a process parameter combination that yields either optimum results for all responses, or at least the best possible compromise. Verification experiments in the so found optimum obtained very satisfying or even excellent results. The coatings featured an average microhardness of 1004 HV 0.1, a roughness Ra = 1.9 μm and a porosity of 1.7%. In addition, a high deposition efficiency of 71% could be obtained.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. Morimoto, Y. Sasaki, S. Fukuhara, N. Abe, and M. Tukamoto, Surface Modification of Cr3C2–NiCr Cermet Coatings by Direct Diode Laser, Vacuum, 2006, 80(11-12), p 1400-1405
R. Nieminen, P. Vuoristo, K. Niemi, T. Mantyla, and G. Barbezat, Rolling Contact Fatigue Failure Mechanisms in Plasma and HVOF Sprayed WC-Co Coatings, Wear, 1997, 212(1), p 66-77
K. Bobzin, F. Ernst, J. Zwick, and G. Matthäus, Analysis of In-Flight Particle Properties of Thermal Sprayed Ultrafine Powders, Mater. Sci. Eng. Technol., 2007, 38(2), p 149-154
S. Zimmermann, H. Keller, and G. Schwier, Improved Coating Properties by Optimized Carbide Powders for Modern HVOF Systems, 6th HVOF Spraying Colloquium, Nov 27-28 (Germany), GTS e.V., 2003, p 31-38
Y. Qiao, T.E. Fischer, and A. Dent, The Effects of Fuel Chemistry and Feedstock Powder Structure on the Mechanical and Tribological Properties of HVOF Thermal-Sprayed WC-Co Coatings with Very Fine Structures, Surf. Coat. Technol., 2003, 172(1), p 24-41
J.M. Guilemany, S. Dosta, J. Nin, and J.R. Miguel, Study of the Properties of WC-Co Nanostructured Coatings Sprayed by High-Velocity Oxyfuel, J. Therm. Spray Technol., 2005, 14(3), p 405-413
K. Bobzin, F. Ernst, J. Zwick, and G. Matthaeus, Analyse von Partikeleigenschaften beim Thermischen Spritzen von Mikropulvern (Analysis of the Particle Properties in Thermal Spraying of Micronpowders), Mat.-wiss. u. Werkstofftech., 2007, 38(2), p 149-154 (in German)
S. Matthews, M. Hyland, and B. James, Microhardness Variation in Relation to Carbide Development in Heat Treated Cr3C2–NiCr Thermal Spray Coatings, Acta Mater., 2003, 51(14), p 4267-4277
W. Tillmann, E. Vogli, I. Baumann, G. Matthaeus, and T. Ostrowski, Influence of the HVOF Gas Composition on the Thermal Spraying of WC-Co Submicron Powders (−8 +1 μm) to Produce Superfine Structured Cermet Coatings, J. Therm. Spray Technol., 2008, 17(5-6), p 924-932
D. Toma, W. Brandl, and G. Marginean, Wear and Corrosion Behaviour of Thermally Sprayed Cermet Coatings, Surf. Coat. Technol., 2001, 138, p 149-158
J.A. Picas, A. Forna, A. Igartuab, and G. Mendozab, Mechanical and Tribological Properties of High Velocity Oxy-Fuel Thermal Sprayed Nanocrystalline CrC-NiCr Coatings, Surf. Coat. Technol., 2003, 174-175, p 1095-1100
D.C. Crawmer, J.D. Krebsbach, and W.L. Riggs, Coating Development for HVOF Process Using Design of Experiment, Thermal Spray: International Advances in Coatings Technology, C.C. Berndt, Ed., ASM International, Materials Park, OH, 1992, p 127-136
L. Russo and M. Dorfmann, Thermal Spraying, Current Status and Future Trends, A. Ohmori, Ed., Japan High Temperature Society, Osaka, 1995, p 681-686
K. Kreye, R. Schwetzke, and S. Zimmermann, High Velocity Oxy-Fuel Flame Spraying-Process and Coating Characteristics, Thermal Spray: Practical Solutions for Engineering Problems, C.C. Berndt, Ed., ASM International, Materials Park, OH, 1996, p 451-456
J.M. Guilemany and J.A. Calero, Structural Evaluation Phenomena During High Velocity (HVOF) of the Composite Material Cr 3 C 2 -NiCr, Surface Modification Technologies XI, T.S. Sudarshan, et al., Ed., The Institute of Materials, Paris, 1997, p 81-85
K. Taoa, X. Zhoua, H. Cuib, and J. Zhanga, Microhardness Variation in Heat-Treated Conventional and Nanostructured NiCrC Coatings Prepared by HVAF Spraying, Surf. Coat. Technol., 2009, 203(10-11), p 1406-1414
G.C. Jia, C.J. Lib, Y.Y. Wang, and W.Y. Lib, Microstructural Characterization and Abrasive Wear Performance of HVOF Sprayed Cr3C2-NiCr Coating, Surf. Coat. Technol., 2006, 200(24), p 6749-6757
V.V. Sobolev and J.M. Guilemany, Effect of Oxidation on Droplet Flattening and Splat-Substrate Interaction in Thermal Spraying, J. Therm. Spray Technol., 1999, 8(4), p 523-530
N. Eigen, F. Gärtner, T. Klassen, E. Aust, R. Bormann, and H. Kreye, Microstructures and Properties of Nanostructured Thermal Sprayed Coatings Using High-Energy Milled Cermet Powders, Surf. Coat. Technol., 2005, 195, p 344-357
L. Gil and M.H. Staia, Influence of HVOF Parameters on the Corrosion Resistance of NiWCrBSi Coatings, Thin Solid Films, 2002, 420-421, p 446-454
G. Derringer and R. Suich, Simultaneous Optimization of Several Response Variables, J. Qual. Technol., 1980, 12, p 214-219
G. Matthaeus, M. Kostecki, and O. Dau, The Fully Automatic, Computer Controlled C-CJS (Computerised Carbide Jet System) HVOF System with 25 bar Combustion-Chamber Pressure by Thermico, 5th Colloquium on HVOF Flame Spraying, Flame Spraying, Nov 16-17 (Germany), GTS e.V., 2000, p 147-158
R-Development Core Team, R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. R-Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. ISBN 3-900051-07-0, 2008
H. Chena, G. Goua, M. Tub, and Y. Liua, Characteristics of Nano Particles and Their Effect on the Formation of Nanostructures in Air Plasma Spraying WC–17Co Coating, Surf. Coat. Technol., 2009, 203(13), p 1785-1789
T.P. Ryan, Modern Experimental Design, Wiley, Hoboken, NJ, 2007
D.C. Montgomery, Statistical Quality Control, 6th ed., Wiley, New York, 2009
W.N. Venables and B.D. Ripley, Modern Applied Statistics with S, 4th ed., Springer, New York, 2002
H. Trautmann, D. Steuer, O. Mersmann, U. Ligges, and C. Weihs, desiRe: Desirability Functions and Indices in Multicriteria Optimization, R-Package v0.9.6., 2008, http://r-forge.r-project.org/projects/desire
O.P. Solonenko, Advanced Thermophysical Fundamentals of Melt-Droplet-Substrate Interaction and its Application in Thermal Spraying, Novosibirrsk, Russia, 2003
K. Jia and T.E. Fisher, Abrasion Resistance of Nanostructured and Conventional Cemented Carbides, Wear, 1996, 1-2(200), p 206
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support of the DFG (German Science Foundation) within the Collaborative Research Centres SFB 475 and SFB 708, and the Transregional Collaborative Research Centre SFB TRR 30.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article is an invited paper selected from presentations at the 2009 International Thermal Spray Conference and has been expanded from the original presentation. It is simultaneously published in Expanding Thermal Spray Performance to New Markets and Applications: Proceedings of the 2009 International Thermal Spray Conference, Las Vegas, Nevada, USA, May 4-7, 2009, Basil R. Marple, Margaret M. Hyland, Yuk-Chiu Lau, Chang-Jiu Li, Rogerio S. Lima, and Ghislain Montavon, Ed., ASM International, Materials Park, OH, 2009.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tillmann, W., Vogli, E., Baumann, I. et al. Desirability-Based Multi-Criteria Optimization of HVOF Spray Experiments to Manufacture Fine Structured Wear-Resistant 75Cr3C2-25(NiCr20) Coatings. J Therm Spray Tech 19, 392–408 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11666-009-9383-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11666-009-9383-5