Abstract
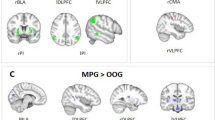
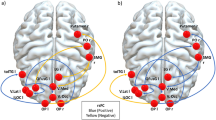
Evidence suggests that women who suffer from intimate partner violence (IPV) and posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) have structural and functional alterations in specific brain regions. Yet, little is known about how brain connectivity may be altered in individuals with IPV, but without PTSD. Women exposed to IPV (n = 18) and healthy controls (n = 18) underwent structural brain imaging using a Siemens 3T MRI. Global and regional brain network connectivity measures were determined, using graph theory analyses. Structural covariance networks were created using volumetric and cortical thickness data after controlling for intracranial volume, age and alcohol use. Nonparametric permutation tests were used to investigate group differences. Findings revealed altered connectivity on a global and regional level in the IPV group of regions involved in cognitive-emotional control, with principal involvement of the caudal anterior cingulate, the middle temporal gyrus, left amygdala and ventral diencephalon that includes the thalamus. To our knowledge, this is the first evidence showing different brain network connectivity in global and regional networks in women exposed to IPV, and without PTSD. Altered cognitive-emotional control in IPV may underlie adaptive neural mechanisms in environments characterized by potentially dangerous cues.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achard, S., Salvador, R., Whitcher, B., Suckling, J., & Bullmore, E. (2006). A resilient, low-frequency, small-world human brain functional network with highly connected association cortical hubs. The Journal of Neuroscience, 26(1), 63–72.
Astolfi, L., Cincotti, F., Mattia, D., De Vico Fallani, F., Salinari, S., Vecchiato, G., et al. (2010). Imaging the social brain: Multi-subjects EEG recordings during the "chicken's game". In Conference proceedings: Annual international conference of the IEEE engineering in medicine and biology society. IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (pp. 1734–1737).
Bassett, D. S., & Bullmore, E. (2006). Small-world brain networks. The Neuroscientist, 12(6), 512–523.
Bassett, D. S., Bullmore, E., Verchinski, B. A., Mattay, V. S., Weinberger, D. R., & Meyer-Lindenberg, A. (2008). Hierarchical organization of human cortical networks in health and schizophrenia. The Journal of Neuroscience, 28(37), 9239–9248.
Bernhardt, B. C., Chen, Z., He, Y., Evans, A. C., & Bernasconi, N. (2011). Graph-theoretical analysis reveals disrupted small-world organization of cortical thickness correlation networks in temporal lobe epilepsy. Cerebral Cortex, 21(9), 2147–2157.
Bohn, M. J., Babor, T. F., & Kranzler, H. R. (1995). The alcohol use disorders identification test (AUDIT): validation of a screening instrument for use in medical settings. Journal of Studies on Alcohol, 56(4), 423–432.
Bush, G., Luu, P., & Posner, M. I. (2000). Cognitive and emotional influences in anterior cingulate cortex. Trends in Cognitive Science, 4(6), 215–222.
Campbell-Meiklejohn, D. K., Kanai, R., Bahrami, B., Bach, D. R., Dolan, R. J., Roepstorff, A., et al. (2012). Structure of orbitofrontal cortex predicts social influence. Current Biology, 22(4), R123–R124.
Cavada, C., Company, T., Tejedor, J., Cruz-Rizzolo, R. J., & Reinoso-Suarez, F. (2000). The anatomical connections of the macaque monkey orbitofrontal cortex. A review. Cerebral Cortex, 10(3), 220–242.
Decker, M. R., Latimore, A. D., Yasutake, S., Haviland, M., Ahmed, S., Blum, R. W., et al. (2015). Gender-based violence against adolescent and young adult women in low- and middle-income countries. The Journal of Adolescent Health, 56(2), 188–196.
Desikan, R. S., Segonne, F., Fischl, B., Quinn, B. T., Dickerson, B. C., Blacker, D., et al. (2006). An automated labeling system for subdividing the human cerebral cortex on MRI scans into gyral based regions of interest. Neuro Image, 31(3), 968–980.
Devries, K. M., Mak, J. Y., Bacchus, L. J., Child, J. C., Falder, G., Petzold, M., et al. (2013). Intimate partner violence and incident depressive symptoms and suicide attempts: a systematic review of longitudinal studies. PLoS Medicine, 10(5), e1001439.
Eippert, F., Veit, R., Weiskopf, N., Erb, M., Birbaumer, N., & Anders, S. (2007). Regulation of emotional responses elicited by threat-related stimuli. Human Brain Mapping, 28(5), 409–423.
Ellsberg, M., Jansen, H. A. F. M., Heise, L., Watts, C. H., & Garcia-Moreno, C. (2008). Intimate partner violence and women’s physical and mental health in the WHO multi-country study on women’s health and domestic violence: an observational study. Lancet, 371(9619), 1165–1172.
Farrow, T. F., Zheng, Y., Wilkinson, I. D., Spence, S. A., Deakin, J. F., Tarrier, N., et al. (2001). Investigating the functional anatomy of empathy and forgiveness. Neuroreport, 12(11), 2433–2438.
Fennema-Notestine, C., Stein, M. B., Kennedy, C. M., Archibald, S. L., & Jernigan, T. L. (2002). Brain morphometry in female victims of intimate partner violence with and without posttraumatic stress disorder. Biological Psychiatry, 52(11), 1089–1101.
Fischl, B., & Dale, A. M. (2000). Measuring the thickness of the human cerebral cortex from magnetic resonance images. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 97(20), 11050–11055.
Fischl, B., Salat, D. H., van der Kouwe, A. J., Makris, N., Segonne, F., Quinn, B. T., et al. (2004). Sequence-independent segmentation of magnetic resonance images. Neuro Image, 23(Suppl 1), S69–S84.
Flegar, S. J., Fouche, J. P., Jordaan, E., Marais, S., Spottiswoode, B., Stein, D. J., et al. (2011). The neural correlates of intimate partner violence in women. African Journal of Psychiatry, 14(4), 310–314.
Fletcher, P. C., Frith, C. D., Baker, S. C., Shallice, T., Frackowiak, R. S., & Dolan, R. J. (1995). The mind's eye--precuneus activation in memory-related imagery. Neuro Image, 2(3), 195–200.
Garcia-Moreno, C., Jansen, H. A., Ellsberg, M., Heise, L., Watts, C. H., & WHO Multi-country Study on Women's Health and Domestic Violence against Women Study Team (2006). Prevalence of intimate partner violence: findings from the WHO multi-country study on women's health and domestic violence. Lancet, 368(9543), 1260–1269.
Golding, J. (1999). Intimate partner violence as a risk factor for mental disorders: a meta-analysis. Journal of Family Violence, 14, 99–132.
Goodman, L. A., Smyth, K. F., Borges, A. M., & Singer, R. (2009). When crises collide: how intimate partner violence and poverty intersect to shape women's mental health and coping? Trauma. Violence & Abuse, 10(4), 306–329.
Gunnar, M. R., Fisher, P. A., Dozier, M., Fox, N., Levine, S., Neal, C., et al. (2006). Bringing basic research on early experience and stress neurobiology to bear on preventive interventions for neglected and maltreated children. Development and Psychopathology, 18, 651–677.
Guye, M., Bettus, G., Bartolomei, F., & Cozzone, P. J. (2010). Graph theoretical analysis of structural and functional connectivity MRI in normal and pathological brain networks. Magma, 23(5–6), 409–421.
He, Y., & Evans, A. (2014). Magnetic resonance imaging of healthy and diseased brain networks. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 8, 890.
He, Y., Chen, Z., & Evans, A. (2008). Structural insights into aberrant topological patterns of large-scale cortical networks in alzheimer's disease. The Journal of Neuroscience, 28(18), 4756–4766.
Hosseini, S. M., Hoeft, F., & Kesler, S. R. (2012). GAT: a graph-theoretical analysis toolbox for analyzing between-group differences in large-scale structural and functional brain networks. PloS One, 7(7), e40709.
Hosseini, S. M., Black, J. M., Soriano, T., Bugescu, N., Martinez, R., Raman, M. M., et al. (2013). Topological properties of large-scale structural brain networks in children with familial risk for reading difficulties. Neuro Image, 71, 260–274.
Jelicic, M., & Merckelbach, H. (2004). Traumatic stress, brain changes, and memory deficits: a critical note. The Journal of Nervous and Mental Disease, 192(8), 548–553.
Jellison, B. J., Field, A. S., Medow, J., Lazar, M., Salamat, M. S., & Alexander, A. L. (2004). Diffusion tensor imaging of cerebral white matter: a pictorial review of physics, fiber tract anatomy, and tumor imaging patterns. American Journal of Neuroradiology, 25(3), 356–369.
Joyner, K., Rees, K., & Honikman, S. (2015). Intimate partner violence (IPV) in South Africa: how to break the vicious cycle. CPMH Policy Brief, 1–6.
Kaiser, M., & Hilgetag, C. C. (2006). Nonoptimal component placement, but short processing paths, due to long-distance projections in neural systems. PLoS Computational Biology, 2(7), e95.
Karl, A., Schaefer, M., Malta, L. S., Dorfel, D., Rohleder, N., & Werner, A. (2006). A meta-analysis of structural brain abnormalities in PTSD. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews, 30(7), 1004–1031.
Kerestes, R., Ladouceur, C. D., Meda, S., Nathan, P. J., Blumberg, H. P., Maloney, K., et al. (2012). Abnormal prefrontal activity subserving attentional control of emotion in remitted depressed patients during a working memory task with emotional distracters. Psychological Medicine, 42(1), 29–40.
Krishnadas, R., Kim, J., McLean, J., Batty, G. D., McLean, J. S., Millar, K., et al. (2013). The envirome and the connectome: exploring the structural noise in the human brain associated with socioeconomic deprivation. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 7, 722.
Kulwicki, A., Ballout, S., Kilgore, C., Hammad, A., & Dervartanian, H. (2015). Intimate partner violence, depression, and barriers to service utilization in Arab American women. Journal of Transcultural Nursing, 26(1), 24–30.
Kwako, L. E., Glass, N., Campbell, J., Melvin, K. C., Barr, T., & Gill, J. M. (2011). Traumatic brain injury in intimate partner violence: a critical review of outcomes and mechanisms. Trauma, Violence & Abuse, 12(3), 115–126.
Kyzar, E. J., & Pandey, S. C. (2015). Molecular mechanisms of synaptic remodeling in alcoholism. Neuroscience Letters, 601, 11–19.
Lanteaume, L., Khalfa, S., Regis, J., Marquis, P., Chauvel, P., & Bartolomei, F. (2007). Emotion induction after direct intracerebral stimulations of human amygdala. Cerebral Cortex, 17(6), 13071313.
Liao, X. H., Xia, M. R., Xu, T., Dai, Z. J., Cao, X. Y., Niu, H. J., et al. (2013). Functional brain hubs and their test-retest reliability: a multiband resting-state functional MRI study. Neuro Image, 83, 969–982.
Lundstrom, B. N., Ingvar, M., & Petersson, K. M. (2005). The role of precuneus and left inferior frontal cortex during source memory episodic retrieval. Neuro Image, 27(4), 824–834.
Marais, S., Jordaan, E., Viljoen, D., & Olivier, L. (2010). Modifying alcohol drinking behaviour by means of screening and brief interventions with the aim of preventing fetal alcohol syndrome in a high risk population – a cluster randomized trial. Early Child Development and Care, 1–12.
Markowitsch, H. (1998). Differential contribution of right and left amygdala to affective information processing. Behavioural Neurology, 11(4), 233–244.
Martini, F. (2006). The brain and cranial nerves. In Fundamentals of anatomy and physiology (pp. 451–494). San Francisco: Pearson Benjamin Cummings.
Maslov, S., & Sneppen, K. (2002). Specificity and stability in topology of protein networks. Science, 296(5569), 910–913.
McCrory, E., De Brito, S. A., & Viding, E. (2010). Research review: the neurobiology and genetics of maltreatment and adversity. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, and Allied Disciplines, 51(10), 1079–1095.
McFarlane, J., Parker, B., Soeken, K., & Bullock, L. (1992). Assessing for abuse during pregnancy. Severity and frequency of injuries and associated entry into prenatal care. JAMA, 267(23), 3176–3178.
Meshi, D., Biele, G., Korn, C. W., & Heekeren, H. R. (2012). How expert advice influences decision making. PloS One, 7(11), e49748.
Milo, R., Shen-Orr, S., Itzkovitz, S., Kashtan, N., Chklovskii, D., & Alon, U. (2002). Network motifs: simple building blocks of complex networks. Science, 298(5594), 824–827.
Murray, E. A., Izquierdo, A., & Malkova, L. (2009). Amygdala function in positive reinforcement. In P. J. Whalen, E. A. Phelps (Eds.), The Human Amygdala. New York: Guilford Press.
Nutt, D. J., & Malizia, A. L. (2004). Structural and functional brain changes in posttraumatic stress disorder. The Journal of Clinical Psychiatry, 65(Suppl 1), 11–17.
Pandya, D. N., Hoesen, G. W., & Mesulam, M. M. (1981). Efferent connections of the cingulate gyrus in the rhesus monkey. Experimental Brain Research, 42(3–4), 19–30.
Patel, R., Spreng, R. N., Shin, L. M., & Girard, T. A. (2012). Neurocircuitry models of posttraumatic stress disorder and beyond: a meta-analysis of functional neuroimaging studies. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews, 36(9), 2130–2142.
Pederson, C. L., Maurer, S. H., Kaminski, P. L., Zander, K. A., Peters, C. M., Stokes-Crowe, L. A., et al. (2004). Hippocampal volume and memory performance in a community-based sample of women with posttraumatic stress disorder secondary to child abuse. Journal of Traumatic Stress, 17(1), 37–40.
Peterson, A., Thome, J., Frewen, P., & Lanius, R. A. (2014). Resting-state neuroimaging studies: a new way of identifying differences and similarities among the anxiety disorders? Canadian Journal of Psychiatry, 59(6), 294–300.
Rauch, S. L., Shin, L. M., & Phelps, E. A. (2006). Neurocircuitry models of posttraumatic stress disorder and extinction: human neuroimaging research--past, present, and future. Biological Psychiatry, 60(4), 376–382.
Roland, P. E., & Gulyas, B. (1995). Visual memory, visual imagery, and visual recognition of large field patterns by the human brain: functional anatomy by positron emission tomography. Cerebral Cortex, 5(1), 79–93.
Rubinov, M., & Sporns, O. (2010). Complex network measures of brain connectivity: uses and interpretations. Neuro Image, 52(3), 1059–1069.
Rushworth, M. F., Noonan, M. P., Boorman, E. D., Walton, M. E., & Behrens, T. E. (2011). Frontal cortex and reward-guided learning and decision-making. Neuron, 70(6), 1054–1069.
Satyanarayana, V. A., Chandra, P. S., & Vaddiparti, K. (2015). Mental health consequences of violence against women and girls. Current Opinion in Psychiatry, 28(5), 350–356.
Seedat, S., Videen, J. S., Kennedy, C. M., & Stein, M. B. (2005). Single voxel proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy in women with and without intimate partner violence-related posttraumatic stress disorder. Psychiatry Research, 139(3), 249–258.
Sheehan, D. V., Lecrubier, Y., Sheehan, K. H., Amorim, P., Janavs, J., Weiller, E., et al. (1998). The mini-international neuropsychiatric interview (M.I.N.I.): the development and validation of a structured diagnostic psychiatric interview for DSM-IV and ICD-10. The Journal of Clinical Psychiatry, 59 Suppl 20, 22–33.
Shin, L. M., Rauch, S. L., & Pitman, R. K. (2006). Amygdala, medial prefrontal cortex, and hippocampal function in PTSD. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 1071, 67–79.
Sibille, E. (2013). Molecular aging of the brain, neuroplasticity, and vulnerability to depression and other brain-related disorders. Dialogues in Clinical Neuroscience, 15(1), 53–65.
Simmons, A. N., Paulus, M. P., Thorp, S. R., Matthews, S. C., Norman, S. B., & Stein, M. B. (2008). Functional activation and neural networks in women with posttraumatic stress disorder related to intimate partner violence. Biological Psychiatry, 64(8), 681–690.
Simmons, A., Strigo, I. A., Matthews, S. C., Paulus, M. P., & Stein, M. B. (2009). Initial evidence of a failure to activate right anterior insula during affective set shifting in posttraumatic stress disorder. Psychosomatic Medicine, 71(4), 373–377.
Squeglia, L. M., Sorg, S. F., Schweinsburg, A. D., Wetherill, R. R., Pulido, C., & Tapert, S. F. (2012). Binge drinking differentially affects adolescent male and female brain morphometry. Psychopharmacology, 220(3), 529–539.
Stein, M. B., Kennedy, C. M., & Twamley, E. W. (2002). Neuropsychological function in female victims of intimate partner violence with and without posttraumatic stress disorder. Biological Psychiatry, 52(11), 1079–1088.
van Oort, E. S., van Cappellen van Walsum, A. M., & Norris, D. G. (2014). An investigation into the functional and structural connectivity of the default mode network. NeuroImage, 90, 381–389.
van Wijk, B. C., Stam, C. J., & Daffertshofer, A. (2010). Comparing brain networks of different size and connectivity density using graph theory. PloS One, 5(10), e13701.
Vyas, A., Mitra, R., Shankaranarayana Rao, B. S., & Chattarji, S. (2002). Chronic stress induces contrasting patterns of dendritic remodeling in hippocampal and amygdaloid neurons. The Journal of Neuroscience, 22(15), 6810–6818.
Wakana, S., Jiang, H., Nagae-Poetscher, L. M., Van Zijl, P. C., & Mori, S. (2004). Fiber tract-based atlas of human white matter anatomy. Radiology, 230(1), 77–87.
Weich, S., Patterson, J., Shaw, R., & Stewart-Brown, S. (2009). Family relationships in childhood and common psychiatric disorders in later life: systematic review of prospective studies. The British Journal of Psychiatry, 194(5), 392–398.
Williams, L. M., Kemp, A. H., Felmingham, K., Barton, M., Olivieri, G., Peduto, A., Gordon, E., & Bryant, R. A. (2006). Trauma modulates amygdala and medial prefrontal responses to consciously attended fear. Neuroimage, 29(2), 347–57.
Wong, J. Y., Fong, D. Y., Lai, V., & Tiwari, A. (2014). Bridging intimate partner violence and the human brain: a literature review. Trauma, Violence & Abuse, 15(1), 22–33.
Woon, F. L., Sood, S., & Hedges, D. W. (2010). Hippocampal volume deficits associated with exposure to psychological trauma and posttraumatic stress disorder in adults: a meta-analysis. Progress in Neuro-Psychopharmacology and Biological Psychiatry, 34(7), 1181–1188.
World Health Organization (2005). WHO multi-country study on women’s health and domestic violence against women: Summary report of initial results on prevalence, health outcomes and women’s responses. Geneva: World Health Organization http://www.who.int/gender/violence/who_multicountry_study/summary_report/summary_report_English2.pdf. Accessed 7 April 2016.
Zhang, S., & Li, C. S. (2012). Functional connectivity mapping of the human precuneus by resting state fMRI. NeuroImage, 59(4), 3548–3562.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the Centre for Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), and by a fellowship from the Brain-Behavior Initiative of Cape Town University (SA). We acknowledge Sandra Marais who was a principal investigator of a larger clinical trial from which participants were drawn, and Bavi Vythilingum who guided study procedures. We also thank the CSIR Centre for High Performance Computing at Cape Town for providing the supercomputing facilities to perform Freesurfer analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
This study was funded by the Centre for Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), and by a fellowship from the Brain-Behavior Initiative of Cape Town University (South Africa).
Conflict of interest
A Roos, JP Fouche and DJ Stein declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This study included human participants. All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Roos, A., Fouche, JP. & Stein, D.J. Brain network connectivity in women exposed to intimate partner violence: a graph theory analysis study. Brain Imaging and Behavior 11, 1629–1639 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-016-9644-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-016-9644-0