Abstract
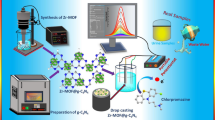
The investigation of synthetic dyes in beverages is significant, owing to their pathogenic and low toxicity a Fe3O4–MWCNTs electrochemical sensor was developed for the determination of sunset yellow (SY) in beverages. A simple one-step hydrothermal method was implemented for the synthesis of Fe3O4–MWCNTs nanocomposite. The structural and surface morphologies of Fe3O4–MWCNTs were studied using XRD, TEM, EDS and FE-SEM techniques. The synthesized nanocomposite showed cubic face centered Fe3O4 nanostructure with a probable crystallite size. The anchoring of Fe3O4 nanoparticles in MWCNTs were further conformed with TEM analysis. The FE-SEM analysis showed that the cubical shaped Fe3O4 nanoparticles were strongly anchored with an estimated granules size. The synthesized composite was utilized for the fabrication of sensitive and selective electrochemical sensor based on the drop casting of Fe3O4–MWCNTs composite on glassy carbon electrode (GCE) (Fe3O4–MWCNTs/GCE). The fabricated sensor was used for the quantification of SY. The sensor exhibited enhanced oxidation activity towards SY determination, by providing operational access to its determination in the field of food safety control. CV, DPV, and EIS techniques were utilized for the investigation of the electrochemical performance of SY. The influence of pH value of phosphate buffer solution (PBS) and effect of scan rate on the peak currents of SY were deliberated. The oxidation peak currents of SY were proportional to its concentrations in the range from 0.2 to 3.5 µM with a low limit of detection of 1.4 nM. The newly fabricated sensor exhibited good selectivity, stability, repeatability and reproducibility. Moreover, it was successfully applied for the detection of SY in soft drinks with acceptable recoveries. The developed sensor was viable with a good sensitivity and simple option for SY detection in the field of food safety.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Arvand, M. Zamani, M.S. Ardaki, Rapid electrochemical synthesis of molecularly imprinted polymers on functionalized multi-walled carbon nanotubes for selective recognition of sunset yellow in food samples. Sens. Actuators B 243, 927–939 (2017)
X. Chen, K. Wu, Y. Sun, X. Song, Highly sensitive electrochemical sensor for sunset yellow based on the enhancement effect of alumina microfibers. Sens. Actuators B 185, 582–586 (2013)
N.E. Llamas, M. Garrido, M.S. Di Nezio, B.S.F. Band, Second-order advantage in the determination of amaranth, sunset yellow FCF and tartrazine by UV–Vis and multivariate curve resolution alternating least squares. Anal. Chim. Acta 655, 38–42 (2009)
L. Magerusan, F. Pogacean, M. Coros, C. Socaci, S. Pruneanu, C. Leostean, I.O. Pana, Green methodology for the preparation of chitosan/graphene nanomaterial through electrochemical exfoliation and its applicability in Sunset Yellow detection. Electrochim. Acta 283, 578–589 (2018)
M. Bijad, H.K. Maleh, M. Farsi, S.A. Shahidi, An electrochemical-amplified-platform based on the nanostructure voltammetric sensor for the determination of carmoisine in the presence of tartrazine in dried fruit and soft drink samples. J. Food Meas. Charact. 12, 634–640 (2018)
M. Elyasi, M.A. Khalilzadeh, H.K. Maleh, High sensitive voltammetric sensor based on Pt/CNTs nanocomposite modified ionic liquid carbon paste electrode for determination of Sudan I in food samples. Food Chem. 141, 4311–4317 (2013)
M. Roosta, M. Ghaedi, R. Sahraei, M.K. Purkait, Ultrasonic assisted removal of sunset yellow from aqueous solution by zinc hydroxide nanoparticle loaded activated carbon: optimized experimental design. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 52, 82–89 (2015)
L. Yu, M. Shi, X. Yue, L. Qu, A novel and sensitive hexadecyltrimethylammonium bromide functionalized graphene supported platinum nanoparticles composite modified glassy carbon electrode for determination of sunset yellow in soft drinks. Sens. Actuators B 209, 1–8 (2015)
X. Wu, X. Zhang, C. Zhao, X. Qian, One-pot hydrothermal synthesis of ZnO/rGO/ZnO@Zn sensor for sunset yellow in soft drinks. Talanta 179, 836–844 (2018)
Y. Songyang, X. Yang, S. Xie, H. Hao, J. Song, Highly-sensitive and rapid determination of sunset yellow using functionalized montmorillonite-modified electrode. Food Chem. 173, 640–644 (2015)
J. Wang, B. Yang, K. Zhang, D. Bin, Y. Shiraishi, P. Yang, Y. Du, Highly sensitive electrochemical determination of Sunset Yellow based on the ultrafine Au–Pd and reduced graphene oxide nanocomposites. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 481, 229–235 (2016)
K. Rovina, S. Siddiquee, S. Md Shaarani, Highly sensitive electrochemical determination of sunset yellow in commercial food products based on CHIT/GO/MWCNTs/AuNPs/GCE. Food Control 82, 66–73 (2017)
H. Yang, Y. Long, H. Li, S. Pan, H. Liu, J. Yang, X. Hu, Carbon dots synthesized by hydrothermal process via sodium citrate and NH4HCO3 for sensitive detection of temperature and sunset yellow. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 516, 192–201 (2018)
O.I. Lipskikh, E.I. Korotkova, Ye.P. Khristunova, J. Barek, B. Kratochvil, Sensors for voltammetric determination of food azo dyes—a critical review. Electrochim. Acta 260, 974–985 (2018)
K. Deng, C. Li, X. Li, H. Huang, Simultaneous detection of sunset yellow and tartrazine using the nanohybrid of gold nanorods decorated graphene oxide. J. Electroanal. Chem. 780, 296–302 (2016)
T. Gan, J. Sun, S. Cao, F. Gao, Y. Zhang, Y. Yang, One-step electrochemical approach for the preparation of graphene wrapped-phosphotungstic acid hybrid and its application for simultaneous determination of sunset yellow and tartrazine. Electrochim. Acta 74, 151–157 (2012)
W. Zhang, T. Liu, X. Zheng, W. Huang, C. Wan, Surface-enhanced oxidation and detection of Sunset Yellow and Tartrazine using multi-walled carbon nanotubes film-modified electrode. Colloids Surf. B 74, 28–31 (2009)
J.J. Berzas, J.R. Flores, M.J.V. Llerena, N.R. Farinas, Spectrophotometric resolution of ternary mixtures of tartrazine, patent blue V and indigo carmine in commercial products. Anal. Chim. Acta 391, 353–364 (1999)
L.F. Capitan-Valley, M.D. Fernandez, I. Orbe, J.L. Vilchez, R. Avidad, Simultaneous determination of the colorants sunset yellow FCF and quinoline yellow by solid-phase spectrophotometry using partial least squares multivariate calibration. Analyst 122, 351–354 (1997)
B.P. Ramanbhai, R.P. Mukesbhai, A.P. Ambubhai, K.S. Arvindbhai, G. Ajaybhai, Separation and determination of food colors in pharmaceutical preparations by column chromatography. Analyst 111, 577–578 (1986)
M. Ma, X. Luo, B. Chen, S. Su, S. Yao, Simultaneous determination of water-soluble and fat-soluble synthetic colorants in foodstuff by high-performance liquid chromatography diode array detection–electrospray mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 1103, 170–176 (2006)
F.J. Liu, C.T. Liu, W. Li, A.N. Tang, Dispersive solid-phase microextraction and capillary electrophoresis separation of food colorants in beverages using diamino moiety functionalized silica nanoparticles as both extractant and pseudo stationary phase. Talanta 132, 366–372 (2015)
K. Yamjala, M.S. Nainar, N.R. Ramisetti, Methods for the analysis of azo dyes employed in food industry: a review. Food Chem. 192, 813–824 (2016)
C. Tatebe, T. Ohtsuki, N. Otsuki, H. Kubota, K. Sato, H. Akiyama, Extraction method and determination of Sudan I present in Sunset Yellow FCF by isocratic high-performance liquid chromatography. Am. J. Anal. Chem. 3, 570–575 (2012)
F. Gosetti, V. Gianotti, S. Polati, M.C. Gennaro, HPLC–MS degradation study of E110 Sunset Yellow FCF in a commercial beverage. J. Chromatogr. A 1090, 107–115 (2005)
H.K. Maleh, K. Cellat, K.A. Aysun Savk, F. Karimi, F. Şen, Palladium–Nickel nanoparticles decorated on Functionalized-MWCNT for high precision non-enzymatic glucose sensing. Mater. Chem. Phys. 250, 123042 (2020)
H.K. Maleh, O.A. Arotiba, Simultaneous determination of cholesterol, ascorbic acid and uric acid as three essential biological compounds at a carbon paste electrode modified with copper oxide decorated reduced graphene oxide nanocomposite and ionic liquid. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 560, 208–212 (2020)
H.K. Maleh, F. Karimi, M. Alizadeh, A.L. Sanati, Electrochemical sensors, a bright future in the fabrication of portable kits in analytical systems. Chem. Rec. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1002/tcr.201900092
A. Baghizadeh, H.K. Maleh, Z. Khoshnama, A. Hassankhani, M. Abbasghorbani, A voltammetric sensor for simultaneous determination of vitamin C and vitamin B6 in food samples using ZrO2 nanoparticle/ionic liquids carbon paste electrode. Food Anal. Methods 8, 549–557 (2015)
Z.S. Azad, M.A. Taher, S. Cheraghi, H.K. Maleh, A nanostructure voltammetric platform amplified with ionic liquid for determination of tert-butylhydroxyanisole in the presence kojic acid. J. Food Meas. Charact. 13, 1781–1187 (2019)
Y. Ya, C. Jiang, T. Li, J. Liao, Y. Fan, Y. Wei, F. Yan, L. Xie, A zinc oxide nanoflower-based electrochemical sensor for trace detection of sunset yellow. Sensors 17, 545 (2017)
J. Wang, B. Yang, H. Wang, P. Yang, Y. Du, Highly sensitive electrochemical determination of Sunset Yellow based on gold nanoparticles/graphene electrode. Anal. Chim. Acta 893, 41–48 (2015)
A. Krolicka, A. Bobrowski, J. Zarebski, I. Tesarowicz, Bismuth film electrodes for adsorptive stripping voltammetric determination of sunset yellow FCF in soft drinks. Electroanalysis 26, 756–765 (2014)
P.S. Dorraji, F. Jalali, Electrochemical fabrication of a novel ZnO/cysteic acid nanocomposite modified electrode and its application to simultaneous determination of sunset yellow and tartrazine. Food Chem. 227, 73–77 (2017)
K. Zhang, P. Luo, J. Wu, W. Wang, B. Ye, Highly sensitive determination of Sunset Yellow in drink using a poly (l-cysteine) modified glassy carbon electrode. Anal. Methods 5, 5044–5050 (2013)
F.T. Javazmi, M.S. Nooshabadi, H.K. Maleh, 3D reduced graphene oxide/FeNi3-ionic liquid nanocomposite modified sensor; an electrical synergic effect for development of tert-butylhydroquinone and folic acid sensor. Composites B 172, 666–670 (2019)
T. Jamali, H.K. Maleh, M.A. Khalilzadeh, A novel nanosensor based on Pt:Co nanoalloy ionic liquid carbon paste electrode for voltammetric determination of vitamin B9 in food samples. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 57, 679–685 (2014)
M. Miraki, H.K. Maleh, M. Taher, S. Cheraghi, F. Karimi, S. Agarwal, V.K. Gupta, Voltammetric amplified platform based on ionic liquid/NiO nanocomposite for determination of benserazide and levodopa. J. Mol. Liq. 278, 672–676 (2019)
H.K. Maleh, M. Sheikhshoaie, I. Sheikhshoaie, M. Ranjbar, J. Alizadeh, N.W. Maxakato, A. Abbaspourrad, A novel electrochemical epinine sensor using amplified CuO nanoparticles and an-hexyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate electrode. N. J. Chem. 43, 2362–2367 (2019)
S.A.R.A. Tabari, M.A. Khalilzadeh, H. Karimi-Maleh, Simultaneous determination of doxorubicin and dasatinib as two breast anticancer drugs uses an amplified sensor with ionic liquid and ZnO nanoparticle. J. Electroanal. Chem. 811, 84–88 (2018)
X. Qiu, L. Lu, J. Leng, Y. Yu, W. Wang, M. Jiang, L. Bai, An enhanced electrochemical platform based on graphene oxide and multi-walled carbon nanotubes nanocomposite for sensitive determination of Sunset Yellow and Tartrazine. Food Chem. 190, 889–895 (2016)
J. Wang, Carbon-nanotube based electrochemical biosensors: a review. Electroanalysis 17, 7–14 (2005)
V. Baia, L.I.N. Tome, C.M.A. Brett, Iron oxide nanoparticle and multiwalled carbon nanotube modified glassy carbon electrodes. Application to levodopa detection. Electroanalysis 30, 1–8 (2018)
T. Zhao, X. Ji, X. Guo, W. Jin, A. Dang, H. Li, T. Li, Preparation and electrochemical property of Fe3O4/MWCNT nanocomposite. Chem. Phys. Lett. 653, 202–206 (2016)
Y. Wang, L. Wang, T. Tian, G. Yao, X. Hu, C. Yang, Q. Xu, A highly sensitive and automated method for the determination of hypoxanthine based on lab-on-valve approach using Fe3O4/MWCNTs/b-CD modified electrode. Talanta 99, 840–845 (2012)
M. Baghayeri, H. Veisi, Fabrication of a facile electrochemical biosensor for hydrogen peroxide using efficient catalysis of hemoglobin on the porous Pd@Fe3O4–MWCNT nanocomposite. Biosens. Bioelectron. 74, 190–198 (2015)
H. Keypour, S.G. Saremi, H. Veisi, M. Noroozi, Electrochemical determination of citalopram on new Schiff base functionalized magnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticle/MWCNTs modified glassy carbon electrode. J. Electroanal. Chem. 780, 160–168 (2016)
H.K. Maleh, C.T. Fakude, N. Mabuba, G.M. Peleyeju, O.A. Arotiba, The determination of 2-phenylphenol in the presence of 4-chlorophenol using nano-Fe3O4/ionic liquid paste electrode as an electrochemical sensor. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 554, 603–610 (2019)
J. Yu, Y. Zhang, H. Li, Q. Wan, Y. Li, N. Yang, Electrochemical properties and sensing applications of nanocarbons: a comparative study. Carbon 129, 301–309 (2018)
A.A. Ensafi, A.R. Allafchian, B. Rezaei, Multiwall carbon nanotubes decorated with FeCr2O4, a new selective electrochemical sensor for amoxicillin determination. J. Nanopart. Res. 14, 1244 (2012)
M. Arvand, Y. Parhizi, S.H. Mirfathi, Simultaneous voltammetric determination of synthetic colorants in foods using a magnetic core–shell Fe3O4@SiO2/MWCNTs nanocomposite modified carbon paste electrode. Food Anal. Methods 9, 63–875 (2016)
M. Arvand, Z. Erfanifar, M.S. Ardaki, A new core@shell silica-coated magnetic molecular imprinted nanoparticles for selective detection of sunset yellow in food samples. Food Anal. Methods 10, 2593–2606 (2017)
G.V. Prasad, T.M. Reddy, A.L. Narayana, O.M. Hussain, P. Shaikshavali, T.V. Gopal, P. Gopal, A facile synthesis of Fe3O4-Gr nanocomposite and its effective use as electrochemical sensor for the determination of dopamine and as anode material in lithium-ion batteries. Sens. Actuators A 293, 87–100 (2019)
T. Zhao, X. Ji, H. Liu, P. Yao, W. Liu, C. Xiong, T. Li, C. Wang, Growth of well-aligned carbon nanotubes with different shapes. Appl. Surf. Sci. 357, 2136–2140 (2015)
C. Ma, W. Lu, H. Zheng, Y. Wang, Y. Luo, Study on preparation of nano-sized carbon/ferroferric oxide composite material. Inorg. Chem. Ind. 41(4), 24–27 (2009)
B. Fang, W. Zhang, S. Wei, N. Zhang, G. Wang, Preparation of CNTs/Fe3O4 modified electrode under the magnetic field and the electrocatalytic determination of dopamine. J. Chizhou Coll. 21(5), 51–53 (2007)
M.R. Shahmiri, A. Bahari, H.K. Maleh, R. Hosseinzadeh, N. Mirni, Ethynylferrocene–NiO/MWCNT nanocomposite modified carbon paste electrode as a novel voltammetric sensor for simultaneous determination of glutathione and acetaminophen. Sens. Actuators B 177, 70–77 (2013)
H.K. Maleh, A.F. Shojaei, F. Karimi, K. Tabatabaeian, S. Shakeri, R. Moradi, Simultaneous determination of 6-mercaptopurine, 6-thioguanine and dasatinib as three important anticancer drugs using nanostructure voltammetric sensor employing Pt/MWCNTs and 1-butyl-3-methyl imidazolium hexafluorophosphate. Biosens. Bioelectron. 86, 879–884 (2016)
Q. Zhang, M. Zhu, Q. Zhang, Y. Li, H. Wang, The formation of magnetite nanoparticles on the sidewalls of multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Compos. Sci. Technol. 69, 633–638 (2009)
X. Wang, Z. Zhao, J. Qu, Z. Wang, J. Qiu, Fabrication and characterization of magnetic Fe3O4–CNT composites. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 71, 673–676 (2010)
A.L. Narayana, M. Dhananjaya, N.G. Prakash, O.M. Hussain, A. Mauger, C.M. Julien, Li2TiO3/graphene and Li2TiO3/CNT composites as anodes for high power Li-ion batteries. ChemistrySelect 3, 9150–9158 (2018)
T. Madrakian, S. Maleki, M. Heidari, A. Afkhami, An electrochemical sensor for rizatriptan benzoate determination using Fe3O4 nanoparticle/multiwall carbon nanotube-modified glassy carbon electrode in real samples. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 63, 637–643 (2016)
P. Shaikshavali, T.M. Reddy, V.N. Palakollu, R. Karpoormath, Y. Subba Rao, G.V. Prasad, T.V. Gopal, P. Gopal, Multi-walled carbon nanotubes supported CuO–Au hybrid nanocomposite for the effective application towards the electrochemical determination of Acetaminophen and 4-Aminophenol. Synth. Met. 252, 29–39 (2019)
P. Gopal, T.M. Reddy, V.N. Palakollu, Development, characterization, and application of a carbon-based nanomaterial composite as an electrochemical sensor for monitoring natural antioxidant (gallic acid) in beverages. ChemistrySelect 2, 3804–3811 (2017)
X. Ye, Y. Du, D. Lu, C. Wang, Fabrication of β-cyclodextrin-coated poly (diallyl dimethylammonium chloride)-functionalized graphene composite film modified glassy carbon-rotating disk electrode and its application for simultaneous electrochemical determination colorants of sunset yellow and tartrazine. Anal. Chim. Acta 779, 22–34 (2013)
P.V. Narayana, T.M. Reddy, P. Gopal, M.M. Reddy, G.R.K. Naidu, Electrocatalytic boost up of epinephrine and its simultaneous resolution in the presence of serotonin and folic acid at poly(serine)/multi-walled carbon nanotubes composite modified electrode: a voltammetric study. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 56, 57–65 (2015)
P. Shaikshavali, T.M. Reddy, G.V. Prasad, P. Gopal, A highly selective electrochemical sensor based on multi-walled carbon nanotubes/poly (Evans blue) composite for the determination of l-dopa in presence of 5-HT and folic acid: a voltammetric investigation. J. Iran. Chem. Soc. 15, 1831–1841 (2018)
E. Laviron, Adsorption, autoinhibition, and autocatalysis in polarography and linear potentials sweep voltammetry. J. Electroanal. Chem. Interracial Electrochem. 52, 355–393 (1974)
E. Laviron, General expression of the linear potential sweep voltammogram in the case of diffusionless electrochemical systems. J. Electroanal. Chem. Interfacial Electrochem. 101, 19–28 (1979)
P. Raghu, T.M. Reddy, K. Reddaiah, B.E.K. Swamy, M. Sreedhar, Acetylcholinesterase based biosensor for monitoring of Malathion and Acephate in food samples: a voltammetric study. Food Chem. 142, 188–196 (2014)
T.V. Gopal, T.M. Reddy, G.V. Prasad, P. Shaikshavalli, P. Gopal, Rapid and sensitive electrochemical monitoring of paracetamol and its simultaneous resolution in presence of epinephrine and tyrosine at GO/poly(Val) composite modified carbon paste electrode. Colloids Surf. A 545, 117–120 (2018)
A. Khodadadi, E.F. Mirzaei, H.K. Maleh, A. Abbaspourrad, S. Agarwal, V.K. Gupta, A new epirubicin biosensor based on amplifying DNA interactions with polypyrrole and nitrogen-doped reduced graphene: experimental and docking theoretical investigations. Sens. Actuators B 284, 568–574 (2019)
M. Bijad, H.K. Maleh, M.A. Khalilzadeh, Application of ZnO/CNTs nanocomposite ionic liquid paste electrode as a sensitive voltammetric sensor for determination of ascorbic acid in food samples. Food Anal. Methods 6, 1639–1647 (2013)
T. Gan, J. Sun, W. Meng, L. Song, Y. Zhang, Electrochemical sensor based on graphene and mesoporous TiO2 for the simultaneous determination of trace colorants in food. Food Chem. 141, 3731–3737 (2013)
Q. He, J. Liu, X. Liu, Y. Xia, G. Li, P. Deng, D. Chen, Novel electrochemical sensors based on cuprous oxide-electrochemically reduced graphene oxide nanocomposites modified electrode toward sensitive detection of sunset yellow. Molecules 23, 2130 (2018)
L. Zhao, F. Zhao, B. Zeng, Preparation and application of sunset yellow imprinted ionic liquid polymer ionic liquid functionalized graphene composite film coated glassy carbon electrodes. Electrochim. Acta 115, 247–254 (2014)
J. Li, X. Wang, H. Duan, Y. Wang, Y. Bu, C. Luo, Based on magnetic graphene oxide highly sensitive and selective imprinted sensor for determination of sunset yellow. Talanta 147, 169–176 (2016)
M. Motahharinia, H.A. Zamani, H.K. Maleh, A sensitive electroanalytical sensor amplified with Pd–ZnO nanoparticle for determination of Sunset Yellow in real samples. Eurasian Chem. Commun. 2, 760–770 (2020)
Acknowledgements
One of the authors P. Shaikshavali is grateful to the University Grants Commission (UGC), New Delhi for providing financial support through the Basic Scientific Research (BSR) Fellowship under Letter No. F. 25-1/2013-14 (BSR)/7-187/2007. The authors are also thankful to TPF Nanomission at Center for Nano and Soft Matter Sciences, Bengaluru and Vellore Institute of Technology (VIT), Vellore, India for providing FE-SEM, XRD, TEM and EDS facilities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There are no conflicts of interest to declare.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shaikshavali, P., Reddy, T.M., Lakshmi Narayana, A. et al. A powerful electrochemical sensor based on Fe3O4 nanoparticles-multiwalled carbon nanotubes hybrid for the effective monitoring of sunset yellow in soft drinks. Food Measure 14, 3319–3332 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11694-020-00569-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11694-020-00569-z