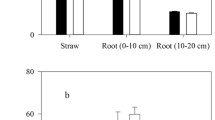
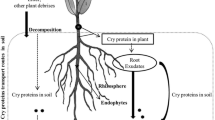
Abstract
Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) transgenic cotton is the unique Bt transgenic crop planted on a large scale in China, and its commercialized varieties and hectareage had increased rapidly in China during the past decade (1997–2006) with broad geographic distribution for the economic, environmental, and health benefits. In 2004, the planting area of Bt transgenic cotton in China ranked first worldwide with up to 370 × 106 hm2. In addition, Bt transgenic rice varieties in field tests have been close to approval for commercialization. However, ecological risks, a complex issue of Bt transgenic crops on soil ecosystem is urgently faced in China due to more than 60 varieties transferred single or bivalent Bt genes grown under diverse geographic regions. Two main pathways, biomass incorporation and root exudates, are involved in the effects of Bt transgenic crops on soil ecosystems. In this paper, the research results in recent years in China involved in the effects of Bt transgenic crops (Bt transgenic cottons and rice) on soil ecosystems were summarized with special attentions paid to the release and persistence of Bt toxins, and the toxicology to microorganisms, as well as the change of soil biochemical properties in soils where Bt transgenic crops were planted or incubated with their biomass. In addition, the complexity and current research defaults of ecological risk evaluation of Bt transgenic crops in China were highlighted.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Angle J S (1994). Release of transgenic plants: biodiversity and population-level considerations. Molecular Ecology, 3: 45–50
Bai Y Y, Jiang M X, Cheng J A (2007). Impacts of environmental factors on degradation of Cry1Ab insecticial protein in leaf-blade powders of transgenic Bt rice. Agricultural Sciences in China, 6(2): 167–174 (in Chinese)
Bai Y Y, Jiang M X, Cheng J A, Shen H M, Yang P, Chen Z X, Jiang Y H, Shu Q Y (2004). Degradation of Cry1Ab toxin protein expressed by Bt transgenic rice in paddy soils. Chinese J Rice Science, 18(3): 255–261 (in Chinese)
Brookes G, Barfoot P (2006). Global impact of biotech crops: socioeconomic and environmental effects in the first ten years of commercial use. AgBioForum, 9(3): 139–151
Bruinsma M, Kowalchuk G A, van Veen J A (2003). Effects of genetically modified plants on microbial communities and processes in soil. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 37: 329–337
Bruns H A, Abel C A (2003). Nitrogen fertility effects on Bt-andotoxin and nitrogen concentrations of maize during early growth. Agron J, 95: 207–211
Castaldini M, Turrini A, Sbrana C, Benedetti A, Marchionni M, Fabiani A, Landi S, Santomassimo F, Pietrangeli B, Nuti M P, Miclaus N, Giovannetti M (2005). Impact of Bt maize on rhizospheric and soil eubacterial communities and on beneficial mycorrhizal symbiosis in experimental microcosms. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 71: 6719–6729
Crecchio C, Stotzky G (1998). Insecticidal activity and biodegradation of the toxin from Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. kurstaki bound to humic acids from soil. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 30: 463–470
Crecchio C, Stotzky G (2001). Biodegradation and insecticidal activity of the toxin from Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. kurstaki bound to complexes of montmorillonite-humic acids-Al hydroxypolymers. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 33: 573–581
Cui J J, Xia J Y (1999). Studies on the resistance dynamic of the Bt transgenic cotton on cotton bollworm. Acta Gossypii Sinica, 11: 141–146 (in Chinese)
Donegan K K, Palm C J, Fieland V J (1995). Changes in levels, species, and DNA fingerprints of soil microorganism associated with cotton expressing the Bacillus thuringiensis var. kurstaki endotoxin. Applied Soil Ecology, 2(2): 111–124
Donegan K K, Seidler R J, Doyle J D, Porteous L A, Digiovanni G, Widmer F, Watrud L S (1999). A field study with genetically engineered alfalfa inoculated with recombinant Sinorhizobium meloloti: Effects on soil ecosystems. J Applied Ecol, 36: 920–936
Dong Z Q, Zhao M, Shu W H, Zhang B M, Hao H J (2006). The subcellular localization of the Bt crystal protein in transgenic Bt cotton cell. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 32(12): 1924–1926 (in Chinese)
Escher N, Kach B, Nentwig W (2000). Decomposition of transgenic Bacillus thuringiensis maize by microorganisms and woodlice Porcello scaber (Crustacea:Isopoda). Bas Appl Ecol, 1, 161–169
Ferry N, Edwards M G, Gatehouse J, Capell T, Christou P, Gatehouse A M R (2006). Transgenic plants for insect pest control: a forward looking scientific perspective. Transgenic Research, 15: 13–19
Firbank L, Lonsdale M, Poppy G (2005). Reassessing the environmental risks of GM crops. Nature Biotechnology, 12: 1475–1476
Flores S, Saxena D, Stotzky G (2005). Transgenic Bt plants decompose less in soil than non-Bt plants. Soil Biology & Biochemistry, 37: 1073–1082
Grayston S J, Wang S, Campbell C D (1998). Selective influence of plant species on microbial diversity in the rhizosphere. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 30: 369–378
Hails R S (2000). Genetically modified plants-the debate continues. Trends in Ecology and Evolution, 15: 14–18
Heritage J (2004). The fate of transgenes in the human gut. Nature Biotechnology, 22: 170–173
Hilbeck A, Moar, W J, Pusztai-Carey M, Filippini A, Bigler F (1998). Toxicityof Bacillus thuringensis Cry1Ab toxin to the predator Chrysoperla carnea. Environmental Entomology, 27: 1255–1263
Huang J K, Hu F R, Pray C, Qiao F B, Rozelle S (2003). Biotechnology as an alternative to chemical pesticides: a case study of Bt cotton in China. Agricultural Economics, 29: 55–67
Huang J K, Rozelle S, Pray C, Wang Q F (2002). Plant biotechnology in China. Nature, 295: 674–676
Jepson, P C, Croft, B A, Pratt, G E (1994). Test systems to determine the ecological risks posed by toxin release from Bacillus thuringiensis genes in crop plants. Molecular Ecology, 3: 81–89
Li Y H, Zhang Y J, Wu K M, Yuan G H, Guo Y Y (2005). Degradation dynamics of Cry1Ac insecticidal protein in leaves of Bt cotton under different environments. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 38(4): 714–718 (in Chinese)
Liu B, Zeng Q W, Yan F M, Xu H G, Xu C R (2005). Effects of transgenic plants on soil microorganisms. Plant and Soil, 271: 1–13
Liu W K, Du L F (2007). Effects of P fertilization on growth of Bt transgenic cotton seedlings. China Cotton, (8): 14–15 (in Chinese)
Liu W K, Du L F (2008). Interactions between Bt transgenic crops and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi: a new urgent soil ecology issue in agroecosystems. Acta Agriculturae Scandinavica, Section B-Plant Soil Science, 58(2): 187–192
Losey J E, Rayor L S, Carter M E (1999). Transgenic pollen harms monarch larvae. Nature, 399: 214
Netherwood T, Matin-Orue S M, O’Donnell A G (2004). Assessing the survival of transgenic plant DNA in the human gastrointestinal tract. Nature Biotechnology, 22: 204–209
Palm C J, Schaller D L, Donegan K K, Seidler R J (1996). Persistence in soil of transgenic plant produced Bacillus thuringiensis var. kurstaki δ-endotoxin. Canadian J Microbiology, 42: 1258–1262
Rui Y K (2005). Dynamics of Bt toxin and plant hormones in rhizosphere system of transgenic insecticidal cotton (Gossy posium L.). Letters in Biotechnology, 16(5): 515–517 (in Chinese)
Rui Y K, Yi G X, Guo J, Guo X, Luo Y B, Wang B M, Li Z H (2007). Transgenic cotton could safely be grown since CpTI toxin rapidly degrades in the rhizosphere soil. Acta Agriculturae Scandinavica, Section B-Plant Soil Science, 57(2): 122–125
Rui Y K, Yi G X, Zhao J, Wang B M, Li Z H, Zhai Z X, He Z P, Li Q X (2005). Changes of Bt toxin in the rhizosphere of transgenic Bt cotton and its influence on soil functional bacteria. World Journal of Microbiology & Biotechnology, 21: 1279–1284
Sachs E S, Benedict J H, Stelly D M, Taylor J F, Altman D W, Berberich S A, Davis S K (1998). Expression and segregation of genes encoding CryIA insecticidal proteins in cotton. Crop Science, 38: 1–11
Saxena D, Flores S, Stotzky G (1999). Insecticidal toxin in root exudates from Bt corn. Nature, 402: 480
Saxena D, Stotzky G (2000). Insecticidal toxin from Bacillus thuringiensis is released from roots of transgenic Bt corn in vitro and in situ. FEMS Microbiological Ecology, 33: 35–39
Saxena D, Stotzky G (2001)a. Bacillus thuringiensis toxin released from root exudates and biomass of Bt corn has no apparent effect on earthworms, nematodes, protozoa, bacteria, and fungi in soil. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 33: 1225–1230
Saxena D, Stotzky G (2001)b. Bt corn has a higher lignin content than non-Bt corn. Am J Bot, 88: 1704–1706
Saxena D, Stotzky G (2001)c. Bt toxin uptake from soil by plants. Nature Biotechnology, 19: 199
Saxena D, Stotzky G (2002). Bt toxin is not taken up from soil or hydroponic by maize, radish, or turnip. Plant and Soil, 239: 165–172
Shen R F, Cai H, Gong W H (2006). Transgenic Bt cotton has no apparent effect on enzymatic activities or functional diversity of microbial communities in rhizosphere soil. Plant and Soil, 285: 149–159
Sims S R, Holden L R (1996). Insect bioassay for determining soil degradation of Bacillus thuringiensis var. kurstaki CryIA (b) protein in corn tissues. Environ Entomology, 25: 659–664
Sims S R, Ream J E (1997). Soil inactivation of the Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. kurstaki CryIIA insecticidal protein within transgenic cotton tissue: laboratory microcosm and field studies. Journal of Agriculture and Food Chemistry, 45: 1502–1505
Snow A, Palma P M (1997). Commercialization of transgenic plants: potential ecological risks. BioScience, 47: 86–96
Stotzky G (2000). Persistence and biological activity in soil of insecticidal proteins from Bacillus thuringiensis and of bacterial DNA bound on clays and humic acids. J Environmental Quality, 29: 691–705
Sun C X, Chen L J, Wu Z J (2005). Bt toxin distribution in transgenic Bt cotton and soil system. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 16(9): 1765–1768 (in Chinese)
Sun C X, Chen L J, Wu Z J, Wu Q, Chen C R (2004). Photosynthetic characters and Bt toxin content of different transgenic Bt cotton. Chinese J of Applied Ecology, 15(10): 1878–1882 (in Chinese)
Sun C X, Chen L J, Wu Z J, Zhou L K (2007)a. Soil persistence of Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) toxin from transgenic Bt cotton tissues and its effect on soil enzyme activities. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 43: 617–620
Sun C X, Zhang L L, Wu Q, Miao L, Wang G W, Li S J (2007)b. Nitrogen metabolism of transgenic Bt cotton and transgenic Bt CpTI cotton at seedling stage. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 26(2): 187–191 (in Chinese)
Tabashnik B E (1994). Evolution of resistance to Bacillus thuringiensis. Annual Review of Entomology, 39: 47–49
Tapp H, Stotzky G (1995). Insecticidal activity of the toxins from Bacillus thuringiensis subspecies kurstaki and tenebrionis adsorbed and bound on pure and soil clays. Appl Environ Microbiol, 61(5): 1786–1790
Tapp H, Stotzky G (1998). Persistence of the insecticidal toxin from Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. kurstaki in soil. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 30: 471–476
Traore S B, Carlson R E, Pilcher C D (2000). Bt and non-Bt maize growth and development as affected by temperature and drought stress. Agron J, 92: 1027–1035
Turrini A, Sbrana C, Nuti M P, Pietrangeli B M, Giovannetti M (2005). Development of a model system to assess the impact of genetically modified maize and aubergine plants on arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. Plant and Soil, 1(2): 69–75
Wang H Y, Ye Q F, Wang W, Wu L C, Wu W X (2006). Cry1Ab protein from Bt transgenic rice does not residue in rhizosphere soil. Environmental Pollution, 143: 449–455
Wang Y Q, Johnston S (2007). The status of GM rice R&D in China. Nature Biotechnology, 25(7): 717–718
Watrud L S, Seidler R J, Huang PM, Adriano D C, Logan T J, Checkai R T (1998). Nontarget ecological effects of plant, microbial and chemical introductions to terrestrial system. In: Huang P M, ed. Soil Chemistry and Ecosystem Health. Madison, Special Publication, Vol 52. Wisconsin: Soil Science Society of America, 313–340
Wolfenbarger L L, Phifer P R (2000). The ecological risks and benefits of genetically engineered plants. Science, 290: 2088–2093
Wu L C, Li X F, Ye Q F, Wang H Y (2004). Expression and root exudation of Cry1Ab toxin protein in cry1Ab transgenic rice and its residue in rhizosphere soil. Environmental Science, 25(5): 116–121
Wu W X, Ye Q F, Min H (2004)a. Effect of straws from Bt-transgenic rice on selected biological activities in water-flooded soil. European Journal of Soil Biology, 40: 15–22
Wu W X, Ye Q F, Min H, Duan X J, Jin W M (2004)b. Bt-transgenic rice straw affects the culturable microbiota and dehydrogenase and phosphatase activities in a flooded paddy soil. Soil Biol Biochem, 36: 289–295
Zhang B H, Liu F, Yao C B, Wang K B (2000). Recent progress in cotton biotechnology and genetic engineering in China. Current Science, 79 (1): 37–44
Zhang B H, Wang Q L (2001). Bt-cotton in China. Current Science, 81 (4): 332–333
Zhang L L, Wu Z J, Chen L J, Sun C X (2006). Effects of transgenic cotton planting on soil hydrolase activity. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 25(11): 1348–1351 (in Chinese)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, W. Effects of Bt transgenic crops on soil ecosystems: a review of a ten-year research in China. Front. Agric. China 3, 190–198 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11703-009-0027-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11703-009-0027-9