Abstract
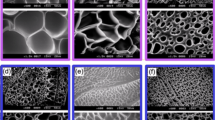
A novel hydrogel composite was prepared via inverse suspension polymerization using starch, acrylic acid and organo-mordenite micropowder with the cross-linker, N,N′-methylenebisacrylamide and the initiator, potassium persulfate. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction spectroscopy, scanning electron microscopy, and energy dispersive spectroscopy confirmed that the acrylic acid was grafted onto the backbone of the corn starch, that the organo-mordenite participated in the polymerization, and that the addition of organo-mordenite improved the surface morphology of the hydrogel composite. The swelling capacity of the hydrogel composite was evaluated in distilled water, and solutions with different pH values, and various salt solutions. It was found that the incorporation of 10 wt-% organo-mordenite enhanced the water absorbency by 144% (from 268 to 655 g∙g–1) and swelling was extremely sensitive to the pH values, the concentration of the salt solution and cation type. Swelling kinetics and water diffusion mechanism of the hydrogel composite in distilled water were also discussed. Moreover, the hydrogel composite showed excellent reversibility of water absorption even after five repetitive cycles and the hydrogel composite exhibited significant environmental-responsiveness by changing the swelling medium from distilled water to 0.1 mol∙L–1 NaCl solution. In addition, the loading and release of urea by the hydrogel composite were tested and the nutrient-slowrelease capability of this material was found to be suitable for many potential applications.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Seetapan N, Wongsawaeng J, Kiatkamjornwong S. Gel strength and swelling of acrylamide-protic acid superabsorbent copolymers. Polymers for Advanced Technologies, 2011, 22(12): 1685–1695
Raju K M, Raju M P. Synthesis and swelling properties of superabsorbent copolymers. Advances in Polymer Technology, 2001, 20(2): 146–154
Swain S K, Shur B, Patra S K. Poly(acrylamide-co-vinyl alcohol)— superabsorbent materials reinforced by modified clay. Polymer Composites, 2013, 34(11): 1794–1800
Li A, Wang A. Synthesis and properties of clay-based superabsorbent composite. European Polymer Journal, 2005, 41(7): 1630–1637
Lokhande H T, Gotmare V D. Utilization of textile loomwaste as a highly absorbent polymer through graft co-polymerization. Bioresource Technology, 1999, 68(3): 283–286
Kazanskii K S, Dubrovskii S A. Chemistry and physics of “agricultural” hydrogels. Advances in Polymer Science, 1992, 104: 97–133
Mohana R K, Padmanabha R M. Synthesis of novel superabsorbing copolymers for agricultural and horticultural applications. Polymer International, 2001, 50(8): 946–951
Chen L P, Ying K L, Hsu K C. Amphibious water-soluble copolymer. I. Its synthesis and dispersing ability on barium titanate. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 2004, 92(4): 2232–2239
Zhang Y H, Wang L M, Li X H, He P X. Salt-resistant superabsorbents from inverse-suspension polymerization of PEG methacrylate, acryamide and partially neutralized acrylic acid. Journal of Polymer Research, 2011, 18(2): 157–161
Hao L, Yang H, Lei Z. Synthesis and properties of thermoresponsive macroporous PAM-co-PNIPAM microspheres. Materials Letters, 2012, 70: 83–85
Wang G, Li M, Chen X. Inverse suspension polymerization of sodium acrylate. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 1997, 65(4): 789–794
Zhang Y, Gu Q, Yin J, Wang Z, He P. Effect of organic montmorillonite type on the swelling behavior of superabsorbent nanocomposites. Advances in Polymer Technology, 2014, 33(2): 21400–21407
Karlsson M E, Leeman A M, Björck I M, Eliasson A C. Some physical and nutritional characteristics of genetically modified potatoes varying in amylose/amylopectin ratios. Food Chemistry, 2007, 100(1): 136–146
Pereira A G B, Paulino A T, Nakamura C V, Britta E A, Rubira A F, Muniz E C. Effect of starch type on miscibility in poly(ethylene oxide)(PEO)/starch blends and cytotoxicity assays. Materials Science and Engineering C, 2011, 31(2): 443–451
Spagnol C, Rodrigues F H, Pereira A G, Fajardo A R, Rubira A F, Muniz E C. Superabsorbent hydrogel nanocomposites based on starch-g-poly (sodium acrylate) matrix filled with cellulose nanowhiskers. Cellulose, 2012, 19(4): 1225–1237
Al E, Güçlü G, Iyim T B, Emik S, Özgümüs S. Synthesis and properties of starch-graft-acrylic acid/Na-montmorillonite superabsorbent nanocomposite hydrogels. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 2008, 109(1): 16–22
Lanthong P, Nuisin R, Kiatkamjornwong S. Graft copolymerization, characterization, and degradation of cassava starch-g-acrylamide/ itaconic acid superabsorbents. Carbohydrate Polymers, 2006, 66(2): 229–245
Irani M, Ismail H, Ahmad Z. Preparation and properties of linear low-density polyethylene-g-poly(acrylic acid)/organo-montmorillonite superabsorbent hydrogel composites. Polymer Testing, 2013, 32(3): 502–512
Subhas S, Samar C D, Dipak R B. Synthesis and characterization of nanoclay-polymer composites from soil clay with respect to their water-holding capacities and nutrient-release behavior. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 2014, 131(6): 3351–3359
Macias A F, Spinola A G, Mendoza T MH, Gonzalez F D, Zelaya F P. Effect of zeolite (clinoptilolite and mordenite) amended andosols on soil chemical environment and growth of oat. Interciencia, 2007, 32(10): 692–696
Ramesh K, Reddy D D, Biswas A K, Rao A S. Zeolites and their potential uses in agriculture. Advances in Agronomy, 2011, 113: 215–236
Komaromine MK, Loksa G, Csereklye K E, Bardoczyne E S, Kallai S. Use of zeolite to improve soil amelioration and takes effects on microclimate. Cereal Research Communications, 2008, 36: 1783–1786
Oste L A, Lexmond T M, van Riemsdijk W H. Metal immobilization in soils using synthetic zeolites. Journal of Environmental Quality, 2002, 31(3): 813–821
Khoonsap S, Amnuaypanich S. Mixed matrix membranes prepared from poly(vinyl alcohol) (PVA) incorporated with zeolite 4A-graftpoly( 2-hydroxyethylmethacrylate) (zeolite-g-PHEMA) for the pervaporation dehydration of water-acetone mixtures. Journal of Membrane Science, 2011, 367(1-2): 182–189
Guo L P, Chen Y Z, Yang J. The surface modification of zeolite-4A by CTAB and its properties. Journal of Wuhan University of Technology-Material, 1999, 14: 18–23 (in Chinese)
Jin S P, Yue G R, Feng L, Han Y Q, Yu X H, Zhang Z H. Preparation and properties of a coated slow-release and water-retention biuret phosphoramide fertilizer with superabsorbent. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2011, 59(1): 322–327
Xie L H, Liu M Z, Ni B L, Wang F Y. New environment-friendly use of wheat straw in slow-release fertilizer formulations with the function of superabsorbent. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2012, 51(10): 3855–3862
Li A, Zhang J P, Wang A Q. Preparation and slow-release property of a poly(acrylic acid)/attapulgite/sodium humate superabsorbent composite. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 2007, 103(1): 37–45
Ladha J K, Pathak H, Krupnik T J, Six J J, van Kessel C. Efficiency of fertilizer nitrogen in cereal production: Retrospects and prospects. Advances in Agronomy, 2005, 87: 85–156
Liu M Z, Zhan F L, Wu L, Guo M Y. Preparation of slow release urea fertilizer with preservation of soil moisture. Journal of Polymer Materials, 2004, 21(2): 213–220
Wang Y F, Liu M Z, Ni B L, Xie L H. Karrageenan-sodium alginate beads and superabsorbent coated nitrogen fertilizer with slow-release, water-retention, and anticompaction properties. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2012, 51(3): 1413–1422
Liu M Z, Liang R, Zhan F L, Liu Z, Niu A Z. Synthesis of a slowrelease and superabsorbent nitrogen fertilizer and its properties. Polymers for Advanced Technologies, 2006, 17(6): 430–438
Zhang Y, Zhao L, Ma K, Mao G Z. The surface modification of zeolite 4a and its effect on the water-absorption capability of starchg- poly(acrylic acid) composite. Clays and Clay Minerals, 2014, 62(3): 211–223
Subhas S, Samar C D, Dipak R B. Synthesis and characterization of nanoclay-polymer composites from soil clay with respect to their water-holding capacities and nutrient-release behavior. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 2014, 131(6): 3351–3359
Watt G W, Chrisp J D. Spectrophotometric method for determination of urea. Analytical Chemistry, 1954, 26(3): 452–453
Zhang M Y, Cheng Z Q, Zhao T Q, Liu M Z, Hu M J, Li J F. Synthesis, characterization, and swelling behaviors of salt-sensitive maize bran-poly(acrylic acid) superabsorbent hydrogel. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2014, 62(35): 8867–8874
Silverstein R M, Webster F X. Spectrometric Identification of Organic Compounds. 6th ed. New York: Wiley, 1998
Lamberti C, Bordiga S, Zecchina A, Salvalaggio M, Geobaldo F, Areán C O. XANES, EXAFS and FTIR characterization of copperexchanged mordenite. Journal of the Chemical Society, Faraday Transactions, 1998, 94(10): 1519–1525
Rožic M, Miljanic S. Sorption of HDTMA cations on croatian natural mordenite tuff. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2011, 185(1): 423–429
Li Z H, Jiang W T, Hong H L. An FTIR investigation of hexadecyltrimethylammonium intercalation into rectorite. Spectrochimica Acta. Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy, 2008, 71(4): 1525–1534
Pourjavadi A, Soleyman R. Novel high capacity swelling superabsorbent composite and its potential for controlled release of fertilizers. Iranian Journal of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering-International English Edition, 2010, 29(4): 113–123
Kaur I, Sharma M. Synthesis and characterization of graft copolymers of Sago starch and acrylic acid. Stärke, 2012, 64(6): 441–451
Zhang J P, Chen H, Wang A Q. Study on superabsorbent composite. III. Swelling behaviors of polyacrylamide/attapulgite composite based on acidified attapulgite and organo-attapulgite. European Polymer Journal, 2005, 41(10): 2434–2442
Wang W B, Xu J X, Wang A Q. A pH-, salt- and solvent-responsive carboxymethylcellulose-g-poly(sodium acrylate)/medical stone superabsorbent composite with enhanced swelling and responsive properties. Express Polymer Letters, 2011, 5(5): 385–400
Wu J, Wei Y, Lin J, Lin S. Study on starch-graft-acrylamide/mineral powder superabsorbent composite. Polymer, 2003, 44(21): 6513–6520
Treacy M M J, Higgins J B. Collection of simulated XRD powder patterns for zeolites. 5th ed. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2007, 284
Mithilesh Y, Somit K S, Kyong Y R. Synthesis of partially hydrolyzed graft copolymer (H-Ipomoea hederacea seed gum-gpolyacrylonitrile). Carbohydrate Polymers, 2013, 95(1): 471–478
Zhang J, Li A, Wang A. Study on superabsorbent composite. VI. Preparation, characterization and swelling behaviors of starch phosphate-graft-acrylamide/attapulgite superabsorbent composite. Carbohydrate Polymers, 2006, 65(2): 150–158
Rashidzadeh A, Olad A, Salari D, Reyhanitabar A. On the preparation and swelling properties of hydrogel nanocomposite based on Sodium alginate-g-poly(acrylic acid-co-acrylamide)/clinoptilolite and its application as slow release fertilizer. Journal of Polymer Research, 2014, 21(2): 1–15
Amnuaypanich S, Patthana J, Phinyocheep P. Mixed matrix membranes prepared from natural rubber/poly(vinyl alcohol) semi-interpenetrating polymer network (NR/PVA semi-IPN) incorporating with zeolite 4A for the pervaporation dehydration of waterethanol mixtures. Chemical Engineering Science, 2009, 64(23): 4908–4918
Elazzouzi H S, Nishiyama Y, Putaux J L, Heux L, Dubreuil F, Rochas C. The shape and size distribution of crystalline nanoparticles prepared by acid hydrolysis of native cellulose. Biomacromolecules, 2008, 9(1): 57–65
Schott H. Swelling kinetics of polymers. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 1992, 81(5): 467–470
Li S, Liu X, Zou T, Xiao W. Removal of cationic dye from aqueous solution by a macroporous hydrophobically modified poly(acrylic acid-acrylamide) hydrogel with enhanced swelling and adsorption properties. Clean-Soil Air Water, 2010, 38(4): 378–386
Kasgoz H, Durmus A. Dye removal by a novel hydrogel-clay nanocomposite with enhanced swelling properties. Polymers for Advanced Technologies, 2008, 19(7): 838–845
Mujumdar S K, Siegel R A. Introduction of pH-sensitivity into mechanically strong nanoclay composite hydrogels based on Nisopropylacrylamide. Journal of Polymer Science. Part A, Polymer Chemistry, 2008, 46(19): 6630–6640
Liang R, Yuan H, Xi G, Zhou Q. Synthesis of wheat straw-g-poly (acrylic acid) superabsorbent composites and release of urea from it. Carbohydrate Polymers, 2009, 77(2): 181–187
Joseph J G. Polymeric gels and hydrogels for biomedical and pharmaceutical applications. Polymers for Advanced Technologies, 2009, 21: 27–47
Flory P J. Principles of Polymer Chemistry. New York: Cornell University Press, 1953
Zhang J P, Li A, Wang A Q. Study on superabsorbent composite. V. Synthesis, swelling behaviors and application of poly(acrylic acidco- acrylamide)/sodium humate/attapulgite superabsorbent composite. Polymers for Advanced Technologies, 2005, 16(11): 813–820
Bardajee G R, Pourjavadi A, Soleyman R. Irradiation synthesis of biopolymer-based superabsorbent hydrogel: Optimization using the Taguchi method and investigation of its swelling behavior. Advances in Polymer Technology, 2009, 28(2): 131–140
Xie J, Liu X, Liang J, Luo Y S. Swelling properties of superabsorbent poly(acrylic acid-co-acrylamide) with different crosslinkers. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 2009, 112(2): 602–608
Zhang M Y, Cheng Z Q, Liu M Z, Zhang Y Q, Hu M J, Li J F. Synthesis and properties of a superabsorbent from an ultravioletirradiated waste nameko mushroom substrate and poly(acrylic acid). Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 2014, 131(13): 4525–4529
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Gao, P., Zhao, L. et al. Preparation and swelling properties of a starch-g-poly(acrylic acid)/organo-mordenite hydrogel composite. Front. Chem. Sci. Eng. 10, 147–161 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11705-015-1546-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11705-015-1546-y