Abstract
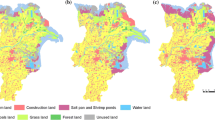
The Tarim River Basin, located in the typical arid region, is one of the key regions of LUCC research in China and plays and important role in maintaining the sustainable development of the western China. In recent years, the ecological environment of the Tarim River Basin has degraded greatly. In the lower reaches, in particular, the riverbed has been dried up for more than 20 years, which accelerated the desertification and has been a great threat to people’s lives. Taking the section of the Tarim River between Qiala Lake and Taitema Lake as a typical region, an investigation on land cover changes was carried out with the support of remote sensing information of 1988 and 2000 respectively. The changes of land cover in this region were obtained: 1) Cropland tended to increase. 2) Urban or Built-up Area in 2000 was 324.4ha more than that in 1988. 3) Waters expanded by 3476.51ha. 4) Woodland and Grassland decreased, while Barren Land increased by 3824.9ha. The total amount of land use/land cover change between 1988 and 2000 is small, which is only 0.355% of the total area. It shows that the developmental pace of the lower reaches of the Tarim River is relative slow. Based on these results, the authors assessed the landscape dynamics of this region and pointed out that the degree of desertification was strengthened and the landscape dominated by sand land was further characterized by salt desert.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
ALEXANDER McR Holm, LAUREN T Bennett, WILLIAM A Loneragan et al., 2002. Relationships between empirical and nominal indices of landscape function in the arid shrubland of Western Australia [J]. Journal of Arid Environments, 50: 1–21.
BAKER W L, 1989. A review of models of landscape change [J]. Landscape Ecology, 2(2):111–133.
FAN Zi-li, 1991. The water chemical changes in the Tarim River and controlling approaches [J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 46(3): 319–325. (in Chinese)
FAN Zi-li, 1998. Resources Environment and Sustainable Development in the Lower Reaches of Tarim River [M]. Beijing: Science Press. (in Chinese)
FAN Zi-li, MA Ying-jie, JI Fang et al., 2001. The ecological environment succession and the realignment of Tarim River watershed [J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 15(1): 11–17. (in Chinese)
FANG Ying-kai, 2001. The rise and decline and preservation of a green corridor along the lower reaches of the Tarim River [J]. Contemporary China History Studies, 8(1):115–123. (in Chinese)
JI Fang, FAN Zi-li, DENG Yong-xin, 1998. Regional characteristics of water resources utilization for the main stream of the Tarim River [J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 12(2): 15–18. (in Chinese)
LI Xin, ZHOU Hong-fei, 1998. Sustainable utilization of water resources of Tarim River under the distubance of human activities [J]. Geographical Research, 17(2): 171–177. (in Chinese)
LIU Ji-yuan, WANG Yi-mou, GUO Huan-cheng et al., 1996. Study on the Chinese Resources and Study on Macroscopically Investigation of Resources and Environment by Remote Sensing in China[M]. Beijing: Chinese Science and Technology Press. (in Chinese)
LOEHLE C, WEIN G, 1994. Landscape habitat diversity: a multiscale information theory approach [J]. Ecological Modeling, 73(3–4): 311–329.
MA Jin-zhu, QIAN Ju, GAO Qian-zhao, 2000. Groundwater evolution and its influence on the fragile ecology in the south edge of Tarim Basin [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 20(2): 145–149.
SONG Yu-dong, FAN Zi-li, LEI Zhi-dong et al., 2000. Study on Water Resources and Ecological Problems in the Tarim River [M]. Urumqi: Xinjiang People’s Press, (in Chinese)
TANG Meng-ling, XU Heng-li, CAO Li-jing, 2001. Significance of groundwater for existence and succession of vegetation in northwest China [J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 20(2): 79–82. (in Chinese)
WANG Rang-hui, FAN Zi-li, 1998. Study on ecological vulnerability assessment in Tarim River basin[J]. Arid Environmental Monitoring, 12(4): 218–253. (in Chinese)
WANG Rang-hui, FAN Zi-li, 2000. Evolution patterns of sandy desertification in the lower reaches of Tarim River in recent 5 decades[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 20(1): 45–50. (in Chinese)
WANG Rang-hui, SONG Yu-dong, FAN Zi-li et al., 2000. A dynamic study on ecological environment in the lower reaches of Tarim River based on “3S” technique[J]. Journal of Nanjing Forestry University, 24(4): 59–63. (in Chinese)
WANG Rang-hui, YOU Xian-xiang, 2000. Progress in the study on fragile ecological environment in the west part of arid zone: taking Tarim River basin as an example [J]. Advance in Earth Sciences, 16(1): 39–44. (in Chinese)
WANG Yong-qin, 2002. The utilization of water resources and ecological agriculture development in Tarim River [J]. Environment Protection of Xinjiang, 2(4): 198–201. (in Chinese)
WU Puerjiang Tuo Heti, 1999. Preliminary approaching to ecological environment problem of the middle and lower reaches of Tarim River [J]. Environmental Protection of Xinjiang, 21(1): 34–39. (in Chinese)
XIAO Du-ning, 1991. Theory, Approach and Application of Landscape Ecology [M]. Beijing: China Forestry Publishing House. (in Chinese)
ZHU Chao-yang, ZHANG Ling, YU Jun, 2000. The character of diversiform-leaved poplar grove habitat of Tarim River and improving measure [J]. Environmental Protection of Xinjiang, 22(2): 101–104. (in Chinese)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Foundation item: Under the auspices of Special Science Foundation for Doctoral Subject of Universities, Ministry of Education (No.20020001019)
Biography: WU Xiu-qin(1974-), femal, a native of Fuxin City of Liaoning Province, Ph. D. candidate, specialized in integrated physical geography and LUCC. E-mail: wu_xiuqin@pku.edu.cn
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, Xq., Cai, Yl. Land cover changes and landscape dynamics assessment in lower reaches of Tarim River in China. Chin. Geograph.Sc. 14, 28–33 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11769-004-0005-3
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11769-004-0005-3